Abstract
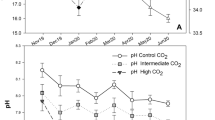
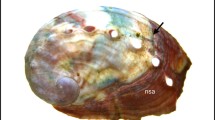
The effects of seawater acidification caused by increasing concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), combined with other climatic stressors, were studied on 3 coastal Mediterranean bivalve species: the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and the clams Chamelea gallina and Ruditapes decussatus. CO2 perturbation experiments produced contrasting responses on growth and calcification of juvenile shells, according to species and location. In the Northern Adriatic (Italy), long-term exposure to reduced pH severely damaged the shells of M. galloprovincialis and C. gallina and reduced growth for the latter species. Seawater in the Ria Formosa lagoon (Portugal) was consistently saturated in carbonates, which buffered the impacts on calcification and growth. After 80 days, no shell damage was observed in Portugal, but mussels in the acidified treatments were less calcified. Reduced clearance, ingestion and respiration rates and increased ammonia excretion were observed for R. decussatus under reduced pH. Clearance rates of juvenile mussels were significantly reduced by acidification in Italy, but not in Portugal. Both locations showed a consistent trend for increased ammonia excretion with decreasing pH, suggesting increased protein catabolism. Respiratory rates were generally not affected. Short-term factorial experiments done in Italy revealed that acidification caused alterations in immunological parameters of adult bivalves, particularly at temperature and salinity values far from the optimal for the species in the Mediterranean. Overall, our results showed large variations in the sensitivities of bivalves to climatic changes, among different species and between local populations of the same species. Expectations of impacts, mitigation and adaptation strategies have to consider such local variability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida C, Silva M (1987) Incidence of agriculture on water quality at Campina de Faro (south Portugal). In: IV Simposio de Hidrogeología de la Asociación Española de Hidrología Subterránea, Palma de Mallorca
Amaral A (2008) Management of aquaculture of clam, R. decussatus (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Ria Formosa lagoon (south of Portugal), effects on the ecosystem and species physiology. Doctoral thesis, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, p 168
Andersson AJ, Mackenzie FT, Gattuso J-P (2011) Effects of ocean acidification on benthic processes, organisms, and ecosystems. In: Gattuso J-P, Hansson L (eds) Ocean acidification. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 122–153
Beesley A, Lowe DM, Pascoe CK, Widdicombe S (2008) Effects of CO2-induced seawater acidification on the health of Mytilus edulis. Clim Res 37:215–225
Beniash E, Ivanina A, Lieb NS, Kurochkin I, Sokolova IM (2010) Elevated level of carbon dioxide affects metabolism and shell formation in oysters Crassostrea virginica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 419:95–108
Berge JA, Bjerkeng B, Pettersen O, Schaanning MT, Øxnevad S (2006) Effects of increased sea water concentrations of CO2 on growth of the bivalve Mytilus edulis L. Chemosphere 62:681–687
Bibby R, Widdicombe S, Parry H, Spicer J, Pipe R (2008) Effects of ocean acidification on the immune response of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Aquat Biol 2:67–74
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Borges A, Gypens N (2010) Carbonate chemistry in the coastal zone responds more strongly to eutrophication than to ocean acidification. Limnol Oceanogr 55:346–353
Brierley AS, Kingsford MJ (2009) Impacts of climate change on marine organisms and ecosystems. Curr Biol 19:R602–R614
Byrne M (2011) Impact of ocean warming and ocean acidification on marine invertebrate life history stages. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 49:1–42
Caldarone E, Wagner M, St Onge-Burns J, Buckley LJ (2001) Protocol and guide for estimating nucleic acids in larval fish using a fluorescence microplate reader. Northeast Fisheries Science Center Reference Document 1
Caldeira K (2010) Adaptation to impacts of greenhouse gases on the ocean (invited). AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts 52:03
Caldeira K, Wickett ME (2003) Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 425:365
Caldeira K, Wickett ME (2005) Ocean model predictions of chemistry changes from carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and ocean. J Geophys Res Oceans 110:C09S04
Casimiro T (2011) Efeitos da acidificação da água do mar na reprodução de Mytilus edulis. Master thesis, Universidade do Algarve, Faro
Chicharo MA, Amaral A, Morais P, Chicharo L (2007) Effect of sex on ratios and concentrations of DNA and RNA in three marine species. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 332:241–245
CIESM (2008) Impacts of acidification on biological, chemical and physical systems in the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Frédéric Briand, Monaco
Cima F, Matozzo V, Marin MG, Ballarin L (2000) Haemocytes of the clam Tapes philippinarum (Adams & Reeve, 1850): morphofunctional characterisation. Fish Shellfish Immun 10:677–693
Coles JA, Farley SR, Pipe RK (1995) Alteration of the immune response of the common marine mussel Mytilus edulis resulting from exposure to cadmium. Dis Aquat Org 22:59–65
Conover RJ (1966) Assimilation of organic matter by zooplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 11:338–345
Cooley SR, Lucey N, Kite-Powell H, Doney SC (2011) Nutrition and income from molluscs today imply vulnerability to ocean acidification tomorrow. Fish Fish 13:182–215
Cushman-Roisin B, Gacic M, Poulain P-M, Artegiani A (2001) Physical oceanography of the Adriatic Sea. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, p 304
Cyronak T, Santos IR, McMahon A, Eyre BD (2013) Carbon cycling hysteresis in permeable carbonate sands over a diel cycle: implications for ocean acidification. Limnol Oceanogr 58:131–143
Dickinson GH, Ivanina AV, Matoo OB, Pörtner HO, Lannig G, Bock C, Beniash E, Sokolova IM (2012) Interactive effects of salinity and elevated CO2 levels on juvenile eastern oysters, Crassostrea virginica. J Exp Biol 215:29–43
Diffenbaugh NS, Pal JS, Giorgi F, Gao X (2007) Heat stress intensification in the Mediterranean climate change hotspot. Geophys Res Lett 34:6
Doney SC, Fabry VJ, Feely RA, Kleypas JA (2009) Ocean acidification: the other CO2 problem. Annu Rev Mar Sci 1:169–192
Duarte CM, Hendriks IE, Moore TS, Olsen YS, Steckbauer A, Ramajo L, Carstensen J, Trotter JA, McCulloch M (2013) Is ocean acidification an open-ocean syndrome? Understanding Anthropogenic Impacts on Seawater pH. Estuar Coasts 36:221–236
Eurostat (2011) EU-27 aquaculture production—quantities (Tonnes live weight): 1984 onwards. http://eu22.eu/aquaculture-production/
Fernández Reiriz MJ, Range P, Álvarez-Salgado XA, Labarta U (2011) Physiological energetics of juvenile clams Ruditapes decussatus in a high CO2 coastal ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 433:97–105
Fernández-Reiriz MJ, Perez-Camacho A, Ferreiro MJ, Blanco J, Planas M, Campos MJ, Labarta U (1989) Biomass production and variation in the biochemical profile (total protein, carbohydrates, RNA, lipids and fatty acids) of seven species of marine microalgae. Aquaculture 83:17–37
Fernández-Reiriz MJ, Range P, Alvarez-Salgado XA, Espinosa J, Labarta U (2012) Tolerance of juvenile Mytilus galloprovincialis to experimental seawater acidification. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 454:65–74
Filgueira R, Labarta U, Fernandez-Reiriz MJ (2006) Flow-through chamber method for clearance rate measurements in bivalves: design and validation of individual chambers and mesocosm. Limnol Oceangr Methods 4:284–292
Findlay HS, Wood HL, Kendall MA, Spicer JI, Twitchett RJ, Widdicombe S (2009) Calcification, a physiological process to be considered in the context of the whole organism. Biogeosci Discuss 6:2267–2284
Galloway TS, Depledge MH (2001) Immunotoxicity in Invertebrates: measurement and ecotoxicological relevance. Ecotoxicology 10:5–23
Gattuso J-P, Hansson L (2011) Ocean Acidification. Oxford University Press
Gattuso J-P, Lavigne H (2009) Approaches and software tools to investigate the impact of ocean acidification. Biogeosciences 6:2121–2133
Hansen J, Sato M, Ruedy R, Lo K, Lea DW, Medina-Elizade M (2006) Global temperature change. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:14288–14293
Harvey BP, Gwynn-Jones D, Moore PJ (2013) Meta-analysis reveals complex marine biological responses to the interactive effects of ocean acidification and warming. Ecol Evol. doi:10.1002/ece3.516
Haugan PM, Drange H (1996) Effects of CO2 on the ocean environment. Energy Convers Manag 37:1019–1022
Hauton C, Hawkins LE, Hutchinson S (1998) The use of the neutral red retention assay to examine the effects of temperature and salinity on haemocytes of the European flat oyster Ostrea edulis (L). Comp Biochem Physiol 119B:619–623
Hendriks IE, Duarte CM, Álvarez M (2010) Vulnerability of marine biodiversity to ocean acidification: a meta-analysis. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 86:157–164
Hildreth DI, Crisp DJ (1976) A corrected formula for calculation of filtration rate of bivalve molluscs in an experimental flowing system. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 56:111–120
Hine PM (1999) The inter-relationships of bivalve haemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:367–385
Hofmann GE, Barry JP, Edmunds PJ, Gates RD, Hutchins DA, Klinger T, Sewell MA (2010) The effect of ocean acidification on calcifying organisms in marine ecosystems: an organism-to-ecosystem perspective. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 41:127–147
Joos F, Frölicher T, Steinacher M, Plattner GK (2011) Impact of climate change mitigation on ocean acidification projections. In: Gattuso J-P, Hansson L (eds) Ocean acidification. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 272–290
Kroeker KJ, Kordas RL, Crim RN, Singh GG (2010) Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol Lett 13:1419–1434
Labarta U, FernandezReiriz MJ, Babarro JMF (1997) Differences in physiological energetics between intertidal and raft cultivated mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 152:167–173
Lannig G, Eilers S, Pörtner HO, Sokolova IM, Bock C (2010) Impact of ocean acidification on energy metabolism of oyster, Crassostrea gigas—changes in metabolic pathways and thermal response. Mar Drugs 8:2318–2339
Lejeusne C, Chevaldonné P, Pergent-Martini C, Boudouresque CF, Pérez T (2010) Climate change effects on a miniature ocean: the highly diverse, highly impacted Mediterranean Sea. Trends Ecol Evol 25:250–260
Liu W, He M (2012) Effects of ocean acidification on the metabolic rates of three species of bivalve from southern coast of China. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 30:206–211
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luchetta A, Cantoni C, Catalano G (2010) New observations of CO2-induced acidification in the northern Adriatic Sea over the last quarter century. Chem Ecol 26(suppl):1–17
Marin MG, Chinellato A, Munari M, Bressan M, Matozzo V (in preparation) Long-term effects of sea water acidification on physiological responses of juvenile bivalves Mytilus galloprovincialis and Chamelea gallina
Martin LB, Hopkins WA, Mydlarz LD, Rohr JR (2010) The effects of anthropogenic global changes on immune functions and disease resistance. Ann NY Acad Sci 1195:129–148
Matozzo V, Marin MG (2010) First evidence of gender-related differences in immune parameters of the clam Ruditapes philippinarum (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Mar Biol 157:1181–1189
Matozzo V, Marin MG (2011) Bivalve immune responses and climate changes: is there a relationship? Invertebr Surviv J 8:70–77
Matozzo V, Chinellato A, Munari M, Finos L, Bressan M, Marin MG (2012) First evidence of immunomodulation in bivalves under seawater acidification and increased temperature. PLoS One 7:e33820
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Noda A, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ (2007) Global climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Melatunan S, Calosi P, Rundle SD, Moody AJ, Widdicombe S (2011) Exposure to elevated temperature and pCO2 reduces respiration rate and energy status in the Periwinkle Littorina littorea. Physiol Biochem Zool 84:583–594
Melzner F, Stange P, Trübenbach K, Thomsen J, Casties I, Panknin U, Gorb SN, Gutowska MA (2011) Food supply and seawater pCO2 impact calcification and internal shell dissolution in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. PLoS One 6:e24223
Metzger R, Sartoris FJ, Langenbuch M, Pörtner HO (2007) Influence of elevated CO2 concentrations on thermal tolerance of the edible crab Cancer pagurus. J Therm Biol 32:144–151
Michaelidis B, Ouzounis C, Paleras A, Portner HO (2005) Effects of long-term moderate hypercapnia on acid-base balance and growth rate in marine mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 293:109
Montecinos LA, Cisterna JA, Cáceres CW, Saldías GS (2009) Equilibrio ácido-base durante la exposición aérea en el molusco bivalvo Perumytilus purpuratus (Lamarck, 1819) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 44:181–187
Morgan ER, Wall R (2009) Climate change and parasitic disease: farmer mitigation? Trends Parasitol 25:308–313
Moschino V, Chicharo LMZ, Marin MG (2008) Effects of hydraulic dredging on the physiological responses of the target species Chamelea gallina (Mollusca: Bivalvia): laboratory experiments and field surveys. Sci Mar 72:493–501
Nicholls RJ, Wong PP, Burkett V, Codignotto J, Hay J, McLean R, Ragoonaden S, Woodroffe CD, Abuodha P, Arblaster J, et al. (2007) Coastal systems and low-lying areas. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 315–356
Parker L, Ross P, O’Connor W, Pörtner H, Scanes E, Wright J (2013) Predicting the response of molluscs to the impact of ocean acidification. Biology 2(2):651–692
Pauly D, Christensen V, Guenette S, Pitcher TJ, Sumaila UR, Walters CJ, Watson R, Zeller D (2002) Towards sustainability in world fisheries. Nature 418:689–695
Philippart CJM, Anadón R, Danovaro R, Dippner JW, Drinkwater KF, Hawkins SJ, O’Sullivan G, Oguz T, Reid PC (2007) Impacts of climate change on the European marine and coastal environment ecosystems approach/European Science Foundation Marine Board. European Science Foundation Marine Board, Strasbourg
Pipe RK, Coles JA (1995) Environmental contaminants influencing immune function in marine bivalve molluscs. Fish Shellfish Immunol 5:581–595
Portner HO (2008) Ecosystem effects of ocean acidification in times of ocean warming: a physiologist’s view. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 373:203–217
Poulin R (2006) Global warming and temperature-mediated increases in cercarial emergence in trematode parasites. Parasitology 132:143–151
Range P, Chicharo MA, Ben-Hamadou R, Piló D, Matias D, Joaquim S, Oliveira AP, Chicharo L (2011) Calcification, growth and mortality of juvenile clams Ruditapes decussatus under increased pCO2 and reduced pH: variable responses to ocean acidification at local scales? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 396:177–184
Range P, Chicharo MA, Ben-Hamadou R, Piló D, Matias D, Joaquim S, Oliveira AP, Chicharo L (2012) Effects of seawater acidification by CO2 on life history traits of juvenile mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis in a coastal lagoon environment. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 424–425:89–98
Ries JB, Cohen AL, McCorkle DC (2009) Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO2-induced ocean acidification. Geology 37:1131–1134
Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Houlbreque F, Tambutte E, Boisson F, Baggini C, Patti FP, Jeffree R, Fine M, Foggo A, Gattuso J-P, Hall-Spencer JM (2011) Coral and mollusc resistance to ocean acidification adversely affected by warming. Nat Clim Chang 1:308–312
Rosa R, Marques A, Nunes ML (2012) Impact of climate change in Mediterranean aquaculture. Rev Aquac 4:163–177
Rufino MM, Gaspar MB, Pereira AM, Vasconcelos P (2006) Use of shape to distinguish Chamelea gallina and Chamelea striatula (Bivalvia: Veneridae): linear and geometric morphometric methods. J Morphol 267:1433–1440
Sokolova IM, Frederich M, Bagwe R, Lannig G, Sukhotin AA (2012) Energy homeostasis as an integrative tool for assessing limits of environmental stress tolerance in aquatic invertebrates. Mar Environ Res 79:1–15
Solorzano L (1969) Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol Oceanogr 14:799–801
Stigter TY, Carvalho Dill AMM, Ribeiro L, Reis E (2006) Impact of the shift from groundwater to surface water irrigation on aquifer dynamics and hydrochemistry in a semi-arid region in the south of Portugal. Agric Water Manage 85:121–132
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1968) A practical handbook of sea water analysis. Queen’s Printer, Ottawa
Thomsen J, Melzner F (2010) Moderate seawater acidification does not elicit long-term metabolic depression in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Biol 157:2667–2676
Thomsen J, Gutowska MA, Saphörster J, Heinemann A, Trübenbach K, Fietzke J, Hiebenthal C, Eisenhauer A, Körtzinger A, Wahl M, Melzner F (2010) Calcifying invertebrates succeed in a naturally CO2-rich coastal habitat but are threatened by high levels of future acidification. Biogeosciences 7:3879–3891
Walther K, Sartoris FJ, Bock C, Pörtner HO (2009) Impact of anthropogenic ocean acidification on thermal tolerance of the spider crab Hyas araneus. Biogeosciences 6:2207–2215
Widdicombe S, Spicer JI, Kitidis V (2011) Effects of ocean acidification on sediment fauna. In: Gattuso J-P, Hansson L (eds) Ocean acidification. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 176–191
Widdows J (1985) Physiological measurements. In: Bayne BL, Brown D, Burns K, Dixon D (eds) The effects of stress and pollution on marine animals. Praeger, New York, pp 3–45
Wollast R (1998) Evaluation and comparison of the global carbon cycle in the coastal zone and in the open ocean. Sea 10:213–225
Acknowledgments
This is a contribution of the ACIDBIV project, which is part of the CIRCLE Med network. Funding was provided by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) of Portugal (ERA-CIRCLE/0004/2007), the Regional Ministry of Innovation and Industry of the Galician Government, and the Italian Ministry for Environment, Land and Sea, in the framework of Circle ERA Net project (which is funded by the European Commission 6th Framework Programme). PR was also supported by a post-doctoral grant from FCT (SFRH/BPD/69959/2010). The authors would like to acknowledge the staff of the Bivalve Production Group at IPMA-Tavira for their continuous support. Comments by the editors of this special issue and two anonymous referees substantially improved the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Range, P., Chícharo, M.A., Ben-Hamadou, R. et al. Impacts of CO2-induced seawater acidification on coastal Mediterranean bivalves and interactions with other climatic stressors. Reg Environ Change 14 (Suppl 1), 19–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0478-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0478-7