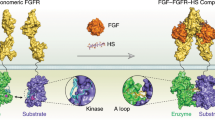
Abstract
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) play important roles in the control of many cellular processes including cell proliferation, cell adhesion, angiogenesis, and apoptosis. Ligand-induced dimerization of RTKs leads to autophosphorylation and activation of RTKs. Structural studies have shown that while isolated ectodomains of several RTKs form symmetric dimers the isolated cytoplasmic kinase domains of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) form asymmetric dimers during their activation. Binding of one kinase molecule of EGFR to a second kinase molecule asymmetrically leads to stimulation of kinase activity and enhanced autophosphorylation. Furthermore, the structures of the kinase domain of FGFR1 and FGFR2 reveal the formation of asymmetric interfaces in the processes of autophosphorylation at their specific phosphotyrosine (pY) sites. Disruption of asymmetric dimer interface of EGFR leads to reduction in enzymatic activity and drastic reduction of autophosphorylation of FGFRs in ligandstimulated live cells. These studies demonstrate that asymmetric dimer formation is as a common phenomenon critical for activation and autophosphorylation of RTKs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avivi, A., Lax, I., Ullrich, A., Schlessinger, J., Givol, D., and Morse, B. (1991). Comparison of EGF receptor sequences as a guide to study the ligand binding site. Oncogene 6, 673–676.
Bae, J.H., Boggon, T.J., Tome, F., Mandiyan, V., Lax, I., and Schlessinger, J. (2010). Asymmetric receptor contact is required for tyrosine autophosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptor in living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 2866–2871.
Bae, J.H., Lew, E.D., Yuzawa, S., Tome, F., Lax, I., and Schlessinger, J. (2009). The selectivity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling is controlled by a secondary SH2 domain binding site. Cell 138, 514–524.
Beenken, A., and Mohammadi, M. (2009). The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 235–253.
Boilly, B., Vercoutter-Edouart, A.S., Hondermarck, H., Nurcombe, V., and Le Bourhis, X. (2000). FGF signals for cell proliferation and migration through different pathways. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11, 295–302.
Burgess, A.W., Cho, H.S., Eigenbrot, C., Ferguson, K.M., Garrett, T.P., Leahy, D.J., Lemmon, M.A., Sliwkowski, M.X., Ward, C.W., and Yokoyama, S. (2003). An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 12, 541–552.
Carpenter, G., and Cohen, S. (1977). Influence of lectins on the binding of 125I-labeled EGF to human fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 79, 545–552.
Chen, H., Ma, J., Li, W., Eliseenkova, A.V., Xu, C., Neubert, T.A., Miller, W.T. and Mohammadi, M. (2007). A molecular brake in the kinase hinge region regulates the activity of receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol. Cell 27, 717–730.
Chen, H., Xu, C.F., Ma, J., Eliseenkova, A.V., Li, W., Pollock, P.M., Pitteloud, N., Miller, W.T., Neubert, T.A., and Mohammadi, M. (2008). A crystallographic snapshot of tyrosine trans-phosphorylation in action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19660–19665.
Cho, H.S., and Leahy, D.J. (2002). Structure of the extracellular region of HER3 reveals an interdomain tether. Science 297, 1330–1333.
Cho, H.S., Mason, K., Ramyar, K.X., Stanley, A.M., Gabelli, S.B., Denney, D.W., Jr., and Leahy, D.J. (2003). Structure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab. Nat. 421, 756–760.
Dailey, L., Ambrosetti, D., Mansukhani, A., and Basilico, C. (2005). Mechanisms underlying differential responses to FGF signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 233–247.
Ezzat, S., and Asa, S.L. (2005). FGF receptor signaling at the crossroads of endocrine homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Horm. Metab. Res. 37, 355–360.
Ferguson, K.M., Berger, M.B., Mendrola, J.M., Cho, H.S., Leahy, D.J., and Lemmon, M.A. (2003). EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol. Cell 11, 507–517.
Furdui, C.M., Lew, E.D., Schlessinger, J., and Anderson, K.S. (2006). Autophosphorylation of FGFR1 kinase is mediated by a sequential and precisely ordered reaction. Mol. Cell 21, 711–717.
Garrett, T.P., McKern, N.M., Lou, M., Elleman, T.C., Adams, T.E., Lovrecz, G.O., Zhu, H.J., Walker, F., Frenkel, M.J., Hoyne, P.A., et al. (2002). Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 110, 763–773.
Garrett, T.P., McKern, N.M., Lou, M., Elleman, T.C., Adams, T.E., Lovrecz, G.O., Kofler, M., Jorissen, R.N., Nice, E.C., Burgess, A.W., et al. (2003). The crystal structure of a truncated ErbB2 ectodomain reveals an active conformation, poised to interact with other ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 11, 495–505.
Hackel, P.O., Gishizky, M., and Ullrich, A. (2001). Mig-6 is a negative regulator of the epidermal growth factor receptor signal. Biol. Chem. 382, 1649–1662.
Hall, H., Walsh, F.S., and Doherty, P. (1996). Review: a role for the FGF receptor in the axonal growth response stimulated by cell adhesion molecules? Cell Adhes. Commun. 3, 441–450.
Hazan, R., Margolis, B., Dombalagian, M., Ullrich, A., Zilberstein, A., and Schlessinger, J. (1990). Identification of autophosphorylation sites of HER2/neu. Cell Growth Differ. 1, 3–7.
Hunter, T. (2000). Signaling—2000 and beyond. Cell 100, 113–127.
Jeffrey, P.D., Russo, A.A., Polyak, K., Gibbs, E., Hurwitz, J., Massague, J., and Pavletich, N.P. (1995). Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature 376, 313–320.
Jura, N., Endres, N.F., Engel, K., Deindl, S., Das, R., Lamers, M.H., Wemmer, D.E., Zhang, X., and Kuriyan, J. (2009). Mechanism for activation of the EGF receptor catalytic domain by the juxtamembrane segment. Cell 137, 1293–1307.
Katoh, M. (2006). FGF signaling network in the gastrointestinal tract (review). Int. J. Oncol. 29, 163–168.
Knights, V., and Cook, S.J. (2010). De-regulated FGF receptors as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 125, 105–117.
Landau, M., Fleishman, S.J., and Ben-Tal, N. (2004). A putative mechanism for downregulation of the catalytic activity of the EGF receptor via direct contact between its kinase and Cterminal domains. Structure 12, 2265–2275.
Lew, E.D., Furdui, C.M., Anderson, K.S., and Schlessinger, J. (2009). The precise sequence of FGF receptor autophosphorylation is kinetically driven and is disrupted by oncogenic mutations. Sci. Signal. 2, ra6.
Margolis, B.L., Lax, I., Kris, R., Dombalagian, M., Honegger, A.M., Howk, R., Givol, D., Ullrich, A., and Schlessinger, J. (1989). All autophosphorylation sites of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and HER2/neu are located in their carboxyl-terminal tails. Identification of a novel site in EGF receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 10667–10671.
Margolis, B., Li, N., Koch, A., Mohammadi, M., Hurwitz, D.R., Zilberstein, A., Ullrich, A., Pawson, T., and Schlessinger, J. (1990). The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 9, 4375–4380.
Mohammadi, M., Honegger, A.M., Rotin, D., Fischer, R., Bellot, F., Li, W., Dionne, C.A., Jaye, M., Rubinstein, M., and Schlessinger, J. (1991). A tyrosine-phosphorylated carboxy-terminal peptide of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (Flg) is a binding site for the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 5068–5078.
Mohammadi, M., Schlessinger, J., and Hubbard, S.R. (1996). Structure of the FGF receptor tyrosine kinase domain reveals a novel autoinhibitory mechanism. Cell 86, 577–587.
Naski, M.C., and Ornitz, D.M. (1998). FGF signaling in skeletal development. Front Biosci. 3, d781–794.
Ogiso, H., Ishitani, R., Nureki, O., Fukai, S., Yamanaka, M., Kim, J.H., Saito, K., Sakamoto, A., Inoue, M., Shirouzu, M., et al. (2002). Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell 110, 775–787.
Pawson, T. (1994). Tyrosine kinase signalling pathways. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 24, 303–322.
Pawson, T., Gish, G.D., and Nash, P. (2001). SH2 domains, interaction modules and cellular wiring. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 504–511.
Plotnikov, A.N., Schlessinger, J., Hubbard, S.R., and Mohammadi, M. (1999). Structural basis for FGF receptor dimerization and activation. Cell 98, 641–650.
Plotnikov, A.N., Hubbard, S.R., Schlessinger, J., and Mohammadi, M. (2000). Crystal structures of two FGF-FGFR complexes reveal the determinants of ligand-receptor specificity. Cell 101, 413–424.
Red Brewer, M., Choi, S.H., Alvarado, D., Moravcevic, K., Pozzi, A., Lemmon, M.A., and Carpenter, G. (2009). The juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor functions as an activation domain. Mol. Cell 34, 641–651.
Robinson, M.L. (2006). An essential role for FGF receptor signaling in lens development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 726–740.
Rotin, D., Margolis, B., Mohammadi, M., Daly, R.J., Daum, G., Li, N., Fischer, E.H., Burgess, W.H., Ullrich, A., and Schlessinger, J. (1992). SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 11, 559–567.
Russo, A.A., Jeffrey, P.D., and Pavletich, N.P. (1996). Structural basis of cyclin-dependent kinase activation by phosphorylation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 3, 696–700.
Sadowski, I., Stone, J.C., and Pawson, T. (1986). A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 4396–4408.
Schlessinger, J. (2000). Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–225.
van der Geer, P., and Pawson, T. (1995). The PTB domain: a new protein module implicated in signal transduction. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20, 277–280.
van der Geer, P., Hunter, T., and Lindberg, R.A. (1994). Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 251–337.
Wilkie, A.O. (2005). Bad bones, absent smell, selfish testes: the pleiotropic consequences of human FGF receptor mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 187–203.
Wood, E.R., Truesdale, A.T., McDonald, O.B., Yuan, D., Hassell, A., Dickerson, S.H., Ellis, B., Pennisi, C., Horne, E., Lackey, K., et al. (2004). A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 64, 6652–6659.
Yarden, Y., and Schlessinger, J. (1987). Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry 26, 1434–1442.
Yuzawa, S., Opatowsky, Y., Zhang, Z., Mandiyan, V., Lax, I., and Schlessinger, J. (2007). Structural basis for activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT by stem cell factor. Cell 130, 323–334.
Zhang, X., Gureasko, J., Shen, K., Cole, P.A., and Kuriyan, J. (2006). An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 125, 1137–1149.
Zhang, X., Pickin, K.A., Bose, R., Jura, N., Cole, P.A., and Kuriyan, J. (2007). Inhibition of the EGF receptor by binding of MIG6 to an activating kinase domain interface. Nature 450, 741–744.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, J.H., Schlessinger, J. Asymmetric tyrosine kinase arrangements in activation or autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol Cells 29, 443–448 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0080-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0080-5