Abstract
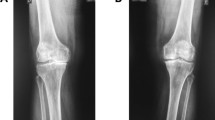
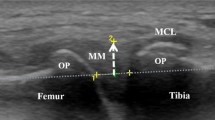
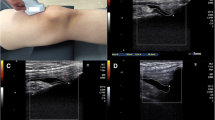
The aim of this study was to determine clinical and US factors associated with pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). The study included 143 patients. Patients were divided into two groups: group 1 consisted of 94 patients with unilateral or bilateral knee pain ≥3 cm during physical activity for at least 48 h prior to inclusion, measured by the visual analog scale from 0 to 10 cm. Group 2 consisted of 49 patients with knee OA without knee pain at least 1 month prior to inclusion. In both knees, range of motion was measured by goniometry and anteroposterior, and lateral knee radiographs were taken during weight-bearing. OA grading was performed in accordance with the Kellgren–Lawrence criteria by a specialist in radiology experienced in this field. A knee ultrasound (US) examination was performed in all patients by a blinded radiologist. Women were more often symptomatic than men (p < 0.005). Patients in group 1 tended to have a higher body mass index (BMI; p < 0.001). Radiographic grades III (52.1%) and II (37.2%) were most frequently found in group 1, whereas I (30.6%), II (46.9%), and III (22.4%) were found in group 2. When radiographic grades in both groups were compared, group 1 had greater radiographic grades than group 2 (p < 0.001). US findings in group 1 were effusion of the suprapatellar pouch (72.3%), Baker’s cyst (42.6%), protrusion of the anterior horn of the medial meniscus associated with medial collateral ligament displacement (9.6%), and loose body (9.6%). In group 2, the only US finding was Baker’s cyst (6.1%). Regression analysis revealed that BMI, degree of knee flexion, and thickness of the quadriceps tendon were factors that were related with pain in the knee. Increased BMI, decrease in the degree of knee flexion, and decreased quadriceps tendon thickness are factors that increase the risk of pain in knee OA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hannan MT, Anderson JJ, Pincus T, Felson DTJ (1992) Educational attainment and osteoarthritis: differential associations with radiographic changes and symptom reporting. Clin Epidemiol 45(2):139–147
Matthew W Rogers, Frances V Wilder (2008) The association of BMI and knee pain among persons with radiographic knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 9:163. Published online 2008 December 12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-163. PMCID: PMC2651875
Sharma L, Kapoor D (2007) Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. In: Moskowitz RW, Altman RD, Hochberg MC, Buckwalter JA, Goldberg VM (eds) Osteoarthritis: diagnosis and medical/surgical management, 4th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 3–26
Duncan R, Peat G, Thomas E, Hay E, McCall I, Croft P (2007) Symptoms and radiographic osteoarthritis: not as discordant as they are made out to be? Ann Rheum Dis 66(1):86–91
Davis MA, Ettinger WH, Neuhaus JM (1990) Obesity and osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES I). Semin Arthritis Rheum 20(Suppl 1):34–41
Davis MA, Ettinger WH, Neuhaus JM, Barclay JD, Segal MR (1992) Correlates of knee pain among US adults with and without radiographic knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 19(12):1943–1949
Monteforte P, Rovetta G (1999) Sonographic assessment of soft tissue alterations in osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Tissue React 21(1):19–23
Monteforte P, Sessarego P, Rovetta G (2008) Sonographic assessment of soft tissue alterations in osteoarthritis of the knee. G Ital Med Lav Ergon 30(1):75–77
de Miguel ME, Cobo Ibáñez T, Usón Jaeger J, Bonilla Hernán G, Martín Mola E (2006) Clinical and ultrasonographic findings related to knee pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14(6):540–544
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K et al (1986) Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum 29:1039–1049
D'Agostino MA, Conaghan P, Le Bars M, Baron G, Grassi W, Martin-Mola E, Wakefield R, Brasseur JL, So A, Backhaus M, Malaise M, Burmester G, Schmidely N, Ravaud P, Dougados M, Emery P (2005) EULAR report on the use of ultrasonography in painful knee osteoarthritis. Part 1: prevalence of inflammation in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(12):1703–9, Epub 2005 May 5
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1987) Radiologic assessment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–501
Falsetti P, Frediani B, Fioravanti A, Acciai C, Baldi C, Filippou C, Marcolongo R (2003) Sonographic study of calcaneal entheses in erosive osteoarthritis, nodal osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 32:229–234
Moskin SH, Bronth DK (2001) Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. In: Ruddy S, Haris DE, Sledge BC (eds) Textbook of Rheumatology. Philadelphia, WB Saunders Company, pp 1391–1409
Lawrence RC, Hochberg MC, Kelsey JL, McDuffie FC, McDuffie FC, Medsger TA Jr et al (1989) Estimates of the prevalence of selected arthritic and musculoskeletal diseases in the United States. J Rheumatol 16:427–441
Felson DT, Zhang Y (1998) An update on the epidemiology of knee and hip osteoarthritis with a view to prevention. Arthritis Rheum 41:1343–1355
Creamer P, Lethbridge-Cejku M, Hochberg MC (2000) Factors associated with functional impairment in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford) 39(5):490–496
Marks R (2007) Obesity profiles with knee osteoarthritis: correlation with pain, disability, disease progression. Obesity 15(7):1867–1874
Felson DT, Chaisson CE, Hill CL, Totterman SM, Gale ME, Skinner KM, Kazis L, Gale DR (2001) The association of bone marrow lesions with pain in knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med 134(7):541–549
Arden N, Nevitt MC (2006) Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(1):3–25
Liikavainio T, Lyytinen T, Tyrväinen E, Sipilä S, Arokoski JP (2008) Physical function and properties of quadriceps femoris muscle in men with knee osteoarthritis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 89(11):2185–2194
Dekker J, Boot B, van der Woude LH, Bijlsma JW (1992) Pain and disability in osteoarthritis: a review of biobehavioral mechanisms. J Behav Med 15:189–214
Pai YC, Rymer WZ, Chang RW, Sharma L (1997) Effect of age and osteoarthritis on knee proprioception. Arthritis Rheum 40:2260–2265
Steultjens MP, Dekker J, van Baar ME, Oostendorp RA, Bijlsma JW (2000) Range of joint motion and disability in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee or hip. Rheumatol (Oxford) 39:955–961
Maly MR, Costigan PA, Olney SJ (2008) Mechanical factors relate to pain in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biomech 23(6):796–805
Hannan MT, Felson DT, Pincus T (2000) Analysis of the discordance between radiographic changes and knee pain in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Rheumatol 27(6):1513–1517
Altman RD, Marcussen KC (2001) Effects of a ginger extract on knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44(11):2531–2538
Peat G, Mc Carney R, Croft P (2001) Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: a review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann Rheum Dis 60(2):91–97
Hurwitz DE, Ryals AR, Block JA, Sharma L, Schnitzer TJ, Andriacchi TP (2000) Knee pain and joint loading in subjects with osteoarthritis of the knee. J Orthop Res 18(4):572–579
Neogi T, Felson D, Niu J, Nevitt M, Lewis CE, Aliabadi P et al (2009) Association between radiographic features of knee osteoarthritis and pain: results from two cohort studies. BMJ 21:339:b2844. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2844
Duncan R, Peat G, Thomas E, Wood L, Hay E, Croft P (2008) How do pain and function vary with compartmental distribution and severity of radiographic knee osteoarthritis? Rheumatol (Oxford) 47(11):1704–1707
McAlindon TE, Cooper C, Kirwan JR, Dieppe PA (1993) Determinants of disability in osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann Rheum Dis 52(4):258–262
Salaffi F, Cavalieri F, Nolli M, Ferraccioli GF (1991) Analysis of disability in knee osteoarthritis. Relationship with age and psychological variables but not with radiographic score. J Rheumatol 18:1581–1586
Acebes JC, Sánchez-Pernaute O, Díaz-Oca A, Herrero-Beaumont G (2006) Ultrasonographic assessment of Baker’s cysts after intra-articular corticosteroid injection in knee osteoarthritis. J Clin Ultrasound 34(3):113–117
Naredo E, Cabero F, Palop MJ, Collado P, Cruz A, Crespo M (2005) Ultrasonographic findings in knee osteoarthritis: a comparative study with clinical and radiographic assessment. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 13(7):568–574
Gale DR, Chaisson CE, Totterman SM, Schwartz RK, Gale ME, Felson D (1999) Meniscal subluxation: association with osteoarthritis and joint space narrowing. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 7(6):526–532
Breitenseher MJ, Trattnig S, Dobrocky I, Kukla C, Nehrer S et al (1997) MR imaging of meniscal subluxation in the knee. Acta Radiol 38(5):876–879
Miller TT, Staron RB, Feldman F, Cepel E (1997) Meniscal position on routine MR imaging of the knee. Skeletal Radiol 26(7):424–427
Ahn JH, Yoo JC, Lee SH (2007) Arthroscopic loose-body removal in posterior compartment of the knee joint: a technical note. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15(1):100–106
McGinty JB (1982) Arthroscopic removal of loose bodies. Orthop Clin North Am 13:313
Bianchi S, Martinoli C (1999) Detection of loose bodies in joints. Radiol Clin North Am 37(4):679–690
Friedman L, Finlay K, Popovich T, Chhem RK (2003) Sonographic findings in patients with anterior knee pain. J Clin Ultrasound 31(2):85–97
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mermerci, B.B., Garip, Y., Uysal, R.S. et al. Clinic and ultrasound findings related to pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 30, 1055–1062 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1701-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1701-x