Abstract
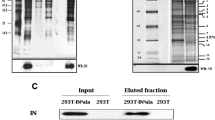
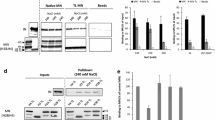
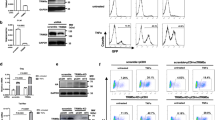
The viral protein integrase (IN) catalyzes the integration of the HIV-1 cDNA into the host cellular genome. We have recently demonstrated that IN is acetylated by a cellular histone acetyltransferase, p300, which modifies three lysines located in the C-terminus of the viral factor (Cereseto et al. in EMBO J 24:3070–3081, 2005). This modification enhances IN catalytic activity, as demonstrated by in vitro assays. Consistently, mutations introduced in the targeted lysines greatly decrease the efficiency of HIV-1 integration. Acetylation was proven to regulate protein functions by modulating protein–protein interactions. HIV-1 to efficiently complete its replication steps, including the integration reaction, requires interacting with numerous cellular factors. Therefore, we sought to investigate whether acetylation might modulate the interaction between IN and the cellular factors. To this aim we performed a yeast two-hybrid screening that differs from the screenings so far performed (Rain et al. in Methods 47:291–297, 2009; Studamire and Goff in Retrovirology 5:48, 2008) for using as bait IN constitutively acetylated. From this analysis we have identified thirteen cellular factors involved in transcription, chromatin remodeling, nuclear transport, RNA binding, protein synthesis regulation and microtubule organization. To validate these interactions, binding assays were performed showing that acetylation increases the affinity of IN with specific factors. Nevertheless, few two-hybrid hits bind with the same affinity the acetylated and the unmodified IN. These results further underlie the relevance of IN post-translational modification by acetylation in HIV-1 replication cycle.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HIV-1:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-1
- IN:
-
Integrase
- PIC:
-
Pre-integration complex
- GDBD:
-
Gal4 DNA binding domain
- GAD:
-
Gal4 activation domain
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferase catalytic domain
- wt:
-
Wild type
- mut:
-
Mutated
- His:
-
Histidine
- Ade:
-
Adenine
- Ac-Lys:
-
Acetylated lysines
- TEV:
-
Tobacco etch virus protease site
- HA:
-
Hemagglutinin epitope tag
- WB:
-
Western blot analysis
- α:
-
Antibodies
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signal
References
Albanese A, Arosio D, Terreni M, Cereseto A (2008) HIV-1 pre-integration complexes selectively target decondensed chromatin in the nuclear periphery. PLoS One 3:e2413
Berchtold MW, Berger MC (1991) Isolation and analysis of a human cDNA highly homologous to the yeast gene encoding L17A ribosomal protein. Gene 102:283–288
Bouyac-Bertoia M, Dvorin JD, Fouchier RA, Jenkins Y, Meyer BE, Wu LI, Emerman M, Malim MH (2001) HIV-1 infection requires a functional integrase NLS. Mol Cell 7:1025–1035
Bushman F, Lewinski M, Ciuffi A, Barr S, Leipzig J, Hannenhalli S, Hoffmann C (2005) Genome-wide analysis of retroviral DNA integration. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:848–858
Bustin M (2001) Chromatin unfolding and activation by HMGN(*) chromosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 26:431–437
Calado A, Treichel N, Muller EC, Otto A, Kutay U (2002) Exportin-5-mediated nuclear export of eukaryotic elongation factor 1A and tRNA. EMBO J 21:6216–6224
Cassimeris L (2002) The oncoprotein 18/stathmin family of microtubule destabilizers. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:18–24
Cereseto A, Manganaro L, Gutierrez MI, Terreni M, Fittipaldi A, Lusic M, Marcello A, Giacca M (2005) Acetylation of HIV-1 integrase by p300 regulates viral integration. EMBO J 24:3070–3081
Cherepanov P, Maertens G, Proost P, Devreese B, Van Beeumen J, Engelborghs Y, De Clercq E, Debyser Z (2003) HIV-1 integrase forms stable tetramers and associates with LEDGF/p75 protein in human cells. J Biol Chem 278:372–381
Christ F, Thys W, De Rijck J, Gijsbers R, Albanese A, Arosio D, Emiliani S, Rain JC, Benarous R, Cereseto A et al (2008) Transportin-SR2 imports HIV into the nucleus. Curr Biol 18:1192–1202
Cimarelli A, Luban J (1999) Translation elongation factor 1-alpha interacts specifically with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag polyprotein. J Virol 73:5388–5401
Ciuffi A, Llano M, Poeschla E, Hoffmann C, Leipzig J, Shinn P, Ecker JR, Bushman F (2005) A role for LEDGF/p75 in targeting HIV DNA integration. Nat Med 11:1287–1289
Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE (1997) Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
de Soultrait VR, Caumont A, Durrens P, Calmels C, Parissi V, Recordon P, Bon E, Desjobert C, Tarrago-Litvak L, Fournier M (2002) HIV-1 integrase interacts with yeast microtubule-associated proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1575:40–48
Desfarges S, Salin B, Calmels C, Andreola ML, Parissi V, Fournier M (2009) HIV-1 integrase trafficking in S. cerevisiae: a useful model to dissect the microtubule network involvement of viral protein nuclear import. Yeast 26:39–54
Devroe E, Engelman A, Silver PA (2003) Intracellular transport of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase. J Cell Sci 116:4401–4408
Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2008) The lentiviral integrase binding protein LEDGF/p75 and HIV-1 replication. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000046
Gallay P, Hope T, Chin D, Trono D (1997) HIV-1 infection of nondividing cells through the recognition of integrase by the importin/karyopherin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9825–9830
Ge H, Si Y, Roeder RG (1998) Isolation of cDNAs encoding novel transcription coactivators p52 and p75 reveals an alternate regulatory mechanism of transcriptional activation. EMBO J 17:6723–6729
Goff SP (2007) Host factors exploited by retroviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:253–263
Gorlich D (1998) Transport into and out of the cell nucleus. EMBO J 17:2721–2727
Guo D, Hazbun TR, Xu XJ, Ng SL, Fields S, Kuo MH (2004) A tethered catalysis, two-hybrid system to identify protein-protein interactions requiring post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol 22:888–892
Hearps AC, Jans DA (2006) HIV-1 integrase is capable of targeting DNA to the nucleus via an importin alpha/beta-dependent mechanism. Biochem J 398:475–484
Hindmarsh P, Ridky T, Reeves R, Andrake M, Skalka AM, Leis J (1999) HMG protein family members stimulate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and avian sarcoma virus concerted DNA integration in vitro. J Virol 73:2994–3003
Hinnebusch AG (2006) eIF3: a versatile scaffold for translation initiation complexes. Trends Biochem Sci 31:553–562
Hock R, Wilde F, Scheer U, Bustin M (1998) Dynamic relocation of chromosomal protein HMG-17 in the nucleus is dependent on transcriptional activity. EMBO J 17:6992–7001
Howell B, Larsson N, Gullberg M, Cassimeris L (1999) Dissociation of the tubulin-sequestering and microtubule catastrophe-promoting activities of oncoprotein 18/stathmin. Mol Biol Cell 10:105–118
Kutay U, Bischoff FR, Kostka S, Kraft R, Gorlich D (1997) Export of importin alpha from the nucleus is mediated by a specific nuclear transport factor. Cell 90:1061–1071
Li L, Yoder K, Hansen MS, Olvera J, Miller MD, Bushman FD (2000) Retroviral cDNA integration: stimulation by HMG I family proteins. J Virol 74:10965–10974
Llano M, Vanegas M, Fregoso O, Saenz D, Chung S, Peretz M, Poeschla EM (2004) LEDGF/p75 determines cellular trafficking of diverse lentiviral but not murine oncoretroviral integrase proteins and is a component of functional lentiviral preintegration complexes. J Virol 78:9524–9537
Maertens G, Cherepanov P, Pluymers W, Busschots K, De Clercq E, Debyser Z, Engelborghs Y (2003) LEDGF/p75 is essential for nuclear and chromosomal targeting of HIV-1 integrase in human cells. J Biol Chem 278:33528–33539
Mitchell RS, Beitzel BF, Schroder AR, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry CC, Ecker JR, Bushman FD (2004) Retroviral DNA integration: ASLV, HIV, and MLV show distinct target site preferences. PLoS Biol 2:E234
Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, Otsuki T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, Wakamatsu A, Hayashi K, Sato H, Nagai K et al (2004) Complete sequencing and characterization of 21, 243 full-length human cDNAs. Nat Genet 36:40–45
Parissi V, Calmels C, de Soultrait VR, Caumont A, Fournier M, Chaignepain S, Litvak S (2001) Functional interactions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase with human and yeast HSP60. J Virol 75:11344–11353
Rachez C, Freedman LP (2001) Mediator complexes and transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:274–280
Rain JC, Cribier A, Gerard A, Emiliani S, Benarous R (2009) Yeast two-hybrid detection of integrase-host factor interactions. Methods 47:291–297
Schroder AR, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry C, Ecker JR, Bushman F (2002) HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell 110:521–529
Shun MC, Raghavendra NK, Vandegraaff N, Daigle JE, Hughes S, Kellam P, Cherepanov P, Engelman A (2007) LEDGF/p75 functions downstream from preintegration complex formation to effect gene-specific HIV-1 integration. Genes Dev 21:1767–1778
Solsbacher J, Maurer P, Bischoff FR, Schlenstedt G (1998) Cse1p is involved in export of yeast importin alpha from the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol 18:6805–6815
Sripathy SP, Stevens J, Schultz DC (2006) The KAP1 corepressor functions to coordinate the assembly of de novo HP1-demarcated microenvironments of heterochromatin required for KRAB zinc finger protein-mediated transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 26:8623–8638
Sterner DE, Berger SL (2000) Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:435–459
Studamire B, Goff SP (2008) Host proteins interacting with the Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase: multiple transcriptional regulators and chromatin binding factors. Retrovirology 5:48
Suzuki Y, Craigie R (2007) The road to chromatin—nuclear entry of retroviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:187–196
Valente ST, Gilmartin GM, Mott C, Falkard B, Goff SP (2009) Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by eIF3f. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4071–4078
Van Maele B, Busschots K, Vandekerckhove L, Christ F, Debyser Z (2006) Cellular co-factors of HIV-1 integration. Trends Biochem Sci 31:98–105
Vandegraaff N, Engelman A (2007) Molecular mechanisms of HIV integration and therapeutic intervention. Expert Rev Mol Med 9:1–19
Wang GP, Ciuffi A, Leipzig J, Berry CC, Bushman FD (2007) HIV integration site selection: analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res 17:1186–1194
West KL (2004) HMGN proteins play roles in DNA repair and gene expression in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans 32:918–919
Wolf D, Goff SP (2007) TRIM28 mediates primer binding site-targeted silencing of murine leukemia virus in embryonic cells. Cell 131:46–57
Wu-Baer F, Lane WS, Gaynor RB (1996) Identification of a group of cellular cofactors that stimulate the binding of RNA polymerase II and TRP-185 to human immunodeficiency virus 1 TAR RNA. J Biol Chem 271:4201–4208
Zheng XM, Black D, Chambon P, Egly JM (1990) Sequencing and expression of complementary DNA for the general transcription factor BTF3. Nature 344:556–559
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from the EU FP7 (THINC, HEALTH-F3-2008-201032) and by the ISS Italian AIDS Program (grant number 40G.17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allouch, A., Cereseto, A. Identification of cellular factors binding to acetylated HIV-1 integrase. Amino Acids 41, 1137–1145 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0444-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0444-3