Abstract
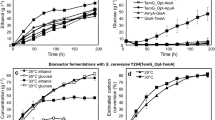
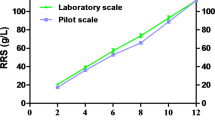
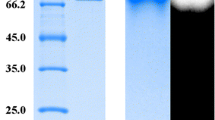
Phytase liberates inorganic phosphate from phytic acid (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate) which is the major phosphate reserve in plant-derived foods and feeds. An industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the Debaryomyces castellii phytase gene (phytDc) and D. occidentalis α-amylase gene (AMY) was developed. The phytDc and AMY genes were constitutively expressed under the ADC1 promoter in S. cerevisiae by using the δ-integration system, which contains DNA derived exclusively from yeast. The recombinant industrial strain secreted both phytase and α-amylase for the efficient degradation of phytic acid and starch as main components of plant seeds. This new strain hydrolyzed 90% of 0.5% (w/v) sodium phytate within 5 days of growth and utilized 100% of 2% (w/v) starch within 48 h simultaneously.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho KM, Yoo YJ, Kang HS (1999) δ-Integration of endo/exo-glucanase and β-glucosidase genes into the yeast chromosomes for direct conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:23–30
Choi JM, Kim DS, Yang MS, Kim HR, Kim JH (2001) Expression of the Aspergillus niger var. awamori phytase gene in Pichia pastoris, and comparison of biological properties. J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:1066–1070
Ghang DM, Yu L, Lim MH, Ko HM, Im SY, Lee HB, Bai S (2007) Efficient one-step starch utilization by industrial strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the glucoamylase and α-amylase genes from Debaryomyces occidentalis. Biotechnol Lett 29:1203–1208
Gietz D, St. Jean A, Woods R, Schiestl RH (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Han Y, Wilson DB, Lei XG (1999) Expression of an Aspergillus niger phytase gene (phyA) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1915–1918
Latta M, Eskin M (1980) A simple and rapid colorimetric method for phytate determination. J Agric Food Chem 28:1313–1315
Lee FWF, Da Silva NA (1997) Improved efficiency and stability of multiple cloned gene insertions at the δ sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:339–345
Lei XG, Han Y (1999) Role of glycosylation in the functional expression of an Aspergillus niger phytase (phyA) in Pichia pastoris. Arch Biochem Biophys 364:83–90
Marin D, Jimenez A, Lobato MF (2001) Construction of an efficient amylolytic industrial yeast strain containing DNA exclusively derived from yeast. FEMS Microbiol Lett 201:249–253
Mayer AF, Hellmuth K, Schlieker H, Lopez-Ulibarri R, Oertel S, Dahlems U, Strasser AW, van Loon AP (1999) An expression system matures: A highly efficient and cost-effective process for phytase production by recombinant strains of Hansenula polymorpha. Biotechnology 63:373–381
Nakamura Y, Fukuhara H, Sano K (2000) Secreted phytase activities of yeasts. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:841–844
Nieto A, Prieto JA, Sanz P (1999) Stable high-copy number integration of Aspergillus orizae α-amylase cDNA in an industrial baker’s yeast strain. Biotechnol Prog 15:459–466
Ragon M, Aumelas A, Chemardin P, Galvez S, Moulin G, Boze H (2008a) Complete hydrolysis of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate by a novel phytase from Debaryomyces castellii CBS 2923. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:47–53
Ragon M, Neugnot-Roux V, Chemardin P, Moulin G, Boze H (2008b) Molecular gene cloning and overexpression of the phatase from Debaryomyces castellii CBS 2923. Protein Exp Purif 58:275–283
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY
Sano K, Fukuhara H, Nakamura Y (1999) Phytase of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans. Biotechnol Lett 21:33–38
Segueilha L, Lambrechts C, Boze H, Moulin G, Galzy P (1992) Purification and properties of the phytase from Schwanniomyces castellii. J Ferm Bioeng 74:7–11
Wodzinski RJ, Ullah AHJ (1996) Phytase. Adv Appl Microbiol 42:263–302
Acknowledgement
Mi-Hyeon Lim and Ok-Hee Lee were supported by the second stage of the Brain Korea 21 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, MH., Lee, OH., Chin, JE. et al. Simultaneous degradation of phytic acid and starch by an industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing phytase and α-amylase. Biotechnol Lett 30, 2125–2130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9799-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9799-x