Abstract
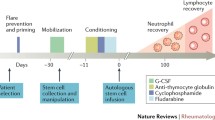
We report on the unique effects and benefits of autologous stem cell transplantation in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and describe this procedure in two young girls with severe and refractory disease. The patients’ stem cells were mobilized with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and collected by CS-3000 Blood Cell Separator (Baxter Healthcare, Round Lake, Ill., USA), and the CliniMACS CD34+ cell selection device (Miltenyi Biotech, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) was used to obtain CD34+ cells. A total of 1.7×106 and 1.0×106/kg CD34+ cells were obtained, with 2.0×105 and 1.0×104/kg of CD3+ cells remaining, respectively. The conditioning regimen consisted of cyclophosphamide (50 mg/kg per day for 4 days) plus antithymocyte globulin (ATG-Fresenius, 5 mg/kg per day for 3 days). Neutrophil counts recovered within 9 days in both cases. Within 15 days, the platelet counts recovered and were sustained over 100×109/l. Cushingoid features disappeared completely 3 months after transplantation because of the removal of corticosteroid medication. One 13-year-old child increased her height by 5 cm in 6 months after stopping steroids. She had not increased her height in her previous 7 years of disease. As of the time of this report, the first patient remains in clinical and laboratory remission for nearly 4 years, while the second suffered a relapse of thrombocytopenia 9 months post-transplantation. One residual effect of their treatment is that their CD4+ cell counts remained in the lower range after one year of transplant. The effect of this conditioning regimen plus CD34+ autologous stem cell transplantation on these two children with refractory SLE was beneficial, but long-term follow-up data and additional experience with this procedure are required. Autologous stem cell transplantation may limit the long-term toxicity of therapy in childhood SLE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tyndall A, Koike T (2002) High-dose immunoablative therapy with hematopoietic stem cell support in the treatment of severe autoimmune disease: current status and future direction. Intern Med 41:608–612
Marmont A, Gratwohl A, Vischer T et al (1995) Haemopoietic precursor cell transplants for autoimmune disease. Lancet 345:978
Traynor AE, Barr WG, Rosa RM, Rodriguez J, Oyama Y, Baker S et al (2002) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe and refractory lupus. Analysis after five years and fifteen patients. Arthritis Rheum 46:2917–2923
Dong L, Chen H, Jiang M (2000) Selected CD34+ cells transplantation: a primary clinical report. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 80:841–844
Traynor AE, Schroeder J, Rosa RM, Cheng D, Stefka J, Mujais S et al (2000) Treatment of severe systemic lupus erythematosus with high-dose chemotherapy and haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase I study. Lancet 356:701–707
Burt RK, Traynor AE, Pope R, Schroeder J, Cohen B, Karlin KH et al (1998) Treatment of autoimmune disease by intense immunosuppressive conditioning and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 92:3505–3514
Wulffraat NM, Sanders EAM, Kamphuis SS, Rijkers GT, Kuis W, Lilien M et al (2001) Prolonged remission without treatment after autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 44:728–731
Trysberg E, Lindgren I, Tarkowski A (2000) Autologous stem cell transplantation in a case of treatment resistant central nervous system lupus. Ann Rheum Dis 59:236–238
McNiece I, Briddel R, Stoney G, Kern B, Zilm K, Recktenwald D et al (1997) Large-scale isolation of CD34+ cell using the Amgen cell selection device results in high levels of purity and recovery. J Hematother 6:5–11
Chang KSF, Lee MMC, Low WD, Chui S, Chow M (1965) Standards of height and weight of southern Chinese children. Far East Med J 1:101–109
Jayne D, Passweg J, Marmont A, Farge D, Zhao X, Arnold R et al (2004) Autologous stem cell transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 13:168–176
Contreras G, Pardo V, Leclerq B, Lenz O, Tozman E, O’Nan P et al (2004) Sequential therapies for proliferative lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med 350:971–980
Petri M, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA (2003) High-dose cyclophosphamide without stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 48:166–173
Gladstone DE, Prestrud AA, Pradhan A, Styler MJ, Topolsky DL, Crilley PA et al (2002) High-dose cyclophosphamide for severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 11:405–410
Slater CA, Liang MH, McCune JW, Christman GM, Laufer MR (1999) Preserving ovarian function in patients receiving cyclophosphamide. Lupus 8:3–10
McDermott EM, Powell RJ (1996) Incidence of ovarian failure in systemic lupus erythematosus after treatment with pulse cyclophosphamide. Ann Rheum Dis 55:224–229
Chen J, Gu LJ, Zhao HJ, Xue HL, Zheng Y, Xie XJ et al (2003) Application of CD34+ autologous peripheral progenitor cell transplant in the treatment of children with refractory SLE (in Chinese). Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 41:426
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Drs. H. James Williams and Hong-Hua Mu for their critical review and assistance with the preparation of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, Y., Kunkel, G. et al. Use of CD34+ autologous stem cell transplantation in the treatment of children with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 24, 464–468 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-1065-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-1065-6