Abstract
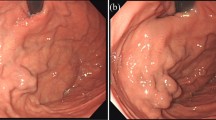
We treated a 74-year-old woman who complained of tarry stool. Neither endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract nor colonoscopy revealed any finding indicative of bleeding, and 99mTc-HSA-D pool scintigraphic imaging showed no accumulation of blood in the digestive tract. Small tortuous collateral veins were observed on computed tomography (CT) in the distal third portion of the duodenum. Color Doppler ultrasonography obtained color flow images of varices in the distal third portion of the duodenum indicating turbulent flow, and color flow imaging showed the outflow vessel from duodenal varices. Duodenoscopy revealed tortuous varices, with erosions and blue in appearance, in the same area. Percutaneous transhepatic portography was carried out 18 days after the treatment of ascites, and hepatofugal blood flow was confirmed in the pancreatic duodenal vein originating near the junction between the splenic and inferior mesenteric veins with the passage of contrast medium into the duodenal varices, which drained into the left ovarian vein. We performed selective catheterization into the afferent vein of the varices, and injected 8 ml of a 5% solution of ethanolamine oleate containing iopamidol. Microcoil embolization using steel coils was added because the therapeutic effect resulting after the relatively rapid washout of sclerosant was insufficient. CT and color Doppler ultrasonography showed absence of blood flow in the varices 1 week after the therapy. This patient has had no episodes of rebleeding in the 24 months after therapy. Color Doppler ultrasonography was useful in diagnosing this case of duodenal varices and in evaluating therapeutic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y Itzchak MG Glickman (1977) ArticleTitleDuodenal varices in extrahepatic portal obstruction Radiology 124 619–24 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2s3jsFWgtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle887749
R Amin R Alexis J Korzis (1985) ArticleTitleFatal ruptured duodenal varix: a case report and review of literature Am J Gastroenterol 80 13–8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M%2FpsVajsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3871304
T Tanaka K Kato T Taniguchi et al. (1988) ArticleTitleA case report of ruptured duodenal varices and review of the literature Jpn J Surg 18 595–600 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02471496 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M7lslyltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3068396
N D'Imperio A Piemontese D Baroncini et al. (1996) ArticleTitleEvaluation of undiluted N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in endoscopic treatment of upper gastrointestinal tract varices Endoscopy 28 239–43 Occurrence Handle8739740 Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2007-1005435
ID Norton JC Andrews PC Kamath (1998) ArticleTitleManagement of ectopic varices Hepatology 28 1154–8 Occurrence Handle10.1002/hep.510280434 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvivFGkuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9755256
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Veterans Affairs Cooperative Variceal Sclerotherapy Group (1991) ArticleTitleProphylactic sclerotherapy for esophageal varices in men with alcoholic liver disease N Engl J Med 324 1779–84 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199106203242505
GV Goff RM Reveille GV Stiegmann (1988) ArticleTitleEndoscopic sclerotherapy versus endoscopic variceal ligation: esophageal symptoms, complications and motility Am J Gastroenterol 83 1240–4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M%2FksleitQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3263792
H Kanagawa S Mima H Kouyama et al. (1996) ArticleTitleTreatment of gastric fundal varices by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11 51–8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283msFCrsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8672742
InstitutionalAuthorNameJapanese Research Society for Portal Hypertension (1991) ArticleTitleThe general rules for recording endoscopic findings of esophageal varices – revised edition (in Japanese with English abstract) Acta Hepatol Jpn 33 277–81
F Khouqeer C Morrow P Jordan (1987) ArticleTitleDuodenal varices as a cause of massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding Surgery (St. Louis) 102 548–52 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2szitVWiug%3D%3D
SS Jonnalagadda S Quiason OJ Smith (1998) ArticleTitleSuccessful therapy of bleeding duodenal varices by TIPS after failure of sclerotherapy Am J Gastroenterol 93 272–4 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.270_3.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7islOkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9468260
CS Wang LB Jeng MF Chen (1995) ArticleTitleDuodenal varices bleeding successfully treated by mesocaval shunt after failure of sclerotherapy Hepatogastroenterology 42 59–61 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2MzgtFantw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle7782038
M Shiraishi S Hiroyasu T Higa et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSuccessful management of ruptured duodenal varices by means of endoscopic variceal ligation: report of a case Gastrointest Endosc 49 255–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-5107(99)70498-0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7isVKksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9925710
Y Yoshida Y Imai M Nishikawa et al. (1997) ArticleTitleSuccessful endoscopic injection sclerotherapy with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate following the recurrence of bleeding soon after endoscopic ligation for ruptured duodenal varices Am J Gastroenterol 92 1227–9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szmtlGitQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9219810
NC Tan S Ibrahim KH Tay (2005) ArticleTitleSuccessful management of a bleeding duodenal varix by endoscopic banding Singap Med J 46 723–5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MnivVSrug%3D%3D
K Ota Z Shirai T Masuzaki et al. (1998) ArticleTitleEndoscopic injection sclerotherapy with n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate for ruptured duodenal varices J Gastroenterol 33 550–5 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s005350050131 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czotlOhsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9719241
H Selcuk F Boyvat S Eren et al. (2004) ArticleTitleDuodenal varices as an unusual cause of gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension: a case report Turk Gastroenterol 15 104–7
T Komatsuda H Ishida K Konno et al. (1998) ArticleTitleColor Doppler findings of gastrointestinal varices Abdom Imaging 23 45–50 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002619900283 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FpvFOjuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9437062
Yamada M, Ishida H, Komatsuda T, et al. Portal systemic shunt through the renal vein. Abdom Imaging 2006 Feb 7; (Epub ahead print)
P Gertsch LH Blumgart (1988) ArticleTitleCure of a bleeding duodenal varix by sclerotherapy Br J Surg 75 717 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bjs.1800750731 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1czislejtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3262004
AW Barbish MN Ehrinpreis (1993) ArticleTitleSuccessful endoscopic injection sclerotherapy of a bleeding duodenal varix Am J Gastroenterol 88 90–2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s7ivVagug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8420280
M Hashiguchi H Tsuji J Shimono et al. (1999) ArticleTitleRuptured duodenal varices: an autopsy case report Hepatogastroenterology 46 1751–4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzlslCjtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10430337
SS Jonnalagadda S Quiason OJ Smith (1998) ArticleTitleSuccessful therapy of bleeding duodenal varices by TIPS after failure of sclerotherapy Am J Gastroenterol 93 272–4 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.270_3.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7islOkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9468260
K Ogawa S Ishikawa Y Naritaka et al. (1999) ArticleTitleClinical evaluation of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy using n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate for gastric variceal bleeding J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14 245–50 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01842.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXit1Wlu7w%3D Occurrence Handle10197494
YH Huang HZ Yeh GH Chen et al. (2000) ArticleTitleEndoscopic treatment of bleeding gastric varices by N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (Histoacryl) injection: long-term efficacy and safety Gastrointest Endosc 52 160–7 Occurrence Handle10.1067/mge.2000.104976 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvlslyhuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10922085
M Ohta K Yasumori M Saku et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSuccessful treatment of bleeding duodenal varices by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration: a transjugular approach Surgery (St. Louis) 126 581–3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mvhs1SltQ%3D%3D
Y Akazawa I Murata T Yamao et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSuccessful management of bleeding duodenal varices by endoscopic variceal ligation and balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration Gastrointest Endosc 58 794–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-5107(03)02008-X Occurrence Handle14595327
T Sonomura K Horihata K Yamahara et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRuptured duodenal varices successfully treated with balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration: usefulness of microcatheters Am J Roentgenol 181 725–7
T Menu B Gayet H Nahum (1987) ArticleTitleBleeding duodenal varices: diagnosis and treatment by percutaneous portography and transcatheter embolization Gastrointest Radiol 12 111–3 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01885117 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s7mtlWqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3493935
K Takamura H Miyake H Mori et al. (2005) ArticleTitleBalloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration and percutaneous transhepatic obliteration for ruptured duodenal varices after operation for rectal cancer with multiple liver metastasis: report of a case J Med Invest 52 212–7 Occurrence Handle10.2152/jmi.52.212 Occurrence Handle16167541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, T., Yamazaki, K., Toyota, J. et al. Efficacy of color Doppler ultrasonography for the diagnosis of duodenal varices successfully treated with percutaneous transhepatic obliteration. J Med Ultrasonics 34, 59–63 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-006-0129-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-006-0129-4