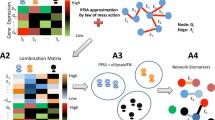
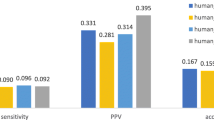
Abstract
Proteins interact with each other within a cell, and those interactions give rise to the biological function and dynamical behavior of cellular systems. Generally, the protein interactions are temporal, spatial, or condition dependent in a specific cell, where only a small part of interactions usually take place under certain conditions. Recently, although a large amount of protein interaction data have been collected by high-throughput technologies, the interactions are recorded or summarized under various or different conditions and therefore cannot be directly used to identify signaling pathways or active networks, which are believed to work in specific cells under specific conditions. However, protein interactions activated under specific conditions may give hints to the biological process underlying corresponding phenotypes. In particular, responsive functional modules consist of protein interactions activated under specific conditions can provide insight into the mechanism underlying biological systems, e.g. protein interaction subnetworks found for certain diseases rather than normal conditions may help to discover potential biomarkers. From computational viewpoint, identifying responsive functional modules can be formulated as an optimization problem. Therefore, efficient computational methods for extracting responsive functional modules are strongly demanded due to the NP-hard nature of such a combinatorial problem. In this review, we first report recent advances in development of computational methods for extracting responsive functional modules or active pathways from protein interaction network and microarray data. Then from computational aspect, we discuss remaining obstacles and perspectives for this attractive and challenging topic in the area of systems biology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamcsek, B., Palla, G., Farkas, I., Derényi, I., and Vicsek, T. (2006). Cfinder: locating cliques and overlapping modules in biological networks. Bioinformatics 22, 1021–1023.
Albert, R., DasGupta, B., Dondi, R., Kachalo, S., Sontag, E., Zelikovsky, A., and Westbrooks, K. (2007). A novel method for signal transduction network inference from indirect experimental evidence. J. Comput. Biol. 14, 927–949.
Alon, N., Yuster, R., and Zwick, U. (1995). Color-coding. J. ACM. 42, 844–856.
Arga, K., Önsan, Z., Kiidar, B., Ölgen, K., and Nielsen, J. (2007). Understanding signaling in yeast: insights from network analysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 97, 1246–1258.
Backes, C., Keller, A., Kuentzer, J., Kneissl, B., Comtesse, N., Elnakady, Y., Müller, R., Meese, E., and Lenhof, H. (2007). Gene Trail-advanced gene set enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W186–W192.
Bader, G., and Hogue, C. (2003). An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks, BMC Bioinformatics 4, 2.
Barabási., A.L., and OltVai, Z.N. (2004). Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 101–113.
Bebek, G., and Yang, J. (2007). Pathfinder: mining signal transduction pathway segments from protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 8, 335.
Bild, A., and Febbo, P. (2005). Application of a priori established gene sets to discover biologically important differential expression in microarray data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15278–15279.
Cabusora, L., Sutton, E., Fulmer, A., and Forst, C. (2005). Differential network expression during drug and stress response. Biofinromatics 21, 2898–2905.
Chen, X., Wang, L., Smith, J., and Zhang, P. (2008). Supervised principal component analysis for gene set enrichment of microarray data with continuous or survival outcomes. Bioinformatics 24, 2474–2481.
Chen, L., Wang, R., and Zhang, X.S. (2009). Biomolecular networks: methods and applications in systems biology (New Jersey, USA: Wiley Interscience).
Cho, Y., Hwang, W., Ramanathan, M., and Zhang, A. (2007). Semantic integration to identify overlapping functional modules in protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 8, 265.
Chu, W., and Ghahramani, Z. (2006). Identifying protein complexes in high-throughput protein interaction screens using an infinite latent feature model. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 11, 231–242.
Chu, H., and Chen, B. (2008). Construction of a cancer-perturbed protein-protein interaction network for discovery of apoptosis drug targets. BMC Syst. Biol. 2, 56.
Chuang, H., Lee, E., Liu, Y., Lee, D., and Ideker, T. (2007). Network-based classification of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3, 140.
Dittrich, M., Klau, G., Rosenwald, A., Dandekarand, T., and Muller, T. (2008). Identifying functional modules in protein-protein interaction networks: an integrated exact approach. Bioinformatics 24, i223–i231.
Guo, Z., Li, Y., Gong, X., Yao, C., Ma, W., Wang, D., Li, Y., Zhu, J., Zhang, M., Yang, D., et al. (2007). Edge-based scoring and searching method for identifying condition-responsive proteinprotein interaction sub-network. Bioinformatics 23, 2121–2128.
Han, J., Bertin, N., Hao, T., Goldberg, D., Berriz, G., Zhang, L., Dupuy, D., Walhout, A., Cusick, M., Roth, F., et al. (2004). Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Nature 430, 88–93.
Hirsh, E., and Sharan, R. (2006). Identification of conserved protein complexes based on a model of protein network evolution. Bioinformatics 23, e170–e176.
Holden, M., Deng, S., Wojnowski, L., and Kulle, B. (2008). GSEASNP: applying gene set enrichment analysis to SNP data from genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 24, 2784–2785.
Huang, R., Wallqvist, A., and Covell, D. (2006). Targeting changes in cancer: assessing pathway stability by comparing pathway gene expression coherence levels in tumor and normal tissues. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 2417–2427.
Hwang, W., Cho, Y., Zhang, A., and Ramanathan, M. (2006). A novel functional module detection algorithm for protein-protein interaction networks. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 1, 24.
Ideker, T., and Sharan, R. (2008). Protein networks in disease. Genome Res. 18, 644–652.
Ideker, T., Ozier, O., schwikowski, B., and Siegel, A. (2002). Discovering regulatory and signalling circuits in molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics 18, S233–S240.
Jansen, R., Greenbaum, D., and Gerstein, M. (2002). Relating whole-genome expression data with protein-protein interactions. Genome Res. 12, 37–46.
Kann, M. (2007). Protein interactions and disease: computational approaches to uncover the etiology of diseases. Brief. Bioinform. 8, 333–346.
King, A., Pržulj, N., and Jurisica, I. (2004). Protein complex prediction via cost-based clustering. Bioinformatics 20, 3013–3020.
Li, S., Assmann, S., and Albert, R. (2006). Predicting essential components of signal transduction networks: a dynamic model of guard cell abscisic acid signaling. PLoS Biol. 4, e312.
Liu, Y., and Zhao, H. (2004). A computational approach for ordering signal transduction pathway components from genomics and proteomics data. BMC Bioinformatics 5, 158.
Liu, M., Liberzon, A., Kong, S., Lai, W., Park, P., Kohane, I., and Kasif, S. (2007). Network-based analysis of affected biological processes in type 2 diabetes models. PLOS Genet. 3, e96.
Mete, M., Tang, F., Xu, X., and Yuruk, N. (2008). A structural approach for finding functional modules from large biological networks. BMC Bioinformatics 9, S19.
Murali, T., and Rivera, C. (2008). Network legos: buiding blocks of cellular wiring diagrams. J. Comput. Biol. 15, 829–844.
Nacu, S., Critchley-Thorne, R., Lee, P., and Holmes, S. (2007). Gene expression network analysis and applications to immunology. Bioinformatics 23, 850–858.
Nettleton, D., Recknor, J., and Reecy, J. (2008). Identification of differentially expressed gene categories in microarray studies using nonparametric multivariate analysis. Bioinformatics 24, 192–201.
Noisel, J., Sanguinetti, G., and Wright, P. (2008). Identifying differentially- expressed subnetworks with MMG. Bioinformatics 24, 2792–2793.
Oron, A., Jiang, Z., and Gentleman, R. (2008). Gene set enrichment analysis using linear models and diagnostics. Bioinformatics 24, 2586–2591.
Pereira-Leal, J., Enright, A., and Ouzounis, C. (2004). Detection of functional modules from protein interaction networks. Proteins 54, 49–57.
Qi, Y., Balem, F., Faloutsos, C., Klein-Seetharaman, J., and Bar-Joseph, Z. (2008). Protein complex identification by supervised graph local clustering. Bioinformatics 24, i250–i258.
Qiu, Y., and Zhang, S. (2008). Uncovering Differentially expressed Pathways with protein Interation and gene expression data. Lecture Notes in Operations Res. 9, 74–82.
Qiu, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, X-S., and Chen, L. (2009). Identifying differentially expressed pathways by high throughput data. IET Syst. Biol. (in press).
Rahnenfuhrer, J., Domingues, F., Maydt, J., and Lengauer, T. (2004). Calculating the statistical significance of changes in pathway activity from gene expression data. Stat. Appl. Gen. Mol. Biol. 3, Article 16.
Rajagopalan, D., and Agarwal, P. (2005). Inferring pathways from gene lists using a literature-derived network of biological relationships. Bioinformatics 21, 788–793.
Scholtens, D., Vidal, M., and Gentleman, R. (2005). Local modeling of global interactome networks. Bioinformatics 21, 3548–3557.
Scott, M., Perkins, T., Bunnell, S., Pepin, F., Thomas, D., and Hallett, M. (2005). Identifying regulatory subnetworks for a set of genes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4, 683–692.
Scott, J., Ideker, T., Karp, R., and Sharan, R. (2006). Efficient algorithms for detecting signaling pathways in protein interaction networks. J. Comput. Biol. 13, 133–144.
Sharan, R., Ideker, T., Kelley, B.P., Shamir, R., and Karp, R.M. (2005). Identification of protein complexes by comparative analysis of yeast and bacterial protein interaction data. J. Comput. Biol. 12, 835–846.
Sohler, F., Hanisch, D., and Zimmer, R. (2004). New methods for joint analysis of biological networks and expression data. Bioinformatics 20, 1517–1521.
Spirin, V., and Mirny, L. (2003). Protein complexes and functional modules in molecular networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 12123–12128.
Steffen, M., Petti, A., Aach, J., D’haeseleer, P., and Church, G. (2002). Automated modelling of signal transduction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 3, 34.
Subramaniana, A., Tamayo, P., Mootha, V., Mukherjee, S., Ebert, B., Gillette, M., Paulovich, A., Pomeroy, S., Golub, T., Lander, E., et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550.
Suderman, M., and Michael, H. (2007). Tools for visually exploring biological networks. Bioinformatics 23, 2651–2659.
Turanalp, M., and Can, T. (2008). Discovering functional interaction patterns in protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 276.
Ulitsky, I., Karp, M., and Shamir, R. (2008). Detecting diseasespecific dysregulated pathways via analysis of clinical expression profiles. Lect. N. Bioinformat. (RECOMB2008) 4955, 347–359.
Wang, Y., and Xia, Y. (2008). Condition specific subnetwork identification using an optimization model. Lecture Notes in Operations Res. 9, 333–340.
Wang, R., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., and Chen, L. (2006). Identifying modules in complex networks by a graph-theoretical method and its application in protein interaction networks. Lect. N. Bioinformat. 4682, 1090–1101.
Watts, D., and Atrogatz, S. (1998). Collective dynamics of ’small word’ networks. Nature 393, 440–442.
Zhang, S., Ning, X., and Zhang, X. (2006). Identification of functional modules in a PPI network by clique percolaion clusering. Comput. Biol. Chem. 30, 445–451.
Zhang, S., Jin, G., Zhang, X., and Chen, L. (2007). Discovering functions and revealing mechanisms at molecular level from biological networks. Proteomics 7, 2856–2869.
Zhao, X., Wang, R., Chen, L., and Aihara, K. (2008a). Automatic modeling of signal pathways from protein-protein interaction networks. In A., Brazma, S., Miyano, and T., Akutsu, eds., Proceedings of The 6th Asia Pacific Bioinformatics Conference, Vol. 6 of Serias on advances in bioinformatics and computational biology Imperial College Press, Singapore, 287–296.
Zhao, X., Wang, R., Chen, L., and Aihara, K. (2008b). Uncovering signal transduction networks from high-throughput data by integer linear programming. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, e48.
Zhao, X., Wang, R., Chen, L., and Aihara, K. (2009). Automatic modeling of signaling pathways based on network flow model. J. Bioinformat. Computational Biol. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhao, X. & Chen, L. Identifying responsive functional modules from protein-protein interaction network. Mol Cells 27, 271–277 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0035-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0035-x