Abstract
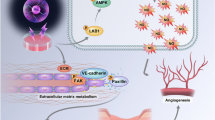
Non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma is being developed for a wide range of medical applications, including wound healing, blood coagulation, and malignant cell apoptosis. However, the effect of non-thermal plasma on the vasculature is unclear. Blood vessels are affected during plasma treatment of many tissues and may be an important potential target for clinical plasma therapy. Porcine aortic endothelial cells were treated in vitro with a custom non-thermal plasma device. Low dose plasma (up to 30 s or 4 J cm−2) was relatively non-toxic to endothelial cells while treatment at longer exposures (60 s and higher or 8 J cm−2) led to cell death. Endothelial cells treated with plasma for 30 s demonstrated twice as much proliferation as untreated cells five days after plasma treatment. Endothelial cell release of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) peaked 3 h after plasma treatment. The plasma proliferative effect was abrogated by an FGF2 neutralizing antibody, and FGF2 release was blocked by reactive oxygen species scavengers. These data suggest that low dose non-thermal plasma enhances endothelial cell proliferation due to reactive oxygen species mediated FGF2 release. Plasma may be a novel therapy for dose-dependent promotion or inhibition of endothelial cell mediated angiogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayan, H., G. Fridman, D. Staack, A. F. Gutsol, V. N. Vasilets, A. A. Fridman, and G. Friedman. Heating effect of dielectric barrier discharges for direct medical treatment. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 37(1):113–120, 2009.
Balasubramanian, M., A. Sebastian, M. Peddinghaus, G. Fridman, A. Fridman, A. Gutsol, G. Friedman, and B. Ari. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma in coagulation and sterilization. Blood 108(11):89b-89b, 2006.
Callaghan, M. J., E. I. Chang, N. Seiser, S. Aarabi, S. Ghali, E. R. Kinnucan, B. J. Simon, and G. C. Gurtner. Pulsed electromagnetic fields accelerate normal and diabetic wound healing by increasing endogenous FGF-2 release. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 121(1):130–141, 2008.
Caplice, N. M., C. N. Aroney, J. H. N. Bett, J. Cameron, J. H. Campbell, N. Hoffmann, P. T. McEniery, and M. J. West. Growth factors released into the coronary circulation after vascular injury promote proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells in culture. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 29(7):1536–1541, 1997.
Chang, P. Y., K. A. Bjornstad, E. Chang, M. McNamara, M. H. Barcellos-Hoff, S. P. Lin, G. Aragon, J. R. Polansky, G. M. Lui, and E. A. Blakely. Particle irradiation induces FGF2 expression in normal human lens cells. Radiat. Res. 154(5):477–484, 2000.
Clyne, A. M., H. Zhu, and E. R. Edelman. Elevated fibroblast growth factor-2 increases tumor necrosis factor-alpha, induced endothelial cell death in high glucose. J. Cell. Physiol. 217(1):86–92, 2008.
Coulombe, S. Live cell permeabilization using the APGD-t. 1st International Conference on Plasma Medicine (ICPM), Corpus Christi, TX, 2007.
Coulombe, S., V. Leveille, S. Yonson, and R. L. Leask. Miniature atmospheric pressure glow discharge torch (APGD-t) for local biomedical applications. Pure Appl. Chem. 78(6):1147–1156, 2006.
Danpure, C. J. Lactate-dehydrogenase and cell injury. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2(3):144–148, 1994.
Eliasson, B., W. Egli, and U. Kogelschatz. Modeling of dielectric barrier discharge chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 66(8):U1766–U1778, 1994.
Fiers, W., R. Beyaert, W. Declercq, and P. Vandenabeele. More than one way to die: apoptosis, necrosis and reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene 18(54):7719–7730, 1999.
Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat. Med. 1(1):27–31, 1995.
Folkman, J. Angiogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med. 57:1–18, 2006.
Fridman, A. Plasma Biology and Plasma Medicine. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2008.
Fridman, G., A. D. Brooks, M. Balasubramanian, A. Fridman, A. Gutsol, V. N. Vasilets, H. Ayan, and G. Friedman. Comparison of direct and indirect effects of non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma on bacteria. Plasma Processes Polym. 4(4):370–375, 2007.
Fridman, G., M. Peddinghaus, H. Ayan, A. Fridman, M. Balasubramanian, A. Gutsol, A. Brooks, and G. Friedman. Blood coagulation and living tissue sterilization by floating-electrode dielectric barrier discharge in air. Plasma. Chem. Plasma Process. 26(4):425–442, 2006.
Fridman, G., A. Shereshevsky, M. M. Jost, A. D. Brooks, A. Fridman, A. Gutsol, V. Vasilets, and G. Friedman. Floating electrode dielectric barrier discharge plasma in air promoting apoptotic behavior in melanoma skin cancer cell lines. Plasma. Chem. Plasma Process. 27(2):163–176, 2007.
Fuks, Z., R. S. Persaud, A. Alfieri, M. Mcloughlin, D. Ehleiter, J. L. Schwartz, A. P. Seddon, C. Cordoncardo, and A. Haimovitzfriedman. Basic fibroblast growth-factor protects endothelial-cells against radiation-induced programmed cell-death in-vitro, and in-vivo. Cancer Res. 54(10):2582–2590, 1994.
Gallicchio, V. S., N. K. Hughes, B. C. Hulette, R. Dellapuca, and L. Noblitt. Basic fibroblast growth-factor (B-Fgf) induces early-stage (Cfu-S) and late-stage hematopoietic progenitor-cell colony formation (Cfu-Gm, Cfu-Meg, and Bfu-E) by synergizing with Gm-Csf, Meg-Csf, and erythropoietin, and is a radioprotective agent in vitro. Int. J. Cell Cloning 9(3):220–232, 1991.
Gebicki, S., and J. M. Gebicki. Formation of peroxides in amino-acids and proteins exposed to oxygen free-radicals. Biochem. J. 289:743–749, 1993.
Gostev, V., and D. Dobrynin. Medical microplasmatron. 3rd International Workshop on Microplasmas (IWM-2006), Greifswald, Germany, 2006.
Haimovitzfriedman, A., N. Balaban, M. Mcloughlin, D. Ehleiter, J. Michaeli, I. Vlodavsky, and Z. Fuks. Protein-kinase-C mediates basic fibroblast growth-factor protection of endothelial-cells against radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 54(10):2591–2597, 1994.
Haimovitzfriedman, A., I. Vlodavsky, A. Chaudhuri, L. Witte, and Z. Fuks. Autocrine effects of fibroblast growth-factor in repair of radiation-damage in endothelial-cells. Cancer Res. 51(10):2552–2558, 1991.
Houchen, C. W., R. J. George, M. A. Sturmoski, and S. M. Cohn. FGF-2 enhances intestinal stem cell survival and its expression is induced after radiation injury. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 276(1):G249–G258, 1999.
Kalghatgi, S. U., G. Fridman, M. Cooper, G. Nagaraj, M. Peddinghaus, M. Balasubramanian, V. N. Vasilets, A. F. Gutsol, A. Fridman, and G. Friedman. Mechanism of blood coagulation by nonthermal atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 35(5):1559–1566, 2007.
Kieft, I. E., D. Darios, A. J. M. Roks, and E. Stoffels. Plasma treatment of mammalian vascular cells: a quantitative description. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 33(2):771–775, 2005.
Kieft, I. E., M. Kurdi, and E. Stoffels. Reattachment and apoptosis after plasma-needle treatment of cultured cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 34(4):1331–1336, 2006.
Ku, P. T., and P. A. Damore. Regulation of basic fibroblast growth-factor (Bfgf) gene and protein expression following its release from sublethally injured endothelial-cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 58(3):328–343, 1995.
Majno, G., and I. Joris. Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis—an overview of cell-death. Am. J. Pathol. 146(1):3–15, 1995.
Morss, A. S., and E. R. Edelman. Glucose modulates basement membrane fibroblast growth factor-2 via alterations in endothelial cell permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 282(19):14635–14644, 2007.
Muthukrishnan, L., E. Warder, and P. L. Mcneil. Basic fibroblast growth-factor is efficiently released from a cytolsolic storage site through plasma-membrane disruptions of endothelial-cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 148(1):1–16, 1991.
Nugent, M. A., and R. V. Iozzo. Fibroblast growth factor-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32(2):115–120, 2000.
Rath, P. C., and B. B. Aggarwal. TNF-induced signaling in apoptosis. J. Clin. Immunol. 19(6):350–364, 1999.
Shekhter, A. B., V. A. Serezhenkov, T. G. Rudenko, A. V. Pekshev, and A. F. Vanin. Beneficial effect of gaseous nitric oxide on the healing of skin wounds. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 12(4):210–219, 2005.
Siemens, C. W. On the electrical tests employed during the construction of the Malta and Alexandria Telegraph, and on insulating and protecting submarine cables. J. Franklin Inst. 74(3):166–170, 1862.
Sudhir, K., K. Hashimura, A. Bobik, R. J. Dilley, G. L. Jennings, and P. J. Little. Mechanical strain stimulates a mitogenic response in coronary vascular smooth muscle cells via release of basic fibroblast growth factor. Am. J. Hypertens. 14(11):1128–1134, 2001.
Tepper, O. M., M. J. Callaghan, E. I. Chang, R. D. Galiano, K. A. Bhatt, S. Baharestani, J. Gan, B. Simon, R. A. Hopper, J. P. Levine, et al. Electromagnetic fields increase in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through endothelial release of FGF-2. FASEB J. 18(9):1231, 2004.
Vargo, J. J. Clinical applications of the argon plasma coagulator. Gastrointest. Endosc. 59(1):81–88, 2004.
Wajant, H., K. Pfizenmaier, and P. Scheurich. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 10(1):45–65, 2003.
Wong, M. K. K., and A. I. Gotlieb. In vitro reendothelialization of a single-cell wound—role of microfilament bundles in rapid lamellipodia-mediated wound closure. Lab. Invest. 51(1):75–81, 1984.
Yamada, H., E. Yamada, N. Kwak, A. Ando, A. Suzuki, N. Esumi, D. J. Zack, and P. A. Campochiaro. Cell injury unmasks a latent proangiogenic phenotype in mice with increased expression of FGF2 in the retina. J. Cell. Physiol. 185(1):135–142, 2000.
Yenpatton, G. P. A., W. F. Patton, D. M. Beer, and B. S. Jacobson. Endothelial-cell response to pulsed electromagnetic-fields—stimulation of growth-rate and angiogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 134(1):37–46, 1988.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Gregory Fridman for building the plasma device.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Julia E. Babensee oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalghatgi, S., Friedman, G., Fridman, A. et al. Endothelial Cell Proliferation is Enhanced by Low Dose Non-Thermal Plasma Through Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Release. Ann Biomed Eng 38, 748–757 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9868-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9868-x