Abstract
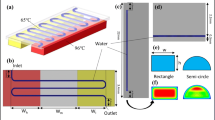
This study develops a new microfluidic DNA amplification strategy for executing parallel DNA amplification in the microfluidic gradient polymerase chain reaction (MG-PCR) device. The developed temperature gradient microfluidic system is generated by using an innovative fin design. The device mainly consists of modular thermally conductive copper flake which is attached onto a finned aluminum heat sink with a small fan. In our microfluidic temperature gradient prototype, a non-linear temperature gradient is produced along the gradient direction. On the copper flake of length 45 mm, width 40 mm and thickness 4 mm, the temperature gradient easily spans the range from 97 to 52°C. By making full use of the hot (90–97°C) and cold (60–70°C) regions on the temperature gradient device, the parallel, two-temperature MG-PCR amplification is feasible. As a demonstration, the MG-PCR from three parallel reactions of 112-bp Escherichia coli DNA fragment is performed in a continuous-flow format, in which the flow of the PCR reagent in the closed loop is induced by the buoyancy-driven nature convection. Although the prototype is not optimized, the MG-PCR amplification can be completed in less than 45 min. However, the MG-PCR thermocycler presented herein can be further scaled-down, and thus the amplification times and reagent consumption can be further reduced. In addition, the currently developed temperature gradient technology can be applied onto other continuous-flow MG-PCR systems or used for other analytical purposes such as parallel and combination measurements, and fluorescent melting curve analysis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Baaske, S. Duhr, D. Braun, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 133901 (2007)
K.M. Balss, D. Ross, H.C. Begley, K.G. Olsen, M.J. Tarlov, J. Am. Chem. Soc 126, 13474–13479 (2004)
D. Braun, N.L. Goddard, A. Libchaber, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 158103 (2003)
J.S. Buch, C. Kimball, F. Rosenberger, W.E. Highsmith Jr. D.L. DeVoe, C.S. Lee, Anal. Chem. 76, 874–881 (2004)
J.S. Buch, F. Rosenberger, W.E. Highsmith Jr. C. Kimball, D.L. DeVoe, C.S. Lee, Lab Chip 5, 392–400 (2005)
M. Chabert, K.D. Dorfman, P. de Cremoux, J. Roeraade, J.L. Viovy, Anal. Chem. 78, 7722–7728 (2006)
M. Chang, H.J. Lee, Anal. Biochem. 340, 174–177 (2005)
J.Y. Cheng, C.J. Hsieh, Y.C. Chuang, J.R. Hsieh, Analyst 130, 931–940 (2005)
N. Crews, T. Ameel, C. Wittwer, B. Gale, Lab Chip 8, 1922–1929 (2008a)
N. Crews, C. Wittwer, B. Gale, Proc. SPIE 6465, 646504 (2007)
N. Crews, C. Wittwer, B. Gale, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 187–195 (2008b)
N. Crews, C. Wittwer, R. Palais, B. Gale, Lab Chip 8, 919–924 (2008c)
N. Crews, C.T. Wittwer, J. Montgomery, R. Pryor, B. Gale, Anal. Chem. 81, 2053–2058 (2009)
M. Curcio, J. Roeraade, Anal. Chem. 75, 1–7 (2003)
K.D. Dorfman, M. Chabert, J.H. Codarbox, G. Rousseau, P. de Cremoux, J.L. Viovy, Anal. Chem. 77, 3700–3704 (2005)
S. Duhr, D. Braun, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 19678–19682 (2006)
H.C. Fan, S.R. Quake, Anal. Chem. 79, 7576–7579 (2007)
J. Grover, R.D. Juncosa, N. Stoffel, M. Boysel, A.I. Brooks, M.P. McLoughlin, D.W. Robbins, IEEE Sens. J. 8, 476–487 (2008)
T. Kajiyama, Y. Miyahara, L.J. Kricka, P. Wilding, D.J. Graves, S. Surrey, P. Fortina, Genome Res. 13, 467–475 (2003)
D.J. Kinahan, T.M. Dalton, M.R.D. Davies, Biomed. Microdevices 11(4), 747–754 (2009)
M.M. Kiss, L. Ortoleva-Donnelly, N.R. Beer, J. Warner, C.G. Bailey, B.W. Colston, J.M. Rothberg, D.R. Link, J.H. Leamon, Anal. Chem. 80, 8975–8981 (2008)
M.U. Kopp, A.J. de Mello, A. Manz, Science 280, 1046–1048 (1998)
M. Krishnan, V.M. Ugaz, M.A. Burns, Science 298, 793 (2002)
Y.Y. Li, D. Xing, C.S. Zhang, Anal. Biochem. 385, 42–49 (2009)
H. Mao, M.A. Holden, M. You, P.S. Cremer, Anal. Chem 74, 5071–5075 (2002a)
H. Mao, T. Yang, P.S. Cremer, J. Am, Chem. Soc. 124, 4432–4435 (2002b)
T. Morrison, J. Hurley, J. Garcia, K. Yoder, A. Katz, D. Roberts, J. Cho, T. Kanigan, S.E. Ilyin, D. Horowitz, J.M. Dixon, C.J. Brenan, Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e123 (2006)
H. Nagai, Y. Murakami, K. Yokoyama, E. Tamiya, Biosens. Bioelectron 16, 1015–1019 (2001)
P.J. Obeid, T.K. Christopoulos, H.J. Crabtree, C.J. Backhouse, Anal. Chem. 75, 288–295 (2003)
T. Ohashi, H. Kuyama, N. Hanafusa, Y. Togawa, Biomed. Microdevices 9, 695–702 (2007)
V.C. Padmakumar, R. Varadarajan, Anal. Biochem. 314, 310–315 (2003)
N. Park, S. Kim, H. Hahn, Anal. Chem. 75, 6029–6033 (2003)
D. Ross, L.E. Locascio, Anal. Chem. 74, 2556–2564 (2002)
W. Rychlik, W.J. Spencer, R.E. Rhoads, Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6409–6412 (1990)
Y. Schaerli, R.C. Wootton, T. Robinson, V. Stein, C. Dunsby, M.A. Neil, P.M. French, A.J. Demello, C. Abell, F. Hollfelder, Anal. Chem. 81, 302–306 (2009)
Y.H. Shim, C.D. Park, D.H. Kim, J.H. Cho, M.H. Cho, H.J. Kim, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28, 671–676 (2005)
N. Stoffel, A. Fisher, S.S. Tan, M. Boysel, Proceedings of 57th Electronic Components & Technology Conference, Reno, NV, 2007, pp, 1561-1566 (2007)
Y. Sun, N.T. Nguyen, Y.C. Kwok, Anal. Chem. 80, 6127–6130 (2008)
W. Sybesma, J. Hugenholtz, I. Mierau, M. Kleerebezem, Biotechniques 31, 466, 468, 470, 472 (2001)
P. Wilding, M.A. Shoffner, L.J. Kricka, Clin. Chem. 40, 1815–1818 (1994)
D.Y. Wu, L. Ugozzoli, B.K. Pal, J. Qian, R.B. Wallace, DNA Cell Biol. 10, 233–238 (1991)
C.S. Zhang, D. Xing, Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 4223–4237 (2007)
C.S. Zhang, D. Xing, Y.Y. Li, Biotechnol. Adv. 25, 483–514 (2007a)
C.S. Zhang, J.L. Xu, W.L. Ma, W.L. Zheng, Biotechnol. Adv. 24, 243–284 (2006)
C.S. Zhang, J.L. Xu, J.Q. Wang, H.P. Wang, Anal. Lett. 40, 497–511 (2007b)
H.D. Zhang, J. Zhou, Z.R. Xu, J. Song, J. Dai, J. Fang, Z.L. Fang, Lab Chip 7, 1162–1167 (2007c)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30700155; 30870676; 30800261), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT0829) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (2007AA10Z204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Xing, D. Microfluidic gradient PCR (MG-PCR): a new method for microfluidic DNA amplification. Biomed Microdevices 12, 1–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9352-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9352-2