Abstract
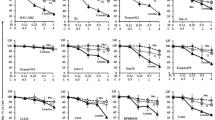
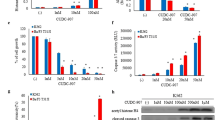
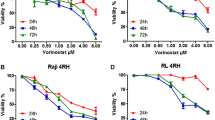
Cell-death signaling through the pro-apoptotic tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors, death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5, has shown tumor-selective apoptotic activity. Here, we examine susceptibility of various leukemia cell lines (HL-60, U937, K562, CCRF-CEM, CEM-CM3, and THP-1) to an anti-DR4 agonistic monoclonal antibody (mAb), AY4, in comparison with TRAIL. While most of the leukemia cell lines were intrinsically resistant to AY4 or TRAIL alone, the two T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) lines, CEM-CM3 and CCRF-CEM cells, underwent synergistic caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death by combination of AY4 or TRAIL with a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI), either suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) or valproic acid (VPA). All of the combined treatments synergistically downregulated several anti-apoptotic proteins (c-FLIP, Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, XIAP, and survivin) without significant changing the expression levels of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax and Bak) or the receptors (DR4 and DR5). Downregulation of c-FLIP to activate caspase-8 was a critical step for the synergistic apoptosis through both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Our results demonstrate that the HDACIs have synergistic effects on DR4-specific mAb AY4-mediated cell death in the T-ALL cells with comparable competence to those exerted by TRAIL, providing a new strategy for the targeted treatment of human T-ALL cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi A (2008) Directing cancer cells to self-destruct with pro-apoptotic receptor agonists. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1001–1012
Fox NL, Humphreys R, Luster TA, Klein J, Gallant G (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-1 and receptor-2 agonists for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:1–18
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ, Smyth MJ (2008) The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8:782–798
Wen J, Ramadevi N, Nguyen D, Perkins C, Worthington E, Bhalla K (2000) Antileukemic drugs increase death receptor 5 levels and enhance Apo-2L-induced apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Blood 96:3900–3906
Hao XS, Hao JH, Liu FT, Newland AC, Jia L (2003) Potential mechanisms of leukemia cell resistance to TRAIL-induced apopotosis. Apoptosis 8:601–607
Hasegawa H, Yamada Y, Harasawa H et al (2005) Sensitivity of adult T-cell leukaemia lymphoma cells to tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Br J Haematol 128:253–265
Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E et al (2000) Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 111:196–203
Thome M, Schneider P, Hofmann K et al (1997) Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 386:517–521
Thorburn A, Behbakht K, Ford H (2008) TRAIL receptor-targeted therapeutics: resistance mechanisms and strategies to avoid them. Drug Resist Updates 11:17–24
Dumitru CA, Carpinteiro A, Trarbach T, Hengge UR, Gulbins E (2007) Doxorubicin enhances TRAIL-induced cell death via ceramide-enriched membrane platforms. Apoptosis 12:1533–1541
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Humphreys R et al (2005) Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of doxorubicin- and bortezomib-induced cell death. Br J Haematol 130:501–510
Kabore AF, Sun J, Hu X, McCrea K, Johnston JB, Gibson SB (2006) The TRAIL apoptotic pathway mediates proteasome inhibitor induced apoptosis in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Apoptosis 11:1175–1193
Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Ricci F et al (2008) Synergistic proapoptotic activity of recombinant TRAIL plus the Akt inhibitor perifosine in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res 68:9394–9403
Mitsiades CS, Treon SP, Mitsiades N et al (2001) TRAIL/Apo2L ligand selectively induces apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 98:795–804
Park SJ, Kim MJ, Kim HB et al (2009) Cotreatment with apicidin overcomes TRAIL resistance via inhibition of Bcr-Abl signaling pathway in K562 leukemia cells. Exp Cell Res 315:1809–1818
Batty N, Malouf GG, Issa JP (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anti-neoplastic agents. Cancer Lett 280:192–200
Lagneaux L, Gillet N, Stamatopoulos B et al (2007) Valproic acid induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through activation of the death receptor pathway and potentiates TRAIL response. Exp Hematol 35:1527–1537
Iacomino G, Medici MC, Russo GL (2008) Valproic acid sensitizes K562 erythroleukemia cells to TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Res 28:855–864
Tsapis M, Lieb M, Manzo F et al (2007) HDAC inhibitors induce apoptosis in glucocorticoid-resistant acute lymphatic leukemia cells despite a switch from the extrinsic to the intrinsic death pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1500–1509
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Dai Y, Grant S (2003) Simultaneous activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) synergistically induces mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2:1273–1284
Shankar S, Singh TR, Fandy TE, Luetrakul T, Ross DD, Srivastava RK (2005) Interactive effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors and TRAIL on apoptosis in human leukemia cells: involvement of both death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Int J Mol Med 16:1125–1138
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Douglas L, Cleveland JL, Humphreys R, Houghton JA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance lexatumumab-induced apoptosis via a p21Cip1-dependent decrease in survivin levels. Cancer Res 67:6987–6994
MacFarlane M, Inoue S, Kohlhaas SL et al (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells exhibit apoptotic signaling via TRAIL-R1. Cell Death Differ 12:773–782
MacFarlane M, Kohlhaas SL, Sutcliffe MJ, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2005) TRAIL receptor-selective mutants signal to apoptosis via TRAIL-R1 in primary lymphoid malignancies. Cancer Res 65:11265–11270
Kelley RF, Totpal K, Lindstrom SH et al (2005) Receptor-selective mutants of apoptosis-inducing ligand 2/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand reveal a greater contribution of death receptor (DR) 5 than DR4 to apoptosis signaling. J Biol Chem 280:2205–2212
van der Sloot AM, Tur V, Szegezdi E et al (2006) Designed tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand variants initiating apoptosis exclusively via the DR5 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8634–8639
Inoue S, Mai A, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2006) Inhibition of histone deacetylase class I but not class II is critical for the sensitization of leukemic cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 66:6785–6792
Sung ES, Park KJ, Lee SH et al (2009) A novel agonistic antibody to human death receptor 4 induces apoptotic cell death in various tumor cells without cytotoxicity in hepatocytes. Mol Cancer Ther 8:2276–2285
Lee SH, Park DW, Sung ES, Park HR, Kim JK, Kim YS (2010) Humanization of an agonistic anti-death receptor 4 single chain variable fragment antibody and avidity-mediated enhancement of its cell death-inducing activity. Mol Immunol 47:816–824
Huang S, Sinicrope FA (2008) BH3 mimetic ABT-737 potentiates TRAIL-mediated apoptotic signaling by unsequestering Bim and Bak in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 68:2944–2951
Park KJ, Lee SH, Kim TI et al (2007) A human scFv antibody against TRAIL receptor 2 induces autophagic cell death in both TRAIL-sensitive and TRAIL-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:7327–7334
Park KJ, Lee SH, Lee CH et al (2009) Upregulation of Beclin-1 expression and phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and p53 are involved in the JNK-mediated autophagic cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 382:726–729
Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, Wilson TR, McLaughlin K, Johnston PG (2005) Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated colon cancer cell death: the roles of p53, TRAIL receptors, and c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther 4:2026–2036
Chou TC (2008) Preclinical versus clinical drug combination studies. Leuk Lymphoma 49:2059–2080
Secchiero P, Milani D, Gonelli A et al (2003) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TNF-alpha promote the NF-kappaB-dependent maturation of normal and leukemic myeloid cells. J Leukoc Biol 74:223–232
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R et al (2005) HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody, induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 92:1430–1441
Guo F, Sigua C, Tao J et al (2004) Cotreatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 enhances Apo-2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced death inducing signaling complex activity and apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Cancer Res 64:2580–2589
Zhang C, Richon V, Ni X, Talpur R, Duvic M (2005) Selective induction of apoptosis by histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells: relevance to mechanism of therapeutic action. J Investig Dermatol 125:1045–1052
Inoue S, MacFarlane M, Harper N, Wheat LM, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Differ 11(Suppl 2):S193–S206
Hernandez A, Thomas R, Smith F et al (2001) Butyrate sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Surgery 130:265–272
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM (2002) Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression. Oncogene 21:2283–2294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the basic research (KRF-2007-313-D00248 and 2009-0064411), and Priority Research Centers Program (2009-0093826) from the National Research Foundation of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and the “GRRC” Project of the Gyeonggi Provincial Government, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest in connection with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, ES., Kim, A., Park, J.S. et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors synergistically potentiate death receptor 4-mediated apoptotic cell death of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Apoptosis 15, 1256–1269 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0521-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0521-9