Abstract
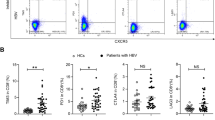
This study addresses the involvement of regulatory T cells in hepatitis E (HE) infection. The study population comprised 77 acute viral HE patients, 52 recovered individuals (overall, 129 individuals with HE) and 53 healthy controls. Peripheral CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and CD4+CD25−Foxp3+ frequencies by flow cytometry and HE-specific cytokines/chemokines quantitation were carried out. The median percentage of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and CD4+CD25−Foxp3+ T cells in acute patients were significantly higher compared to controls and recovered individuals. Both of the T regulatory (Treg) subset populations in overall HE were significantly elevated compared to controls. Comparisons of cytokines/chemokines revealed that the levels of IL-10 were elevated in: (a) acute viral hepatitis E (AVH-E) versus recovered individuals and controls, and (b) HE versus controls. Overall, the elevation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and CD4+CD25−Foxp3+ frequencies and the rise in IL-10 suggest that Treg cells might be playing a pivotal role in hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HEV:
-
Hepatitis E virus
- HE:
-
Hepatitis E
- AVH:
-
Acute viral hepatitis
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- HAV:
-
Hepatitis A virus
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- Treg:
-
T regulatory
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- Foxp3:
-
Forkhead box protein 3
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- EBV:
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- HTLV:
-
Human T-lymphotropic virus
References
Khuroo MS (1980) Study of an epidemic of non-A, non-B hepatitis. Possibility of another human hepatitis virus distinct from post-transfusion non-A, non-B type. Am J Med 68:818–824
Aggarwal R, Krawczynski K (2000) Hepatitis E: an overview and recent advances in clinical and laboratory research. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:9–20
Tam AW, Smith MM, Guerra ME, Huang CC, Bradley DW, Fry KE et al (1991) Hepatitis E virus (HEV): molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 185:120–131
Khuroo MS, Kamili S, Dar MY, Moecklii R, Jameel S (1993) Hepatitis E and long-term antibody status. Lancet 341:1355
Deshmukh TM, Lole KS, Tripathy AS, Arankalle VA (2007) Immunogenicity of candidate hepatitis E virus DNA vaccine expressing complete and truncated ORF2 in mice. Vaccine 25:4350–4360
Srivastava R, Aggarwal R, Jameel S, Puri P, Gupta VK, Ramesh VS et al (2007) Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein. Viral Immunol 20:56–65
Srivastava R, Aggarwal R, Bhagat MR, Chowdhury A, Naik S (2008) Alterations in natural killer cells and natural killer T cells during acute viral hepatitis E. J Viral Hepat 15:910–916
Sakaguchi S (2005) Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol 6:345–352
Baecher-Allan C, Brown JA, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA (2001) CD4+CD25high regulatory cells in human peripheral blood. J Immunol 167:1245–1253
Suvas S, Kumaraguru U, Pack CD, Lee S, Rouse BT (2003) CD4+CD25+ T cells regulate virus-specific primary and memory CD8+ T cell responses. J Exp Med 198:889–901
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Deshmukh TM, Chobe LP, Gandhe SS (2007) Evaluation of human (genotype 1) and swine (genotype 4)-ORF2-based ELISAs for anti-HEV IgM and IgG detection in an endemic country and search for type 4 human HEV infections. J Viral Hepat 14:435–445
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Deshmukh TM, Srivastava S, Shaligram US (2009) Challenge studies in Rhesus monkeys immunized with candidate hepatitis E vaccines: DNA, DNA-prime-protein-boost and DNA-protein encapsulated in liposomes. Vaccine 27:1032–1039
Saravanabalaji S, Tripathy AS, Dhoot RR, Chadha MS, Kakrani AL, Arankalle VA (2009) Viral load, antibody titers and recombinant open reading frame 2 protein-induced TH1/TH2 cytokines and cellular immune responses in self-limiting and fulminant hepatitis E. Intervirology 52:78–85
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Arya RP, Tripathy AS, Ramdasi AY, Chadha MS et al (2010) Role of host immune response and viral load in the differential outcome of pandemic H1N1 (2009) influenza virus infection in Indian patients. PLoS ONE 5:e13099
Xu D, Fu J, Jin L, Zhang H, Zhou C, Zou Z et al (2006) Circulating and liver resident CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B. J Immunol 177:739–747
Bolacchi F, Sinistro A, Ciaprini C, Demin F, Capozzi M, Carducci FC et al (2006) Increased hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes and reduced HCV-specific CD4+ T cell response in HCV-infected patients with normal versus abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels. Clin Exp Immunol 144:188–196
Quinn KM, McHugh RS, Rich FJ, Goldsack LM, de Lisle GW, Buddle BM et al (2006) Inactivation of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells during early mycobacterial infection increases cytokine production but does not affect pathogen load. Immunol Cell Biol 84:467–474
Tran DQ, Shevach EM (2009) Therapeutic potential of FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells and their interactions with dendritic cells. Hum Immunol 70:294–299
Lee DCP, Harker JAE, Tregoning JS, Atabani SF, Johansson C, Schwarze J et al (2010) CD25+ natural regulatory T cells are critical in limiting innate and adaptive immunity and resolving disease following respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Virol 84:8790–8798
Lühn K, Simmons CP, Moran E, Dung NT, Chau TN, Quyen NT et al (2007) Increased frequencies of CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells in acute dengue infection. J Exp Med 204:979–985
Franzese O, Kennedy PT, Gehring AJ, Gotto J, Williams R, Maini MK et al (2005) Modulation of the CD8+-T-cell response by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 79:3322–3328
Prabhu SB, Gupta P, Durgapal H, Rath S, Gupta SD, Acharya SK et al (2010) Study of cellular immune response against Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). J Viral Hepat [Epub ahead of print]
Acknowledgements
We thank the Director of the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for all the encouragement given. Special thanks are due to Mr. Babbar, Mr. Tilekar, Mr. Jawalkar, Miss Thorat, Mr. Vaidya and Mr. Sukhare for their excellent technical help. Statistical assistance by Mr. Walimbe is gratefully acknowledged. This study was funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rumki Das and Sanjay B Rathod have contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathy, A.S., Das, R., Rathod, S.B. et al. Peripheral T regulatory cells and cytokines in hepatitis E infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31, 179–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1291-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1291-1