Abstract
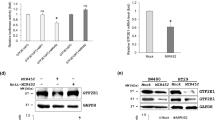
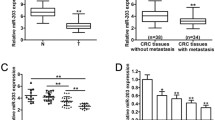
MicroRNAs play important roles in carcinogenesis by negatively regulating the expression of target genes. Here we explore the biological function of miR-155 and the underlying mechanism in colorectal carcinoma. We validate, for the first time, that E2F2 is a direct target of miR-155 using western blot and a luciferase reporter assay and that miR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2 using siRNA technology. We also found, for the first, time that E2F2 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal carcinoma. Overall, miR-155 plays an important role in colorectal carcinoma tumorigenesis by negative regulation of its targets including E2F2 and may be a potential therapeutic target for colorectal carcinoma treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babar IA, Cheng CJ, Booth CJ et al (2012) Nanoparticle-based therapy in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155) dependent mouse model of lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E1695–E1704
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Calame K (2007) microRNA-155 function in B cells. Immunity 27:825–827
Carrington JC, Ambros V (2003) Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301:336–338
Dai Y, Qiu Z, Diao Z et al (2012) MicroRNA-155 inhibits proliferation and migration of human extravillous trophoblast derived HTR-8/SVneo cells via down-regulating cyclin D1. Placenta 33:824–829
DeGregori J (2002) The genetics of the E2F family of transcription factors shared functions and unique roles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1602:131–150
Dimova DK, Dyson NJ (2005) The E2F transcriptional network: old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 24:2810–2826
Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J et al (2009) miR-155 gene: a typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:497–505
Foshay KM (2007) Small RNAs, big potential: the role of MicroRNAs in stem cell function. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 2:264–271
Infante A, Laresgoiti U, Fernández-Rueda J et al (2008) E2F2 represses cell cycle regulators to maintain quiescence. Cell Cycle 7:3915–3927
Jha K, Shukla M, Pandey M (2012) Survivin expression and targeting in breast cancer. Surg Oncol 21:125–131
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH et al (2010) MicroRNA-155 functions as an oncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res 70:3119–3127
Johnson DG, DeGregori J (2006) Putting the oncogenic and tumor suppressive activities of E2F into context. Curr Mol Med 6:731–738
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W et al (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Lee TAFP (2000) Exogenous E2F expression is growth inhibitory before, during, and after cellular transformation. Oncogene 19:2257–2268
Li S, Chen T, Zhong Z et al (2012) microRNA-155 silencing inhibits proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis by upregulating BACH1 in renal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 5:949–954
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM et al (2012) The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21:1236–1243
McClellan KA, Ruzhynsky VA, Douda DN et al (2007) Unique requirement for Rb/E2F3 in neuronal migration evidence for cell cycle-independent functions. Mol Cell Biol 27:4823–4825
Meltzer PS (2005) Cancer genomics: small RNAs with big impacts. Nature 435:745–746
O’Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WSJ et al (2010) MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity 33:607–619
Opavsky R, Tsai S-Y, Guimond M et al (2007) Specific tumor suppressor function for E2F2 in Myc-induced T cell lymphomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15400–15405
Pusapati RV, Weaks RL, Rounbehler RJ et al (2010) E2F2 suppresses Myc-induced proliferation and tumorigenesis. Mol Carcinog 49:152–156
Rogoff HA, Kowalik TF (2004) Life, death and E2F. Cell Cycle 3:845–846
Sun Y, Wang M, Lin G et al (2012) Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e47003
Timmers C, Sharma N, Opavsky R et al (2006) E2f1, E2f2, and E2f3 control E2F target expression and cellular proliferation via a p53-dependent negative feedback loop. Mol Cell Biol 27:65–78
Vigorito E, Perks KL, Abreu-Goodger C et al (2007) MicroRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity 27:847–859
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG et al (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2257–2261
Wenzel PL, Chong J-L, Sáenz-Robles MT et al (2011) Cell proliferation in the absence of E2F1-3. Dev Biol 351:35–45
Wong CF, Barnes LM, Dahle AL et al (2003) E2F modulates keratinocyte squamous differentiation. J Biol Chem 278:28516–28522
Xanthoulis A, Tiniakos DG (2013) E2F transcription factors and digestive system malignancies: how much do we know. World J Gastroenterol 19:3189–3198
Xie Q, Chen X, Lu F et al (2012) Aberrant expression of microRNA 155 may accelerate cell proliferation by targeting sex-determining region Y box 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 118:2431–2442
Zhang G, Xiao G, Tian H et al (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1 expression. Int J Mol Med 31:1375–1380
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81372331). We thank Drs. Yihua Ma, Meijuan Xie and Yan Wang for helpful comments on the manuscript and all members of the Tao Xi laboratory for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Yang, J., Lv, X. et al. miR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Biotechnol Lett 36, 1743–1752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1540-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1540-3