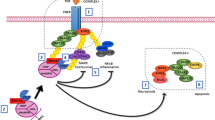
Abstract
Apoptosis plays a major role in controlling both the rate of sperm production and chromosomal abnormalities in adult male testes. However, little is known on the mechanisms controlling induction and execution of apoptosis under physiological conditions. In this work we have uncovered a major role for the cell death receptor Fas in both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in normal germ cell apoptosis. We show here that Fas levels increased significantly in a group of germ cell in 25 d old rats, which were identified as spermatocytes and only a few spermatogonia. In addition, we show that isolated spermatocytes expressing high levels of Fas display activation of caspase-8, -9, -3, -6 and -2, as well as increased levels of intracellular calcium and decreased pH, which coincides with stabilization of p53, and transcriptional activation of PUMA and Fas. Therefore, our data strongly suggests that transcriptional up regulation of Fas could predispose a group of spermatocytes to Fas ligand triggering apoptosis by the extrinsic and intrinsic pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eguchi J, Koji T, Nomata K, Yoshii A, Shin M, Kanetake H (2002) Fas-Fas ligand system as a possible mediator of spermatogenic cell apoptosis in human maturation-arrested testes. Hum Cell 15(1):61–68
Francavilla S, D′Abrizio P, Cordeschi G, Pelliccione F, Necozione S, Ulisse S, et al (2002) Fas expression correlates with human germ cell degeneration in meiotic and post-meiotic arrest of spermatogenesis. Mol Hum Reprod 8(3):213–220
Francavilla S, D′Abrizio P, Rucci N, Silvano G, Properzi G, Straface E, et al (2000) Fas and Fas ligand expression in fetal and adult human testis with normal or deranged spermatogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(8):2692–2700
Furuchi T, Masuko K, Nishimune Y, Obinata M, Matsui Y (1996) Inhibition of testicular germ cell apoptosis and differentiation in mice misexpressing Bcl-2 in spermatogonia. Development 122(6):1703–1709
Knudson CM, Tung KS, Tourtellotte WG, Brown GA, Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Bax-deficient mice with lymphoid hyperplasia and male germ cell death. Science 270(5233):96–99
Yamamoto CM, Hikim AP, Lue Y, Portugal AM, Guo TB, Hsu SY, et al (2001) Impairment of spermatogenesis in transgenic mice with selective overexpression of Bcl-2 in the somatic cells of the testis. J Androl 22(6):981–991
Lee J, Richburg JH, Shipp EB, Meistrich ML, Boekelheide K (1999) The Fas system, a regulator of testicular germ cell apoptosis, is differentially up-regulated in Sertoli cell versus germ cell injury of the testis. Endocrinology 140(2):852–858
Lee J, Richburg JH, Younkin SC, Boekelheide K (1997) The Fas system is a key regulator of germ cell apoptosis in the testis. Endocrinology 138(5):2081–2088
Pentikainen V, Erkkila K, Dunkel L (1999) Fas regulates germ cell apoptosis in the human testis in vitro. Am J Physiol 276(2 Pt 1):E310–316
Yin Y, Stahl BC, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A (2002) P53 and Fas are sequential mechanisms of testicular germ cell apoptosis. J Androl 23(1):64–70
Krammer PH (2000) CD95's deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 407(6805):789–795
Henkler F, Behrle E, Dennehy KM, Wicovsky A, Peters N, Warnke C, et al (2005) The extracellular domains of FasL and Fas are sufficient for the formation of supramolecular FasL-Fas clusters of high stability. J Cell Biol 168(7):1087–1098
Sanchez-Gomez MV, Alberdi E, Ibarretxe G, Torre I, Matute C (2003) Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent oligodendrocyte death mediated by AMPA and kainate receptors. J Neurosci 23(29):9519–9528
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, et al (1998) Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. Embo J 17(6):1675–1687
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(11):897–907
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:269–290
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407(6805):770–776
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Zha J, Korsmeyer SJ, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1999) Differential modulation of apoptosis sensitivity in CD95 type I and type II cells. J Biol Chem 274(32):22532–22538
Moreno RD, Lizama C, Urzua N, Vergara SP, Reyes JG (2006) Caspase activation throughout the first wave of spermatogenesis in the rat. Cell Tissue Res 325(3):533–540
Richburg JH, Nanez A (2003) Fas- or FasL-deficient mice display an increased sensitivity to nitrobenzene-induced testicular germ cell apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 139(1):1–10
Richburg JH, Nanez A, Williams LR, Embree ME, Boekelheide K (2000) Sensitivity of testicular germ cells to toxicant-induced apoptosis in gld mice that express a nonfunctional form of Fas ligand. Endocrinology 141(2):787–793
Chandrasekaran Y, McKee CM, Ye Y, Richburg JH (2006) Influence of TRP53 status on FAS membrane localization, CFLAR (c-FLIP) ubiquitinylation, and sensitivity of GC-2spd (ts) cells to undergo FAS-mediated apoptosis. Biol Reprod 74(3):560–568
Embree-Ku M, Venturini D, Boekelheide K (2002) Fas is involved in the p53-dependent apoptotic response to ionizing radiation in mouse testis. Biol Reprod 66(5):1456–1461
Sinha Hikim AP, Lue Y, Diaz-Romero M, Yen PH, Wang C, Swerdloff RS (2003) Deciphering the pathways of germ cell apoptosis in the testis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 85(2–5):175–182
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L, Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD, Green DR (2005) PUMA couples the nuclear and cytoplasmic proapoptotic function of p53. Science 309(5741):1732–1735
Lu X (2005) p53: a heavily dictated dictator of life and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15(1):27–33
Levine AJ, Hu W, Feng Z (2006) The P53 pathway: what questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ 13(6):1027–1036
Yu J, Zhang L (2005) The transcriptional targets of p53 in apoptosis control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(3):851–858
Schwartz D, Goldfinger N, Kam Z, Rotter V (1999) p53 controls low DNA damage-dependent premeiotic checkpoint and facilitates DNA repair during spermatogenesis. Cell Growth Differ 10(10):665–675
Sjoblom T, Lahdetie J (1996) Expression of p53 in normal and gamma-irradiated rat testis suggests a role for p53 in meiotic recombination and repair. Oncogene 12(12):2499–2505
Yin Y, Stahl BC, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A (1998) p53-mediated germ cell quality control in spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 204(1):165–171
Griffith KJ, Chan EK, Lung CC, Hamel JC, Guo X, Miyachi K, et al (1997) Molecular cloning of a novel 97-kd Golgi complex autoantigen associated with Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1693–1702
Ding HF, Lin YL, McGill G, Juo P, Zhu H, Blenis J, et al (2000) Essential role for caspase-8 in transcription-independent apoptosis triggered by p53. J Biol Chem 275(49):38905–38911
Bright GR, Whitaker JE, Haugland RP, Taylor DL (1989) Heterogeneity of the changes in cytoplasmic pH upon serum stimulation of quiescent fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 141(2):410–419
Rink TJ, Tsien RY, Pozzan T (1982) Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol 95(1):189–196
Kao JP, Harootunian AT, Tsien RY (1989) Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem 264(14):8179–8184
Sun XY, Li FX, Li J, Tan YF, Piao YS, Tang S, et al (2004) Determination of genes involved in the early process of embryonic implantation in rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) by suppression subtractive hybridization. Biol Reprod 70(5):1365–1373
Yamauchi H, Katayama K, Ueno M, Uetsuka K, Nakayama H, Doi K (2004) Involvement of p53 in 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-induced rat fetal brain lesions. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26(4):579–586
Sokal RR (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistic in biological research. W. H. Freeman, New York, p 887
Mishra DP, Shaha C (2005) Estrogen-induced spermatogenic cell apoptosis occurs via the mitochondrial pathway: role of superoxide and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 280(7):6181–6196
Nair R, Shaha C (2003) Diethylstilbestrol induces rat spermatogenic cell apoptosis in vivo through increased expression of spermatogenic cell Fas/FasL system. J Biol Chem 278(8):6470–6481
Richburg JH (2000) The relevance of spontaneous- and chemically-induced alterations in testicular germ cell apoptosis to toxicology. Toxicol Lett 112–113:79–86
Richburg JH, Nanez A, Gao H (1999) Participation of the Fas-signaling system in the initiation of germ cell apoptosis in young rat testes after exposure to mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 160(3):271–278
Boulogne B, Olaso R, Levacher C, Durand P, Habert R (1999) Apoptosis and mitosis in gonocytes of the rat testis during foetal and neonatal development. Int J Androl 22(6):356–365
Rodriguez I, Ody C, Araki K, Garcia I, Vassalli P (1997) An early and massive wave of germinal cell apoptosis is required for the development of functional spermatogenesis. Embo J 16(9):2262–2270
Zheng S, Turner TT, Lysiak JJ (2006) Caspase 2 activity contributes to the initial wave of germ cell apoptosis during the first round of spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 74(6):1026–1033
Boekelheide K, Lee J, Shipp EB, Richburg JH, Li G (1998) Expression of Fas system-related genes in the testis during development and after toxicant exposure. Toxicol Lett 102–103:503–508
Grataroli R, Vindrieux D, Gougeon A, Benahmed M (2002) Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and its receptors in rat testis during development. Biol Reprod 66(6):1707–1715
Suominen JS, Wang Y, Kaipia A, Toppari J (2004) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) promotes cell survival during spermatogenesis, and this effect can be blocked by infliximab, a TNF-alpha antagonist. Eur J Endocrinol 151(5):629–640
Jimbo A, Fujita E, Kouroku Y, Ohnishi J, Inohara N, Kuida K, et al (2003) ER stress induces caspase-8 activation, stimulating cytochrome c release and caspase-9 activation. Exp Cell Res 283(2):156–166
Chan SW, Hegyi L, Scott S, Cary NR, Weissberg PL, Bennett MR (2000) Sensitivity to Fas-mediated apoptosis is determined below receptor level in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 86(10):1038–1046
Bentele M, Lavrik I, Ulrich M, Stosser S, Heermann DW, Kalthoff H, et al (2004) Mathematical modeling reveals threshold mechanism in CD95-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 166(6):839–851
Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2005) Caspase-2 function in response to DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(3):859–867
Tinel A, Tschopp J (2004) The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress. Science 304(5672):843–846
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G, Shi L, Sun Y, Jurisicova A, et al (1998) Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 12(9):1304–1314
Allemand I, Anglo A, Jeantet AY, Cerutti I, May E (1999) Testicular wild-type p53 expression in transgenic mice induces spermiogenesis alterations ranging from differentiation defects to apoptosis. Oncogene 18(47):6521–6530
Beumer TL, Roepers-Gajadien HL, Gademan IS, van Buul PP, Gil-Gomez G, Rutgers DH, et al (1998) The role of the tumor suppressor p53 in spermatogenesis. Cell Death Differ 5(8):669–677
Fujisawa M, Shirakawa T, Fujioka H, Gotoh A, Okada H, Arakawa S, et al (2001) Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer to rat testis impairs spermatogenesis. Arch Androl 46(3):223–231
Kilinc F, Guvel S, Kayaselcuk F, Aygun C, Egilmez T, Ozkardes H (2004) p53 expression and apoptosis in varicocele in the rat testis. J Urol 172(6 Pt 1):2475–2478
Irminger-Finger I, Busquets S, Calabrio F, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM (2006) BARD1 content correlates with increased DNA fragmentation associated with muscle wasting in tumour-bearing rats. Oncol Rep 15(6):1425–1428
Fabbro M, Savage K, Hobson K, Deans AJ, Powell SN, McArthur GA, et al (2004) BRCA1-BARD1 complexes are required for p53Ser-15 phosphorylation and a G1/S arrest following ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem 279(30):31251–31258
Feki A, Jefford CE, Durand P, Harb J, Lucas H, Krause KH, et al (2004) BARD1 expression during spermatogenesis is associated with apoptosis and hormonally regulated. Biol Reprod 71(5):1614–1624
Liu Z, Lu H, Shi H, Du Y, Yu J, Gu S, et al (2005) PUMA overexpression induces reactive oxygen species generation and proteasome-mediated stathmin degradation in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 65(5):1647–1654
Luo X, He Q, Huang Y, Sheikh MS (2005) Transcriptional upregulation of PUMA modulates endoplasmic reticulum calcium pool depletion-induced apoptosis via Bax activation. Cell Death Differ 12(10):1310–1318
Scoltock AB, Bortner CD, St JBG, Putney JW Jr, Cidlowski JA (2000) A selective requirement for elevated calcium in DNA degradation, but not early events in anti-Fas-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275(39):30586–30596
Sharma M, Sahu K, Dube A, Gupta PK (2005) Extracellular pH influences the mode of cell death in human colon adenocarcinoma cells subjected to photodynamic treatment with chlorin p6. J Photochem Photobiol B 81(2): 107–113
Collins MK, Furlong IJ, Malde P, Ascaso R, Oliver J, Lopez Rivas A (1996) An apoptotic endonuclease activated either by decreasing pH or by increasing calcium. J Cell Sci 109(Pt 9): 2393–2399
Vera Y, Diaz-Romero M, Rodriguez S, Lue Y, Wang C, Swerdloff RS, et al (2004) Mitochondria-dependent pathway is involved in heat-induced male germ cell death: lessons from mutant mice. Biol Reprod 70(5):1534–1540
Vera Y, Rodriguez S, Castanares M, Lue Y, Atienza V, Wang C, et al (2005) Functional role of caspases in heat-induced testicular germ cell apoptosis. Biol Reprod 72(3):516–522
Coureuil M, Fouchet P, Prat M, Letallec B, Barroca V, Dos Santos C, et al (2006) Caspase-independent death of meiotic and postmeiotic cells overexpressing p53: calpain involvement. Cell Death Differ
Leist M, Jaattela M (2001) Four deaths and a funeral: from caspases to alternative mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(8):589–598
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by a grant from FONDECYT (1040800). C.L and I.A. are PhD fellows from the National Commission for Scientific Research and Technology (FONDECYT 1040800). We thank Mrs Connie Mefalle for her excellent assistance in English grammar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lizama, C., Alfaro, I., Reyes, J.G. et al. Up-regulation of CD95 (Apo-1/Fas) is associated with spermatocyte apoptosis during the first round of spermatogenesis in the rat. Apoptosis 12, 499–512 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0012-1