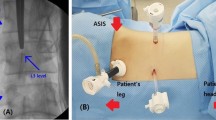
Summary
BACKGROUND: Video-assisted retroperitoneoscopy is a relatively new surgical technique for performing lumbar sympathectomies and is used increasingly for the treatment of primary plantar hyperhidrosis. In this paper, we report on our clinical experience with this procedure. METHODS: Between December 2004 and August 2011, 306 retroperitoneoscopic lumbar sympathectomies have been performed on 154 patients with severe refractory plantar hyperhidrosis. The perioperative course as well as the postoperative results were analysed in a retrospective analysis. RESULTS: All 306 lumbar sympathectomies were performed in retroperitoneoscopic technique and in none of the cases a conversion to open surgery was necessary. Mortality was zero, and there were no serious intraoperative complications. In approx. 25% of the patients, the surgery was classified as technically difficult for a number of reasons. Postoperative complications occurred in 4 patients (2.6%) in the form of an abdominal wall haematoma, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism and a thrombosis of the right iliac vein. In all patients, the hyperhidrosis was eliminated immediately after surgery. 121 patients (79%) underwent follow-up controls 24 months after surgery on average. Three patients (2.5%) suffered a hyperhidrosis relapse. Adverse events occurred in form of compensatory sweating in 63 patients (52%) and in form of post-sympathectomy neuralgia in 47 patients (39%). Three men developed a temporary ejaculation disorder. CONCLUSIONS: Lumbar sympathectomy can be performed safely and effectively with retroperitoneoscopic surgical technique. Morbidity is low and the procedure is suited very well for the treatment of plantar hyperhidrosis. Since this surgery may be technically difficult because of the anatomic particularities of the retroperitoneum, high expertise with endoscopic surgical techniques is required.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Royle ND. A new operative procedure in the treatment of spastic paralysis and its experimental basis. Med J Aust 1924;1:77
Adson A, Brown GE. Treatment of Raynaud's disease by lumbar ramisection and ganglionectomy and perivascular sympathectneurectomy. JAMA 1925;84:1908–10
Enjalbert A, Gedeon A, Castany R. Indications and results of lumbar sympathectomy. J Cardiovasc Surg 1968;9:146–9
Lee BY, Da Silva MC, Aquino-Chu G, et al. Surgery of the sympathetic nervous system. J Spinal Cord Med 1996;19:20–6
Simeone FA. The lumbar sympathetic. Anatomy and surgical implications. Acta Chir Belg 1977;1:17–26
Wittmoser R. Die Retroperitoneoskopie als neue Methode der lumbalen Sympathektomie. Fortschritte der Endoskopie 1973;4:219–21
Gill IS, Clayman RV, Albala DM, et al. Retroperitoneal and pelvic extraperitoneal laparoscopy: an international experience. Urology 1998;52:566–71
Beglaibter N, Berlatzky Y, Zamir O, et al. Retroperitoneoscopic lumbar sympathectomy. J Vasc Surg 2002;35:815–7
Hourlay P, Vangertruyden G, Verduyckt F, et al. Endoscopic extraperitoneal lumbar sympathectomy. Surg Endosc 1995;9:530–5
Rieger R, Pedevilla S, Pöchlauer S. Endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy for plantar hyperhidrosis. Br J Surg 2009;96:1422–8
Rieger R, Loureiro MP, Pedevilla S, et al. Endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy following thoracic sympathectomy in patients with palmoplantar hyperhidrosis. World J Surg 2011;35:49–53
Reisfeld R. Endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy for focal plantar hyperhidrosis using the clamping method. J Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2010;20:231–6
Loureiro MP, Milanez De Campos JR, et al. Endoscopic lumbar sympathectomy for women: effect on compensatory sweat. Clinics 2008;63:189–96
Nicolas C, Grosdidier G, Granel F, et al. Endoscopic sympathectomy for palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis: results in 107 patients. Ann dermatol venereol 2000;127:1057–63
Rieger R, Pedevilla S. Retroperitoneoscopic lumbar sympathectomy for the treatment of plantar hyperhidrosis: technique and preliminary findings. Surg Endosc 2007;21:129–35
Rose SS. An investigation into sterility after lumbar ganglionectomy. Br Med J 1953;1:247–50
Whitelaw GP, Smithwick RH. Some secondary effects of sympathectomy. With particular reference to disturbance of sexual function. N Engl J Med 1951;245:121–30
Gordon A, Zechmeister K, Collin J. The role of sympathectomy in current surgical practice. Eur J Vasc Surg 1994;8:129–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*: A tribute to Wolfgang Wayand, Head of Department, 1 January 1985–31 March 2012, Department of Surgery II, General Hospital Linz, Linz, Austria
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieger, R. Video-assisted retroperitoneoscopic lumbar sympathectomy* . Eur Surg 44, 10–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-011-0055-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-011-0055-6