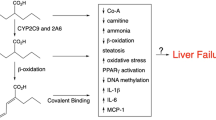
Summary
Valproic acid (VPA; 2-n-propylpentanoic acid) is widely used as a major drug in the treatment of epilepsy and in the control of several types of seizures. Being a simple fatty acid, VPA is a substrate for the fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) pathway, which takes place primarily in mitochondria. The toxicity of valproate has long been considered to be due primarily to its interference with mitochondrial β-oxidation. The metabolism of the drug, its effects on enzymes of FAO and their cofactors such as CoA and/or carnitine will be reviewed. The cumulative consequences of VPA therapy in inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) and the importance of recognizing an underlying IEM in cases of VPA-induced steatosis and acute liver toxicity are two different concepts that will be emphasized.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CoA:
-
coenzyme A
- DILI:
-
drug-induced liver injury
- FAO:
-
fatty acid β-oxidation
- FFA:
-
free fatty acids
- IEM:
-
inborn error of metabolism
- RLM:
-
rat liver mitochondria
- VPA:
-
valproic acid
References
Abbott FS, Anari MR (1999) Chemistry and biotransformation. In: Löscher W, ed. Milestones in Drug Therapy-Valproate, Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag, 47–75.
Abbott Laboratories (2007) Clinical Pharmacology of Divalproex, Abbott Laboratories Inc., USA: http://www.rxabbott.com/pdf/depakote.pdf.
Aires CCP, Ruiter JPN, Luis PBM, et al (2007) Studies on the extra-mitochondrial CoA-ester formation of valproic and Δ4-valproic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771: 533–543.
Bailey MJ, Dickinson RG (1996) Chemical and immunochemical comparison of protein adduct formation of four carboxylate drugs in rat liver and plasma. Chem Res Toxicol 9: 659–666.
Baillie TA (1988) Metabolic activation of valproic acid and drug-mediated hepatotoxicity. Role of the terminal olefin, 2-n-propyl-4-pentenoic acid. Chem Res Toxicol 1: 195–199.
Baldwin GS, Abbott FS, Nau H (1996) Binding of a valproate metabolite to the trifunctional protein of fatty acid oxidation. FEBS Lett 8: 384, 1: 58–60.
Battino D, Estienne M, Avanzini G (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics of antiepileptic drugs in paediatric patients Part I: phenobarbital, primidone, valproic acid, ethosuximide and mesuximide. Clin Pharmacokinet 29: 257–286.
Becker CM, Harris RA (1983) Influence of valproic acid on hepatic carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys 223: 381–392.
Begriche K, Igoudjil A, Pessayre D, Fromenty B (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction in NASH: causes, consequences and possible means to prevent it. Mitochondrion 6: 1–28.
Bjorge SM, Baillie TA (1991) Studies on the β-oxidation of valproic acid in rat liver mitochondrial preparations. Drug Metab Dispos 19: 823–829.
Bohan TP, Helton E, McDonald I, et al (2001) Effect of l-carnitine treatment for valproate-induced hepatotoxicity. Neurology 56: 1405–1409.
Booth CL, Pollack GM, Brouwer KLR (1996) Hepatobiliary disposition of valproic acid and valproate glucuronide: use of a pharmacokinetic model to examine the rate-limiting steps and potential sites of drug interactions. Hepatology 23: 771–780.
Bryant AE, Dreifuss FE (1996) Valproic acid fatalities. III: US experience since 1986. Neurology 46: 465–469.
Burchell B (1999) Transformation reactions: glucuronidation. In: Woolf TF, ed. Handbook of Drug Metabolism, New York: Marcel Dekker, 153–173.
Burton BS (1882) On the propyl derivatives and decomposition products of ethylacetoacetate. Am Chem J 3: 385–395.
Chabrol B, Mancini J, Chretien D, Rustin P, Munnich A, Pinsard N (1994) Valproate-induced hepatic failure in a case of cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Eur J Pediatr 153: 133–135.
Chang TKH, Abbot FS (2006) Oxidative stress as a mechanism of valproic acid-associated hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 38: 627–639.
Corkey BE, Hale DE, Glennon MC, et al (1988) Relationship between unusual hepatic acyl Coenzyme A profiles and the pathogenesis of Reye syndrome. J Clin Invest 82: 782–788.
Cotariu D, Zaidman J (1988) Valproic acid and the liver. Clin Chem 34: 890–897.
Davis R, Peters DH, McTavish D (1994) Valproic acid-a reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs 47: 332–372.
De Vivo DC, Bohan TP, Coulter DL, et al (1998) l-Carnitine supplementation in childhood epilepsy: current perspectives. Epilepsia 39: 1216–1225.
Delarue A, Paut O, Guys JM, et al (2000) Inappropriate liver transplantation in a child with Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome misdiagnosed as valproate-induced acute liver failure. Pediatr Transplant 4: 67–71.
DeVane CL (2003) Pharmacokinetics, drug interactions and tolerability of valproic acid. Psychopharmacol Bull 37(Supplement 2): 25–40.
Dreifuss FE, Langer DH, Moline A, Maxwell E (1989) Valproic acid fatalities. II US experience since 1984. Neurology 39: 201–207.
Dutta S, Zhang Y, Conway J, et al (2004) Divalproex ER-pharmacokinetics in older children and adolescents. Pediatr Neurol 30: 330–337.
Evans AM, Fornasini G (2003) Pharmacokinetics of l-carnitine. Clin Pharmacokinet 42: 941–967.
Farkas V, Bock I, Csako J, Sandor A (1996) Inhibition of carnitine biosynthesis by valproic acid in rats-the biochemical mechanism of inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol 52: 1429–1433.
Fong JC, Schulz H (1978) On the rate-limiting step of fatty acid oxidation in heart: inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by 4-pentenoic acid. J Biol Chem 253: 6917–6922.
Fromenty B, Pessayre D (1997) Impaired mitochondrial function in microvesicular steatosis: effects of drugs, ethanol, hormones and cytokines. J Hepatol 26(Supplement 2): 43–53.
Gerber N, Dickinson RG, Harland RC, et al. (1979) Reye-like syndrome associated with valproic acid therapy. J Pediatr 95: 142–144.
Gopaul SV, Farrell K, Abbott FS (2000) Identification and characterization of N-acetylcysteine conjugates of valproic acid in humans and animals. Drug Metab Dispos 28: 823–832.
Granneman GR, Wang S-I, Kesterson JW, Machinist JM (1984) Hepatotoxicity of valproic acid and its metabolites II Intermediary and valproic acid metabolism. Hepatology 4: 1153–1158.
Gugler R, van Unruh GE (1980) Clinical pharmacokinetics of valproic acid. Clin Pharmacokinet 5: 67–83.
Hjelm M, Silva LVK, Seakins JWT, Oberholzer VG, Rolles CJ (1986) Evidence of inherited urea cycle defect in a case of fatal valproate toxicity. Br Med J 292: 23–24.
Holt MP and Ju C (2006) Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury, AAPS J 8: 1, E48–E59.
Ito M, Ikeda Y, Arnez JG, Finochiaro G, Tanaka K (1990) Theenzymatic basis for the metabolism and inhibitory effects ofvalproic acid: dehydrogenation of valproyl-CoA by 2-methyl-branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. BiochimBiophys Acta 1034: 213–218.
Jakobs C, Löscher W (1978) Identification of metabolites of valproic acid in serum of humans, dog, rat and mouse. Epilepsia 19: 591–602.
Kassahun K, Farrell K, Abbott FS (1991) Identification and characterization of the glutathione and N-acetylcysteine conjugates of (E)-2-propyl-2,4-pentadienoic acid, a toxic metabolite of valproic acid, in rats and humans. Drug Metab Dispos 19: 525–535.
Kassahun K, Hu P, Grillo P, Davis MR, Jin L, Baillie TA (1994) Metabolic activation of unsaturated derivatives of valproic acid. Identification of novel glutathione adducts formed through coenzyme A—dependent and -independent processes. Chem-Biol Interact 90: 253–275.
Katayama H, Watanabe M, Yoshitomi H, et al (1998) Urinary metabolites of valproic acid in epileptic patients. Biol Pharm Bull 21: 304–307.
Kesterson JW, Granneman GR, Machinist JM (1984) The hepatotoxicity of valproic acid and its metabolites in rats. I. Toxicologic, biochemical and histopathologic studies. Hepatology 4: 1143–1152.
Kibayashi M, Nagao M, Chiba S (1999) Influence of valproic acid on the expression of various acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in rats. Pediatr Int 41: 1:52–60.
König SA, Siemes H, Bläker F, et al (1994) Severe hepatotoxicity during valproate therapy: an update and report of eight new fatalities. Epilepsia 35: 1005–1015.
König SA, Schenk M, Sick C, et al (1999) Fatal liver failure associated with valproate therapy in a patient with Friedreich’s disease: a review of valproate hepatotoxicity in adults. Epilepsia 40: 1036–1040.
Kottlors M, Jaksch M, Ketelsen UP, Weiner S, Glocker FX, Lucking CH (2001) Valproic acid triggers acute rhabdomyolysis in a patient with carnitine palmitoyltransferase type II deficiency. Neuromuscul Disord 11: 8, 757–759.
Krähenbühl S, Brandner S, Kleinle S, Liechti S, Straumann D (2000) Mitochondrial diseases represent a risk factor for valproate-induced fulminant liver failure. Liver 20: 4, 346–348.
Kuendgen A, Gattermann N (2007) Valproic acid for the treatment of myeloid malignancies. Cancer 110: 943–954.
Kuhara T, Hirohata Y, Yamada S, Matsumoto I (1978) Metabolism of sodium dipropylacetate in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 3: 171–177.
Lam CW, Lou CH, Williams JC, Chan YW, Wong L (1997) Mitochondrial miopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke like episodes (MELAS) triggered by valproate therapy. Eur J Pediatr 156: 562–564.
Leão M (1995) Valproate as a cause of hyperammonemia in heterozygotes with ornitine-transcarbamylase deficiency. Neurology 45: 593–595.
Lee M-H, HongI, Kim M, et al (2007) Gene expression profiles of murine fatty liver induced by the administration of valproic acid, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 220: 45–59.
Levy RH, Rettenmeier AW, Anderson GD, et al (1990) Effects of polytherapy with phenytoin, carbamazepine and stiripentol on formation of 4-ene-valproate, a hepatotoxic metabolite of valproic acid. Clin Pharmacol Ther 48: 225–235.
Lheureux PER, Penaloza A, Zahir S, Gris M (2005) Science review: carnitine in the treatment of valproic acid-induced toxicity—what is the evidence? Critical Care 9: 431–440.
Li J, Norwood DL, Mao L-F, Schultz H (1991) Mitochondrial metabolism of valproic acid. Biochemistry 30: 388–394.
Löscher W (1999) Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. In: Löscher W, ed. Milestones in Drug Therapy—Valproate, Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag 7–45.
Löscher W (2002) Basic Pharmacology of valproate: a review ater 35 years of clinical use for the treatment of epilepsy, CNS Drugs, 16: 669–694.
Löscher W, Böhme G, Schäfer H, Kochen W (1981) Effect of metabolites of valproic acid on the metabolism of GABA in brain and brain nerve endings. Neuropharmacology 20: 1187–1192.
Matsumoto I, Kuhara T, Yoshino M (1976) Metabolism of branched medium chain length fatty acid II—β-oxidation of sodium dipropylacetate in rats. Biomed Mass Spectrom 3: 235–240.
Meunier H, Carraz G, Meunier Y, Eymard P, Aimard M (1963) Propriétés pharmacodynamiques de l’acide n-dipropylacétique. 1er Mémoire: propriétés antiépileptiques. Thérapie 18: 435–438.
Millington DS, Bohan TP, Roe CR, Yergey AL, Liberato DJ (1985) Valproylcarnitine: a novel drug metabolite identified by fast atom bombardment and thermospray liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta 145: 69–76.
Moore KH, Decker BP, Schreefel FP (1988) Hepatic hydrolysis of octanoyl-CoA and valproyl-CoA in control and valproate-treated animals. Int J Biochem 20: 175–178.
Mortensen PB, Gregersen N, Kølvraa S, Christensen E (1980) The occurrence of C6–C10 dicarboxylic acids in urine from patients and rats treated with dipropylacetate. Biochem Med 24: 153–161.
Nau H, Löscher W (1982) Valproic acid: brain and plasma levels of the drug and its metabolites, anticonvulsant effects and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) metabolism in the mouse. JPharmacol Exp Ther 220: 654–659.
Nau H, Rating D, Koch S, Hauser I, Helge H (1981) Valproic acid and its metabolites: placental transfer, neonatal pharmacokinetics, transfer via mother’s milk and clinical status in neonates of epileptic mothers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 219: 768–777.
Nau H, Löscher W, Löscher W (1984) Valproic acid and metabolites: pharmacological and toxicological studies. Epilepsia 25: 14–22.
Oechsner M, Steen C, Sturenburg HJ, Kohlschutter A (1998) Hyperammonaemic encephalopathy after initiation of valproate therapy in unrecognised ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. J Neurol Neurosur Psychiatr 64: 680–682.
Ohashi R, Tamai I, Yabuuchi H, et al (1999) Na+-dependent carnitine transport by organic cation transporter (OCTN2): its pharmacological and toxicological relevance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291: 778–784.
Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (2003) Pharmacology of valproate. Psychopharmacol Bulletin 37(Supplement 2): 17–24.
Papadimitriou A, Servidei S (1991) Late onset lipid storage myopathy due to multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency triggered by valproate. Neuromuscular Disord 1: 247–252.
Perucca E (2002) Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of valproate. CNS Drugs 16: 695–714.
Pessayre D, Mansouri A, Haouzi D, Fromenty B (1999) Hepatotoxicity due to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Biol Toxicol 15: 367–373.
Ponchault S, van Hoof F, Veitch K (1992) In vitro effects of valproate and valproate metabolites on mitochondrial oxidations: relevance of CoA sequestration to the observed inhibitions. Biochem Pharmacol 43: 11 2435–2442.
Porter RJ, Meldrum BS (2001) Antiseizure drugs. In: Katzung BG, ed. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill, 395–418.
Radatz M, Nau H (1999) Toxicity. In: Löscher W, ed. Milestones in Drug Therapy—Valproate, Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag, 91–128.
Raskind JY, El-Chaar GM (2000) The role of carnitine supplementation during valproic acid therapy. Ann Pharmacother, 34: 630–638.
Rettenmeier AW, Prickett KS, Gordon WP, et al (1985) Studies on the biotransformation in the perfused rat liver of 2-n-propyl-4-pentenoic acid, a metabolite of the antiepileptic drug valproic acid. Evidence for the formation of chemically reactive intermediates. Drug Metab Dispos 13: 81–96.
Rettenmeier AW, Gordon WP, Prickett KS, Levy RH, Baillie TA (1986) Biotransformation and pharmacokinetics in the rhesus monkey of 2-n-propyl-4-pentenoic acid, a toxic metabolite of valproic acid. Drug Metab Dispos 14: 454–464.
Rettenmeier AW, Gordon WP, Barnes H, Baillie TA (1987) Studies on the metabolic fate of valproic acid in the ratusing stable isotope techniques. Xenobiotica 17: 1147–1157.
Rettie AE, Rettenmeier AW, Howald WN, Baillie TA (1987) Cytochrome P450-catalysed formation of delta 4-VPA, a toxic metabolite of valproic acid. Science 235: 890–893.
Russell S (2007) Carnitine as an antidote for acute valproate toxicity in children. Curr Opin Pediatr 19: 206–210.
Sadeque AJM, Fisher MB, Korzekwa KR, Gonzalez FJ, Rettie AE (1997) Human CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 mediate formation of the hepatotoxin 4-ene-valproic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283: 698–703.
Scheffner D, König SA, Rauterberg-Ruland I, Kochen W, Hofmann WJ, Unkelbach St (1988) Fatal liver failure in 16 children with valproate therapy. Epilepsia 29: 530–542.
Schmidt D (1999) Adverse effects and interactions with other drugs. In: Löscher W, ed. Milestones in Drug Therapy—Valproate, Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag, 223–264.
Sewell AC, Bohles HJ, Herwig J, Demirkol M (1995) Neurological deterioration in patients with urea cycle disorders under valproate therapy-a cause for concern. Eur J Pediatr 154: 593–594.
Shenn DD (1999) Absorption, distribution and excretion. In: Löscher W, ed. Milestones in Drug Therapy—Valproate, Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag 77–90.
Shirley MA, Hu P, Baillie TA (1993) Stereochemical studies on the β-oxidation of valproic acid in isolated rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 21: 580–586.
Shorvon SD (1990) Epidemiology, classification, natural history and genetics of epilepsy. Lancet 336: 93–96.
Silva MFB, Ruiter JPN, IJlst L, et al (2001a) Synthesis and intramitochondrial levels of valproyl-CoA metabolites. Anal Biochem 290: 60–67.
Silva MFB, Ruiter JPN, IJlst L, et al (2001b) Differential effect of valproate and its Δ2- and Δ4-unsaturated metabolites, on the β-oxidation rate of long-chain and medium-chain fatty acids. Chem-Biol Interact 137: 203–212.
Silva MFB, Selhorst J, Overmars H, et al (2001c) Characterization of plasma acylcarnitines in patients under valproate monotherapy using ESI-MS/MS. Clin Biochem 34: 635–638.
Silva MFB, Ruiter JPN, Overmars H, et al (2002) Complete β-oxidation of valproate: cleavage of 3-oxovalproyl-CoA by a mitochondrial 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase. Biochem J 362: 755–760.
Silva MFB, IJlst L, Allers P, et al (2004) Valproyl-dephosphoCoA: a novel metabolite of valproate formed in vitro in rat liver mitochondria. Drug Metab Dispos 32(11): 1304–1310.
Spahn-Langguth H, Benet LZ (1992) Acylglucuronides revisited: is the glucuronidation process a toxification as well as a detoxification mechanism? Drug Metab Rev 24, 5–47.
Sztajnkrycer MD (2002) Valproic acid toxicity: overview and management. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 40: 789–801.
Tein I, Xie ZW (1994) Reversal of valproic acid-associated impairment of carnitine uptake in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 204: 753–758.
Thurston JH, Carroll JE, Dodson WE, Hauhart RE, Tash V (1983) Chronic valproate administration reduces fasting ketonemia in children. Neurology 33: 1348–1350.
Tong V, Teng XW, Chang TKH, Abbot FS (2005) Valproic acid I: time course of lipid peroxidation biomarkers, liver toxicity and valproic acid metabolite levels in rats. Toxicol Sci 86: 427–435.
Turnbull DM, Bone AJ, Bartlett K, Koundakjian PP, Sherratt HAS (1983) The effects of valproate on intermediary metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes and intact rats. Biochem Pharmacol 32: 1887–1892.
Vajda FJ, Donnan GA, Phillips J, Bladin PF (1981) Human brain, plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentration of sodium valproate after 72 h of therapy. Neurology 31: 486–487.
Verrotti A, Trotta D, Morgese G, Chiarelli F (2002) Valproate-induced hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 17: 367–373.
Wagner CA, Lukewille U, Kaltenbach S, et al (2000) Functional and pharmacological characterization of human Na+-carnitine cotransporter hOCTN2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279: F584–591.
Watkins PB, Seeff LB (2006) Drug-induced liver injury: summary of a single topic clinical research conference, Hepatology 43: 3, 618–631.
Werner T, Treiss I, Kohlmueller D, et al (2007) Effects of valproate on acylcarnitines in children with epilepsy using ESI-MS/MS. Epilepsia 48: 72–76.
Williams AM, Worrall S, de Jersey J, Dickinson RG (1992) Studies on the reactivity of acylglucuronides – III. Glucuronide-derived adducts of valproic acid and plasma protein and anti-adduct antibodies in humans. Biochem Pharmacol 43: 745–755.
Wu SP, Shyu MK, Liou HH, Gau CS, Lin CJ (2004) Interaction between anticonvulsants and human placental carnitine transporter. Epilepsia 43: 204–210.
Yao K-W, Mao L-F, Luo MJ, Schulz H (1994) The relationship between mitochondrial activation and toxicity of some substituted carboxylic acids. Chem-Biol Interact 90: 225–234.
Zaccara G, Messori A, Moroni F (1988) Clinical pharmacokinetics of valproic acid. Clin Pharmacokinet 15: 367–389.
Zimmerman HJ, Ishak HJ (1982) Valproate-induced hepatic injury: analysis of 23 fatal cases. Hepatology 2: 591–597.
Zschocke J, Ruiter JP, Brand J, et al (2000) Progressive infantile neurodegeneration caused by 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: a novel inborn error of branched-chain fatty acid and isoleucine metabolism. Pediatr Res 48: 852–855.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Michael Gibson
Competing interests: None declared
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, M.F.B., Aires, C.C.P., Luis, P.B.M. et al. Valproic acid metabolism and its effects on mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation: A review. J Inherit Metab Dis 31, 205–216 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0841-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0841-x