Abstract
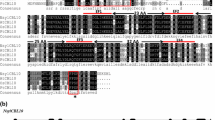
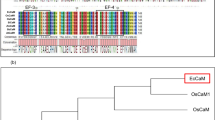
Calcium serves as a critical messenger in many adaptation and developmental processes. Cellular calcium signals are detected and transmitted by sensor molecules such as calcium-binding proteins. In plants, the calcineurin B-like protein (CBL) family represents a unique group of calcium sensors and plays a key role in decoding calcium transients by specifically interacting with and regulating a family of CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs). In this study, we report the role of Arabidopsis CBL5 gene in high salt or drought tolerance. CBL5 gene is expressed significantly in green tissues, but not in roots. CBL5 was not induced by abiotic stress conditions such as high salt, drought or low temperature. To determine whether the CBL5 gene plays a role in stress response pathways, we ectopically expressed the CBL5 protein in transgenic Arabidopsis plants (35S-CBL5) and examined plant responses to abiotic stresses. CBL5-overexpressing plants displayed enhanced tolerance to high salt or drought stress. CBL5 overexpression also rendered plants more resistant to high salt or hyperosmotic stress during early development (i.e., seed germination) but did not alter their response to abiscisic acid (ABA). Furthermore, overexpression of CBL5 alters the gene expression of stress gene markers, such as RD29A, RD29B and Kin1 etc. These results suggest that CBL5 may function as a positive regulator of salt or drought responses in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, V., Ritz, O., Linder, S., Harter, K., and Kudla, J. (2001). The NAF domain defines a novel protein-protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. EMBO J. 20, 1051–1063.
Albrecht, V., Weinl, S., Blazevic, D., D’Angelo, C., Batistic, O., Kolukisaoglu, U., Bock, R., Schulz, B., Harter, K., and Kudla, J. (2003). The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J. 36, 457–470.
Batistic, O., and Kudla, J. (2004). Integration and channeling of calcium signaling through the CBL calcium sensor/CIPK protein kinase network. Planta 219, 915–924.
Batistic, O., and Kudla, J. (2009). Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793, 985–992.
Batistic, O., Sorek, N., Schultke, S., Yalovsky, S., and Kudla, J. (2008). Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 1346–1362.
Cheong, Y.H., Kim, K.N., Pandey, G.K., Gupta, R., Grant, J.J., and Luan, S. (2003). CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15, 1833–1845.
Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., Grant, J.J., Batistic, O., Li, L., Kim, B.G., Lee, S.-C., Kudla, J., and Luan, S. (2007). Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 52, 223–239.
Chinnusamy, V., Schumaker, K., and Zhu, J.K. (2004). Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signalling in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 55, 225–236.
Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743.
D’Angelo, C., Weinl, S., Batistic, O., Pandey, G.K., Cheong, Y.H., Schültke, S., Albrecht, V., Ehlert, B., Schulz, B., Harter, K., et al. (2006). Alternative complex formation of the Ca-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 48, 857–872.
Gilmour, S.J., Zarka, D.G., Stockinger, E.J., Salazar, M.P., Houghton, J.M., and Thomashow, M.F. (1998). Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J. 16, 433–442.
Ishitani, M., Liu, J., Halfter, U., Kim, C.S., Shi, W., and Zhu, J.K. (2000). SOS3 function in plant salt tolerance requires N-myristoylation and calcium binding. Plant Cell 12, 1667–1678.
Kim, B.G., Waadt, R., Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., Dominguez-Solis, J.R., Schültke, S., Lee, S.C., Kudla, J., and Luan, S. (2007). The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 52, 473–484.
Kim, S.J., Lee, S.C., Hong, S.K., An, K., An, G., and Kim, S.R. (2009) Ectopic expression of a cold-responsive OsAsr1 cDNA gives enhanced cold tolerance in transgenic rice plants. Mol. Cells 27, 449–458.
Knight, H. (2000). Calcium signaling during abiotic stress in plants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 195, 269–324.
Lee, S.C., Lan, W.Z., Kim, B.G., Li, L., Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., Lu, G., Buchanan, B.B., and Luan, S. (2007). A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15959–15964.
Lee, S.C., Lim, M.H., Kim, J.A., Lee, S.I., Kim, J.S., Jin, M., Kwon, S.J., Mun, J.H., Kim, Y.K., Kim, H.U., et al. (2008). Transcriptome analysis in Brassica rapa under the abiotic stresses using Brassica 24K oligo microarray. Mol. Cells 26, 595–605.
Li, L., Kim, B.G., Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., and Luan, S. (2006). A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12625–12630.
Liu, J., and Zhu, J.K. (1998). A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280, 1943–1945.
Liu, Q., Kasuga, M., Sakuma, Y., Abe, H., Miura, S., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., and Shinozaki, K. (1998). Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10, 1391–1406.
Luan, S. (2008). The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 37–42.
Luan, S., Kudla, J., Rodriguez-Concepcion, M., Yalovsky, S., and Gruissem, W. (2002). Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: Calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14, S389–S400.
Luan, S., Lan W., and Lee, S.C. (2009). Potassium nutrition, sodium toxicity, and calcium signaling: connections through the CBL-CIPK network. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12, 1–8.
Murashige, T., and Skoog, F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15, 473–497.
Pandey, G.K., Cheong, Y.H., Kim, K.N., Grant, J.J., Li, L., Hung, W., D’Angelo, C., Weinl, S., Kudla, J., and Luan, S. (2004). The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 1912–1924.
Pandey, G.K., Grant, J.J., Cheong, Y.H., Kim, B.G., Li, L.G.., and Luan, S. (2008). The calcineurin B-like protein CBL9 and its interacting kinase CIPK3 functions in ABA-regulated seed germination. Mol. Plant 1, 238–248.
Quan, R., Lin, H., Mendoza, I., Zhang, Y., Cao, W., Yang, Y., Shang, M., Chen, S., Pardo, J.M., and Guo, Y. (2007). SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19, 1415–1431.
Sanders, D., Pelloux, J., Brownlee, C., and Harper, J.F. (2002). Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14, S401–S417.
Shi, H., Ishitani, M., Kim, C., and Zhu, J.K. (2000). The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6896–6901.
Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2000). Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3, 217–223.
Tahtiharju, S., Sangwan, V., Monroy, A.F., Dhindsa, R.S., and Borg, M. (1997). The induction of kin genes in cold-acclimating Arabidopsis thaliana: evidence of a role for calcium. Planta 203, 442–447.
Xiong, L.M., Schumaker, K.S., and Zhu, J.K. (2002). Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14, 165–183.
Xu, J., Li, H.D., Chen, L.Q., Wang, Y., Liu, L.L., He, L., and Wu, W.H. (2006). A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin Blike proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125, 1347–1360.
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., and Shinozaki, K. (1994). A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6, 251–264.
Zhu, J.K. (2003). Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 6, 441–445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Cheong, Y.H., Sung, S.J., Kim, BG. et al. Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis . Mol Cells 29, 159–165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0025-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0025-z