Abstract
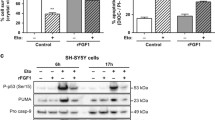
Fenretinide induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via a signaling pathway involving the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), 12-lipoxygenase activity and the induction of the GADD153 transcription factor. NF-κ B is a key element of many cell signaling pathways and adopts a pro- or anti-apoptotic role in different cell types. Studies have suggested that NF-κ B may play a pro-apoptotic role in SH-SY5Y cells, and in other cell types NF-κ B activation may be linked to lipoxygenase activity. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that NF-κ B activity mediates fenretinide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Using a dominant-negative construct for Iκ Bα stably transfected into SH-SY5Y cells, we show that apoptosis, but not the induction of ROS, in response to fenretinide was blocked by abrogation of NF-κ B activity. In parental SH-SY5Y cells, fenretinide induced NF-κ B activity and Iκ Bα phosphorylation. These results suggest that NF-κ B activity links fenretinide-induced ROS to the induction of apoptosis in SH-SH5Y cells, and may be a target for the future development of drugs for neuroblastoma therapy
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabichi AL, Modiano MR, Lee JJ, et al. Breast tissue accumulation of retinamides in a randomized short-term study of fenretinide. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 2400–2405.
Garaventa A, Luksch R, Piccolo MS, et al. Phase I trial and pharmacokinetics of fenretinide in children with neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 2032–2039.
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, et al. Treatment of high risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis retinoic acid. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1165–1173.
Lasorella A, Iavarone A, Israel MA. Differentiation of neuroblastoma enhances Bcl-2 expression and induces alterations of apoptosis and drug resistance. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 4711–4716.
Meister B, Fink FM, Hittmair A, Marth C, Widschwendter M. Antiproliferative activity and apoptosis induced by retinoic acid receptor-γ selectively binding retinoids in neuroblastoma. Anticancer Res 1998; 18: 1777–1786.
Maurer BJ, Metelitsa LS, Seeger RC, Cabot MC, Reynolds CP. Increase of ceramide and induction of mixed apoptosis/necrosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide in neuroblastoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999; 91: 1138–1146.
Lovat PE, Ranalli M, Bernassola F, et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis of neuroblastoma by fenretinide or CD437 in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Int J Cancer 2000; 88: 977–985.
Lovat PE, Ranalli M, Annichiarrico-Petruzzelli M, et al. Effector mechanisms of fenretinide-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Exp Cell Res 2000; 260: 50–60.
Lovat PE, Oliverio S, Ranalli M, et al. GADD153 and 12-Lipoxygenase Mediate Fenretinide-induced Apoptosis of Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 5158–5167.
Lovat PE, Oliverio S, Corazzari M, et al. Induction of GADD153 and Bak: novel molecular targets of fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett 2003; 197: 157–163.
Jan JT, Chen BH, Ma SH, et al. Potential dengue virus-triggered apoptotic pathway in human neuroblastoma cells: arachidonic acid, superoxide anion, and NF-kappaB are sequentially involved. J Virol 2000; 74: 8680–8691.
Bian X, McAllister-Lucas LM, Shao F, et al. NF-kappa B activation mediates doxorubicin-induced cell death in N-type neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 48921–48929.
Chen L, Gao X. Neuronal Apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurochemistry Research 2002; 27: 891–898.
Korner M, Tarantino N, Pleskoff O, Lee LM, Debre P. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurochem 1994; 62: 1716–1726.
Bonizzi G, Piette J, Merville M-P, Bours V. Distinct signal transduction pathways mediate nucelar factor-KB induction by IL-1beta in epithelial and lymphoid cells. J Immunol 1997; 159: 5264–5272.
Campbell Hewson QD, Lovat PE, Pearson ADJ, Redfern CPF. Retinoid signalling and gene expression in neuroblastoma cells: RXR agonist and antagonist effects on CRABP-II and RAR expression. J Cell Biochem 2002; 87: 284–291.
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Fernandez B, Dominguez, I, Jacque JM, et al. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis activates NF-kB and increases human immunodeficiency virus replication in human monocytes and lymphocytes. J Virol 1993; 67: 6596–6604.
Rana B, Veal GJ, Pearson ADJ, Redfern CPF. Retinoid X receptors and retinoid response in neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Biochem 2002; 86: 67–78.
Hewson QC, Lovat PE, Malcolm AJ, Pearson AD, Redfern CPF. Receptor mechanisms mediating differentiation and proliferation effects of retinoids on neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 2000; 279: 113–116.
Corazzari M, Lovat PE, Oliverio S, Pearson ADJ, Piacentini M, Redfern CPF. GADD153 mediates apoptosis in response to fenretinide but not synergy between fenretinide and chemotherapeutic drugs in neuroblastoma. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 64: 1370–1378.
Whiteside ST, Ernst MK, LeBail O, Laurent-Winter C, Rice N, Israel A. N- and C-terminal sequences control degradation of MAD3/I kappa B alpha in response to inducers of NF-kappa B activity. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 5339–5345.
Traenckner EB, Pahl HL, Henkel T, Schmidt KN, Wilk S, Baeuerle PA. Phosphorylation of human I kappa B-alpha on serines 32 and 36 controls I kappa B-alpha proteolysis and NF-kappa B activation in response to diverse stimuli. EMBO J 1995; 14: 2876–2883.
Feng Z, Porter AG. NF-kappaB/Rel proteins are required for neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 30341–30344.
Bian X, Opipari A, Ratanaproeksa AB, Boitano AE, Lucas PC, Castle VP. Constitutively active NFkappa B is required for the survival of S-type neuroblastoma. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 42144–42150.
Lin KI, DiDonato JA, Hoffmann A, Hardwick JM, Ratan RR. Suppression of steady-state, but not stimulus-induced NF-kappaB activity inhibits alphavirus-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1998; 141: 1479–1487.
Song YS, Park HJ, Kim SY, et al. Protective role of Bcl-2 on beta-amyloid-induced cell death of differentiated PC12 cells: Reduction of NF-kappaB and p38 MAP kinase activation. Neurosci Res 2004; 49: 69–80.
Uberti D, Carsana T, Francisconi S, Toninelli GF, Canonico PL, Memo M. A novel mechanism for pergolide-induced neuroprotection: Inhibition of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 67: 1743–1750.
Kaltschmidt B, Heinrich M, Kaltschmidt C. Stimulus-dependent activation of NF-kappaB specifies apoptosis or neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells. Neuromolecular Med 2002; 2: 299–309.
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, Vousden KH. Role of NF-kappaB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 2000; 404: 892–897.
Perfettini JL, Roumier T, Castedo M, et al. NF-κB and p53 Are the Dominant Apoptosis-inducing Transcription Factors Elicited by the HIV-1 Envelope. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 629–640.
Fujioka S, Schmidt C, Sclabas GM, et al. Stabilization of p53: A novel mechanism for proapoptotic function of NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 2004.
Yount GL, Afshar G, Ries S, et al. Transcriptional activation of TRADD mediates p53-independent radiation-induced apoptosis of glioma cells. Oncogene 2001; 20: 2826–2835.
Boya P, Morales MC, Gonzalez-Polo RA, et al. The chemopreventive agent N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway regulated by proteins from the Bcl-2 family. Oncogene 2003; 22: 6220–6230.
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Kishi M, Yonehara S, Konishi N. Contributions of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa B to N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 2002; 35: 127–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by The North of England Children’s Cancer Research Fund and CLIC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hewson, Q.D.C., Lovat, P.E., Corazzari, M. et al. The NF-κB pathway mediates fenretinide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Apoptosis 10, 493–498 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-005-1878-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-005-1878-z