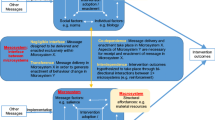
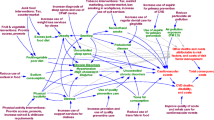
Abstract
The Interactive Systems Framework for Dissemination and Implementation (ISF) was introduced as a heuristic systems level model to help bridge the gap between research and practice (Wandersman et al., in Am J Commun Psychol 41:171–181, 2008). This model describes three interacting systems with distinct functions that (1) distill knowledge to develop innovations; (2) provide supportive training and technical assistance for dissemination to; (3) a prevention delivery system responsible for implementation in the field. The Strategic Prevention Framework (SPF) is a major prevention innovation launched by the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). The SPF offers a structured, sequential, data-driven approach that explicitly targets environmental conditions in the community and aims for change in substance use and problems at the population level. This paper describes how the ISF was applied to the challenges of implementing the SPF in 14 Rhode Island communities, with a focus on the development of a new Training and Technical Assistance Resources Center to support SPF efforts. More specifically, we (1) describe each of the three ISF interacting systems as they evolved in Rhode Island; (2) articulate the lines of communication between the three systems; and (3) examine selected evaluation data to understand relationships between training and technical assistance and SPF implementation and outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
While described here briefly, selecting state priorities and identifying localities contributing most to those state priorities was, in fact, a time and labor intensive project that involved choices of indicators and epidemiological judgments. A full description of the SEOW process is available within Rhode Island’s SPF Strategic Plan that was approved by SAMHSA.
All assessment instruments, workbook materials and evaluation instruments mentioned in this article are available upon request to the first author.
As there were many task forces represented by only one participant, identification of task force membership was not asked in order to preserve anonymity.
References
Aguirre-Molina, M., & Gorman, D. M. (1996). Community-based approaches for the prevention of alcohol, tobacco, and other drug use. Annual Review of Public Health, 17, 337–358.
Birckmayer, J., Holder, H. D., Yacoubian, G. S., & Friend, K. B. (2004). A general causal model to guide alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drug prevention: Assessing the research evidence. Journal of Drug Education, 34(2), 121–153.
Chavis, D. M., Florin, P., & Felix, M. R. J. (1992). Nurturing grassroots initiatives for community development: The role of enabling systems. In T. Mizrahi & J. Morrison (Eds.), Community organization and social administration: Advances, trends and emerging principles. Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press.
Chinman, M., Hannah, G., Wandersman, A., Ebener, P., Hunter, S. B., Imm, P., et al. (2005). Developing a community science research agenda for building community capacity for effective prevention interventions. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35(3/4), 143–157.
Dent, C. W., Grube, J. W., & Biglan, A. (2005). Community level alcohol availability and enforcement of possession laws as predictors of youth drinking. Preventive Medicine, 40(3), 355–362.
Emshoff, J. G. (2008). Researchers, practitioners, and funders: Using the framework to get us on the same page. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 393–403.
Fixsen, D. L., Blase, K. A., Naoom, S. F., & Wallace, F. (2009). Core implementation components. Research on Social Work Practice, 19(5), 531–540.
Florin, P., Mitchell, R., & Stevenson, J. (1993). Identifying training and technical assistance needs in coalitions: A developmental approach. Health Education Research: Theory and Practice, 8, 417–432.
Foster-Fishman, P. G., Berkowitz, S. L., Lounsbury, D. W., Jacobson, S., & Allen, N. A. (2001). Building collaborative capacity in community coalitions: A review and integrative framework. American Journal of Community Psychology, 29(1), 241–261.
Friend, K., & Levy, D. T. (2002). Reductions in smoking prevalence and consumption associated with mass media campaigns. Health Education Research, 17(1), 85–98.
Green, L. (2001). From research to “Best Practices” in other settings and populations. American Journal of Health Behavior, 25, 165–178.
Greenberg, M. T., Domitrovich, C. E., Graczyk, P. A., & Zins, J. E. (2004). The study of implementation in school-based preventive interventions: Theory, research, and practice. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Mental Health Services. Final project report.
Hoagwood, K. E., Radigan, M., Rodriguez, J., Levitt, J. M., Fernandez, D., & Foster, J. (2006). Final report on the child and adolescent trauma treatment and services (CATS) project for the substance abuse and mental health services administration (SAMHSA). New York: Office of Mental Health.
Holder, H. D. (1999). Alcohol and the community. A systems approach to prevention. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Holder, H. D. (2002). Prevention of alcohol and drug “abuse” problems at the community level: What research tells us. Substance Use and Misuse, 37(8–10), 901–921.
Levy, D. T., & Friend, K. (2002). A computer simulation model of mass media interventions directed at tobacco use. Preventive Medicine, 32(3), 284–294.
Lewin, S., Lavis, J. N., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2008). Alma-Ata: Rebirth and revision 2: Supporting the delivery of cost-effective interventions in primary health-care systems in low-income and middle-income countries: An overview of systematic reviews. Lancet, 372, 928–939.
Mitchell, R., Florin, P., & Stevenson, J. (2002). Supporting community-based prevention and health promotion initiatives. Developing effective technical assistance systems. Health, Education and Behavior, 29, 620–639.
Mitchell, R., Stone-Wiggins, B., Stevenson, J. F., & Florin, P. (2004). Cultivating capacity: Outcomes of a statewide support system for prevention coalitions. Journal of Prevention and Intervention in the Community, 27, 67–87.
Pentz, M. A. (1998). Preventing drug abuse through the community: Multicomponent programs make the difference. In A. Sloboda & W. B. Hansen (Eds.), Putting research to work for the community (NIDA Publication No. 98-4293; pp. 73–86). Rockville, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Pentz, M. A. (2000). Institutionalizing community-based prevention through policy change. Journal of Community Psychology, 28, 257–270.
Pentz, M. A. (2003). Evidence-based prevention: Characteristics, impact, and future direction. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 35(Suppl), 143–152.
Wagenaar, A. C., Murray, D. M., Gehan, J. P., Wolfson, M., Forster, J. M., Toomey, T. L., et al. (2000). Communities mobilizing for change on alcohol: Outcomes from a randomized community trial. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 61, 85–94.
Wandersman, A., Duffy, J., Flaspohler, P., Noonan, R., Lubell, K., Stillman, L., et al. (2008). Bridging the gap between prevention research and practice: The interactive systems framework for dissemination. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 171–181.
Wandersman, A., & Florin, P. (2003). Community interventions and effective prevention. American Psychologist, 58(6/7), 441–448.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank numerous individuals for their assistance with the successful implementation of the SPF grant. These include Charles Williams and the Rhode Island Department of Behavioral Health, Hospitals, and Developmental Disabilities; the Northeast Center for the Application of Prevention Technologies, the task forces and SPF communities of Bristol, Cranston, East Providence, Middletown, Newport, North Kingstown, North Providence, Pawtucket, Providence, Smithfield, Warwick, Westerly, West Warwick, and Woonsocket; and the local evaluators, including DATACORP, John Mattson, Brad Crowther, Barbara Slyvia, Johnelle Luciani, and Peter Kreiner. Funding for the SPF grant was provided by CSAP (Grant No. 7003119).
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest. That is, there are no financial and personal relationships with individuals or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) this work. The authors alone are responsible for the content of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Florin, P., Friend, K.B., Buka, S. et al. The Interactive Systems Framework Applied to the Strategic Prevention Framework: The Rhode Island Experience. Am J Community Psychol 50, 402–414 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-012-9527-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-012-9527-5