Abstract
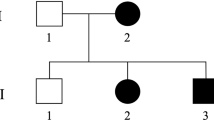
We identified a family in Mali with two sisters affected by spastic paraplegia. In addition to spasticity and weakness of the lower limbs, the patients had marked atrophy of the distal upper extremities. Homozygosity mapping using single nucleotide polymorphism arrays showed that the sisters shared a region of extended homozygosity at chromosome 19p13.11-q12 that was not shared by controls. These findings indicate a clinically and genetically distinct form of hereditary spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy, designated SPG43.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanein S, Martin E, Boukhris A et al (2008) Identification of the SPG15 gene, encoding spastizin, as a frequent cause of complicated autosomal-recessive spastic paraplegia, including Kjellin syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 82:992–1002
Dürr A (2008) Genetic testing for the spastic paraplegias: drowning by numbers. Neurology 71:236–238
Leutenegger A, Labalme A, Génin E, Toutain A, Steichen E, Clerget-Darpoux F, Edery P (2006) Using genomic inbreeding coefficient estimates for homozygosity mapping of rare recessive traits: application to Taybi-Linder syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 79:62–66
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PIW, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Geppert M, Goda Y, Stevens CF, Sudhof TC (1997) The small GTP-binding protein Rab3A regulates a late step in synaptic vesicle fusion. Nature 387:810–814
Harter C, Wieland FT (1998) A single binding site for dilysine retrieval motifs and p23 within the gamma subunit of coatomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11649–11654
Nielsen JV, Mitchelmore C, Pedersen KM et al (2004) FKBP8: novel isoforms, genomic organization, and characterization of a forebrain promoter in transgenic mice. Genomics 83:181–192
Shirane M, Nakayama KI (2006) Protrudin induces neurite formation by directional membrane trafficking. Science 314:818–821
Martignoni M, Riano E, Rugarli EI (2008) The role of ZFYVE27/protrudin in hereditary spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet 83:127–128, author reply 128-30
Lander ES, Botstein D (1987) Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science 236:1567–1570
Gibbs JR, Singleton A (2006) Application of genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism typing: simple association and beyond. PLoS Genet 2:e150
Garshasbi M, Motazacker MM, Kahrizi K et al (2006) SNP array-based homozygosity mapping reveals MCPH1 deletion in family with autosomal recessive mental retardation and mild microcephaly. Hum Genet 118:708–715
Morrow EM, Yoo SY, Flavell SW et al (2008) Identifying autism loci and genes by tracing recent shared ancestry. Science 321:218–223
Camargos S, Scholz S, Simon-Sanchez J et al (2008) (2008) DYT16, a novel young-onset dystonia-parkinsonism disorder: Identification of a segregating mutation in the stress-response protein PRKRA. Lancet Neurol 7:207–215
Paisan-Ruiz C, Bhatia KP, Li A et al (2009) Characterization of PLA2G6 as a locus for dystonia-parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 65:19–23
Bakowska JC, Wang H, Xin B et al (2008) Lack of spartin protein in Troyer syndrome: a loss-of-function disease mechanism? Arch Neurol 65:520–524
Patel H, Cross H, Proukakis C et al (2002) SPG20 is mutated in Troyer syndrome, an hereditary spastic paraplegia. Nat Genet 31:347–348
Windpassinger C, Wagner K, Petek E, Fischer R, Auer-Grumbach M (2003) Refinement of the ‘Silver syndrome locus’ on chromosome 11q12-q14 in four families and exclusion of eight candidate genes. Hum Genet 114:99–109
Rainier S, Bui M, Mark E et al (2008) Neuropathy target esterase gene mutations cause motor neuron disease. Am J Hum Genet 82:780–785
Hadano S, Nichol K, Brinkman RR et al (1999) A yeast artificial chromosome-based physical map of the juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS2) critical region on human chromosome 2q33-q34. Genomics 55:106–112
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and staff of the Neurology Department of Point G Hospital for their warmth, participation, and flexibility. The Center for Research on Genomics and Global Health provided statistical expertise and the Intramural Research Programs of the NINDS, NINR, and NIA provided funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meilleur, K.G., Traoré, M., Sangaré, M. et al. Hereditary spastic paraplegia and amyotrophy associated with a novel locus on chromosome 19. Neurogenetics 11, 313–318 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0230-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0230-0