Abstract
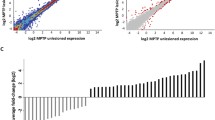
The novel anti-Parkinson’s disease (PD) drug, rasagiline (N-propargyl-1-(R)-aminoindan), is a second generation of irreversible selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-B follows selegiline. In light of the recent large clinical study (phase III ADAGIO) reporting benefits in PD patients, it has been suggested that rasagiline could be the first PD treatment to receive the label neuroprotective “disease-modifying” drug. Indeed, rasagiline has been shown to have a broad neuroprotective activity against a variety of neurotoxins in preclinical models of neurodegenerative diseases and in cultured neuronal cells. In the present study, we have investigated the status of various molecular and biochemical markers in the rat midbrain following chronic treatments with rasagiline and selegiline, using proteomic and genomic analyses. Our findings demonstrated significant molecular changes induced by both drugs, at the protein and transcriptional levels, associated with neuronal differentiation, cell survival and death pathways, metabolism/oxidation stress, signaling system, and biomarkers of neurodegenerative disorders, which may be reflected in the clinical studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abassi ZA, Binah O, Youdim MBH (2004) Cardiovascular activity of rasagiline, a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B: comparison with selegiline. Br J Pharmacol 143:371–378
Abu-Raya S, Tabakman R, Blaugrund E, Trembovler V, Lazarovici P (2002) Neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors and derived metabolites under ischemia in PC12 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 434:109–116
Akao Y, Maruyama W, Shimizu S, Yi H, Nakagawa Y, Shamoto-Nagai M, Youdim MBH, Tsujimoto Y, Naoi M (2002) Mitochondrial permeability transition mediates apoptosis induced by N-methyl(R)salsolinol, an endogenous neurotoxin, and is inhibited by Bcl-2 and Rasagiline, N-Propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan. J Neurochem 82:913–923
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Bar-Am O, Amit T, Youdim MBH (2004a) Contrasting neuroprotective and neurotoxic actions of respective metabolites of anti-Parkinson drugs rasagiline and selegiline. Neurosci Lett 355:169–172
Bar-Am O, Yogev-Falach M, Amit T, Sagi Y, Youdim MBH (2004b) Regulation of protein kinase C by the anti-Parkinson drug, MAO-B inhibitor, rasagiline and its derivatives, in vivo. J Neurochem 89:1119–1125
Bar-Am O, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2005) Regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins, neurotrophic factors, and APP processing in the neurorescue activity of propargylamine. FASEB J 19:1899–1901
Bar-Am O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2007) Aminoindan and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolites of rasagiline and ladostigil, respectively, exert neuroprotective properties in vitro. J Neurochem 103:500–508
Beer I, Barnea E, Ziv T, Admon A (2004) Improving large-scale proteomics by clustering of mass spectrometry data. Proteomics 4:950–960
Berg D, Holzmann C, Riess O (2003) 14-3-3 proteins in the nervous system. Nat Rev 4:752–762
Binda C, Hubalek F, Li M, Herzig Y, Sterling J, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2004) Crystal structures of monoamine oxidase B in complex with four inhibitors of the N-propargylaminoindan class. J Med Chem 47:1767–1774
Birkmayer W, Danielczyk W, Neumayer E, Riederer P (1975) Dopaminergic supersensitivity in parkinsonism. Adv Neurol 9:121–129
Birkmayer W, Riederer P, Ambrozi L, Youdim MBH (1977) Implications of combined treatment with ‘Madopar’ and l-deprenil in Parkinson’s disease: a long-term study. Lancet 1:439–443
Birkmayer W, Knoll J, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1983) (−)-Deprenyl leads to prolongation of l-dopa efficacy in Parkinson’s disease. Mod Probl Pharmacopsychiatr 19:170–176
Birkmayer W, Knoll J, Riederer P, Youdim MBH, Hars V, Marton J (1985) Increased life expectancy resulting from addition of l-deprenyl to Madopar treatment in Parkinson’s disease: a longterm study. J Neural Transm 64:113–127
Blandini F (2005) Neuroprotection by rasagiline: a new therapeutic approach to Parkinson’s disease? CNS Drug Rev 11:183–194
Blandini F, Armentero MT, Fancellu R, Blaugrund E, Nappi G (2004) Neuroprotective effect of rasagiline in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 187:455–459
Carrillo MC, Kitani K, Kanai S, Sato Y, Ivy GO, Miyasaka K (1996) Long term treatment with (−)deprenyl reduces the optimal dose as well as the effective dose range for increasing antioxidant enzyme activities in old mouse brain. Life Sci 59:1047–1057
Carrillo MC, Minami C, Kitani K, Maruyama W, Ohashi K, Yamamoto T, Naoi M, Kanai S, Youdim MBH (2000) Enhancing effect of rasagiline on superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in the dopaminergic system in the rat. Life Sci 67:577–585
Chen JJ, Ly AV (2006) Rasagiline: a second-generation monoamine oxidase type-B inhibitor for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63:915–928
Chen JJ, Swope DM (2005) Clinical pharmacology of rasagiline: a novel, second-generation propargylamine for the treatment of Parkinson disease. J Clin Pharmacol 45:878–894
Chen JJ, Swope DM, Dashtipour K (2007) Comprehensive review of rasagiline, a second-generation monoamine oxidase inhibitor, for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Ther 29:1825–1849
Chuang DM, Ishitani R (1996) A role for GAPDH in apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Nat Med 2:609–610
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA (2003) DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol 4:P3
Ebadi M, Ramana Kumari MV, Hiramatsu M, Hao R, Pfeiffer RF, Rojas P (1998) Metallothionein, neurotrophins and selegiline in providing neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Restor Neurol Neurosci 12:103–111
Ebadi M, Sharma S, Shavali S, El Refaey H (2002) Neuroprotective actions of selegiline. J Neurosci Res 67:285–289
Finberg JP, Youdim MBH (1985) Modification of blood pressure and nictitating membrane response to sympathetic amines by selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors, types A and B, in the cat. Br J Pharmacol 85:541–546
Finberg JPM, Tenne M, Youdim MBH (1981) Selective irreversible propargyl derivative inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (MAO) without the cheese effect. In: Youdim MBH, Peykel ES (eds) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors—the state of the art. Wiley, Chichester, pp 31–41
Foley P, Gerlach M, Youdim MBH, Riederer P (2000) MAO-B inhibitors: multiple roles in the therapy of neurodegenerative disorders? Park Relat Disord 6:25–47
Goggi J, Theofilopoulos S, Riaz SS, Jauniaux E, Stern GM, Bradford HF (2000) The neuronal survival effects of rasagiline and deprenyl on fetal human and rat ventral mesencephalic neurones in culture. NeuroReport 11:3937–3941
Grasing K, Azevedo R, Karuppan S, Ghosh S (2001) Biphasic effects of selegiline on striatal dopamine: lack of effect on methamphetamine-induced dopamine depletion. Neurochem Res 26:65–74
Hu Y, Russek SJ (2008) BDNF and the diseased nervous system: a delicate balance between adaptive and pathological processes of gene regulation. J Neurochem 105:1–17
Iwasaki Y, Ikeda K, Shiojima T, Kobayashi T, Tagaya N, Kinoshita M (1994) Deprenyl enhances neurite outgrowth in cultured rat spinal ventral horn neurons. J Neurol Sci 125:11–13
Kitani K, Minami C, Isobe K, Maehara K, Kanai S, Ivy GO, Carrillo MC (2002) Why (−)deprenyl prolongs survivals of experimental animals: increase of anti-oxidant enzymes in brain and other body tissues as well as mobilization of various humoral factors may lead to systemic anti-aging effects. Mech Ageing Dev 123:1087–1100
Knoll J, Magyar K (1972) Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 5:393–408
Kontkanen O, Castren E (1999) Trophic effects of selegiline on cultured dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 829:190–192
Lees AJ, Shaw KM, Kohout LJ, Stern GM, Elsworth JD, Sandler M, Youdim MBH (1977) Deprenyl in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2:791–795
LeWitt PA (2004) Clinical trials of neuroprotection for Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 63:S23–S31
Magyar K, Palfi M, Jenei V, Szoko E (2006) Deprenyl: from chemical synthesis to neuroprotection. J Neural Transm Suppl 71:143–156
Maruyama W, Naoi M, Kasamatsu T, Hashizume Y, Takahashi T, Kohda K, Dostert P (1997) An endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxin, N-methyl-(R)-salsolinol, induces DNA damage in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 69:322–329
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Youdim MBH, Naoi M (2000a) Neurotoxins induce apoptosis in dopamine neurons: protection by N-propargylamine-1(R)- and (S)-aminoindan, rasagiline and TV1022. J Neural Transm (Suppl) 60:171–186
Maruyama W, Youdim MBH, Naoi M (2000b) Antiapoptotic function of N-propargylamine-1(R)- and (S)-aminoindan, Rasagiline and TV1022. Ann NY Acad Sci 939:320–329
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Carrillo M, Kitani K, Youdium M, Naoi M (2002a) Neuroprotection by propargylamines in Parkinson’s disease: suppression of apoptosis and induction of prosurvival genes. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:675–682
Maruyama W, Takahashi T, Youdim MBH, Naoi M (2002b) The anti-parkinson drug, rasagiline, prevents apoptotic DNA damage induced by peroxynitrite in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neural Transm 109:467–481
Nadon R, Shoemaker J (2002) Statistical issues with microarrays: processing and analysis. Trends Genet 18:265–271
Oakes D (1993) Antiparkinson efficacy of deprenyl. DATATOP Steering Committee of Parkinson Study Group. Ann Neurol 34:634
Olanow CW, Hauser RA, Jankovic J, Langston W, Lang A, Poewe W, Tolosa E, Stocchi F, Melamed E, Eyal E, Rascol O (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, delayed start study to assess rasagiline as a disease modifying therapy in Parkinson’s disease (the ADAGIO study): rationale, design, and baseline characteristics. Mov Disord 23:2194–2201
Parkinson Study Group (1989) Effect of deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 321:176–183
Parkinson Study Group (1993) Effects of tocopherol and deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 328:176–183
Parkinson Study Group (2002) A controlled trial of rasagiline in early Parkinson disease: the TEMPO Study. Arch Neurol 59:1937–1943
Parkinson Study Group (2004) A controlled, randomized, delayed-start study of rasagiline in early Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 61:561–566
Parkinson Study Group (2005) A randomized placebo-controlled trial of rasagiline in levodopa-treated patients with Parkinson disease and motor fluctuations: the PRESTO study. Arch Neurol 62:241–248
Quackenbush J (2001) Computational analysis of microarray data. Nat Rev Genet 2:418–427
Rabey JM, Sagi I, Huberman M, Melamed E, Korczyn A, Giladi N, Inzelberg R, Djaldetti R, Klein C, Berecz G (2000) Rasagiline mesylate, a new MAO-B inhibitor for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind study as adjunctive therapy to levodopa. Clin Neuropharmacol 23:324–330
Reynolds GP, Riederer P, Sandler M, Jellinger K, Seemann D (1978) Amphetamine and 2-phenylethylamine in post-mortem Parkinsonian brain after (−) deprenyl administration. J Neural Transm 43:271–277
Riederer P, Youdim MB, Birkmayer W, Jellinger K (1978a) Monoamine oxidase activity during (−)-deprenil therapy: human brain post-mortem studies. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 19:377–382
Riederer P, Youdim MB, Rausch WD, Birkmayer W, Jellinger K, Seemann D (1978b) On the mode of action of l-deprenyl in the human central nervous system. J Neural Transm 43:217–226
Riederer P, Gille G, Muller T, Przuntek H, Reichmann H, Riess O, Schwartz A, Schwarz J, Vogt T (2002) Practical importance of neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249(Suppl 3):III/53–III/56
Sabbagh A, Youdim MBH (1978) Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase type B by propargyl-containing drugs. Isr J Med Sci 14:1097
Sagi Y, Mandel S, Y MBH (2003) Genomic and proteomic profiling of the neuroprotective mechanisms of rasagiline in the mouse MPTP model of PD. Neural Plas 10:227
Sagi Y, Mandel S, Amit T, Youdim MB (2007) Activation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway by rasagiline facilitates neurorescue and restoration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in post-MPTP-induced Parkinsonism. Neurobiol Dis 25:35–44
Salonen T, Haapalinna A, Heinonen E, Suhonen J, Hervonen A (1996) Monoamine oxidase B inhibitor selegiline protects young and aged rat peripheral sympathetic neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol 91:466–474
Semkova I, Wolz P, Schilling M, Krieglstein J (1996) Selegiline enhances NGF synthesis and protects central nervous system neurons from excitotoxic and ischemic damage. Eur J Pharmacol 315:19–30
Shen L, Figurov A, Lu B (1997) Recent progress in studies of neurotrophic factors and their clinical implications. J Mol Med (Berlin, Germany) 75:637–644
Shoulson I (1992) An interim report of the effect of selegiline (l-deprenyl) on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease: the Parkinson Study Group. Eur Neurol 32 Suppl 1:46–53
Speiser Z, Levy R, Cohen S (1998) Effects of N-propargyl-1-(R)aminoindan (rasagiline) in models of motor and cognition disorders. J Neural Transm Suppl 52:287–300
Sterling J, Veinberg A, Lerner D, Goldenberg W, Levy R, Youdim M, Finberg J (1998) (R)(+)-N-propargyl-1-aminoindan (rasagiline) and derivatives: highly selective and potent inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B. J Neural Transm Suppl 52:301–305
Streifler M, Rabey MJ (1983) Long-term effects of l-deprenyl in chronic levodopa treated parkinsonian patients. J Neural Transm Suppl 19:265–272
Szende B, Bokonyi G, Bocsi J, Keri G, Timar F, Magyar K (2001) Anti-apoptotic and apoptotic action of (−)-deprenyl and its metabolites. J Neural Transm 108:25–33
Tatton WG (1993) Selegiline can mediate neuronal rescue rather than neuronal protection. Mov Disord 8:S20–S30
Tatton WG, Ju WY, Holland DP, Tai C, Kwan M (1994) (−)-Deprenyl reduces PC12 cell apoptosis by inducing new protein synthesis. J Neurochem 63:1572–1575
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman RM, Ju WJ, Mammen M, Carlile GW, Pong AW, Tatton NA (2002) Propargylamines induce antiapoptotic new protein synthesis in serum- and nerve growth factor (NGF)-withdrawn, NGF-differentiated PC-12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:753–764
Ting JT, Kelley BG, Sullivan JM (2006) Synaptotagmin IV does not alter excitatory fast synaptic transmission or fusion pore kinetics in mammalian CNS neurons. J Neurosci 26:372–380
Weiner M (1982) Update on antiparkinsonian agents. Geriatrics 37(81–84):89–91
Weinreb O, Mandel S, Youdim MBH (2003) Gene and protein expression profiles of anti- and pro-apoptotic actions of dopamine, R-apomorphine, green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechine-3-gallate, and melatonin. Ann NY Acad Sci 993:351–361
Weinreb O, Bar-Am O, Amit T, Chillag-Talmor O, Youdim MBH (2004) Neuroprotection via pro-survival protein kinase C isoforms associated with Bcl-2 family members. FASEB J 18:1471–1473
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Chillag-Talmor O, Youdim MB (2005) Novel neuroprotective mechanism of action of rasagiline is associated with its propargyl moiety: interaction of Bcl-2 family members with PKC Pathway. Ann NY Acad Sci 1053:348–355
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Sagi Y, Mandel S, Youdim MB (2006) Involvement of multiple survival signal transduction pathways in the neuroprotective, neurorescue and APP processing activity of rasagiline and its propargyl moiety. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:457–465
Weinreb O, Drigues N, Sagi Y, Reznick AZ, Amit T, Youdim MB (2007) The application of proteomics and genomics to the study of age-related neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:169–179
Westermeier R, Marouga R (2005) Protein detection methods in proteomics research. Biosci Rep 25:19–32
Yates JR 3rd, Eng JK, McCormack AL, Schieltz D (1995) Method to correlate tandem mass spectra of modified peptides to amino acid sequences in the protein database. Anal Chem 67:1426–1436
Yogev-Falach M, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Sagi Y, Weinstock M, Youdim MBH (2002) The involvement of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in the regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing by novel cholinesterase inhibitors derived from rasagiline. FASEB J 16:1674–1676
Yogev-Falach M, Amit T, Bar-AM O, Youdim MBH (2003) The importance of propargylamine moiety in the anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline and its derivatives for MAPK-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing. FASEB J 17:2325–2327
Yoshida T, Yamada Y, Yamamoto T, Kuroiwa Y (1986) Metabolism of deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase (MAO) B inhibitor in rat: relationship of metabolism to MAO-B inhibitory potency. Xenobiotica 16:129–136
Youdim MB (2006) The path from anti Parkinson drug selegiline and rasagiline to multifunctional neuroprotective anti Alzheimer drugs ladostigil and M30. Curr Alzheimer Res 3:541–550
Youdim MBH, Riederer PF (2004) A review of the mechanisms and role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 63:S32–S35
Youdim MB, Tipton KF (2002) Rat striatal monoamine oxidase-B inhibition by l-deprenyl and rasagiline: its relationship to 2-phenylethylamine-induced stereotypy and Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:247–253
Youdim MBH, Finberg JPM, Levy R, Sterling J, Lerner D, Berger-Paskin T, Yallin H (1995) R-Enantiomers of N-propargyl-aminoindan compounds: their preparation and pharmaceutical composition containing them. In: United States Patent. United States, p 133
Youdim MBH, Gross A, Finberg JPM (2001) Rasagiline [N-Propargyl-1R(+)-aminoindant], A selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B. Br J Pharmacol 132:500–506
Youdim MBH, Bar-Am O, Yogev-Falach M, Weinreb O, Maruyama W, Naoi M, Amit T (2004) Rasagiline: neurodegeneration, neuroprotection, and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Neurosci Res 79:172–179
Youdim MB, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2005) Neuropharmacological, neuroprotective and amyloid precursor processing properties of selective MAO-B inhibitor antiparkinsonian drug, rasagiline. Drugs Today 41:369–391
Zhu W, Xie W, Pan T, Jankovic J, Li J, Youdim MB, Le W (2008) Comparison of neuroprotective and neurorestorative capabilities of rasagiline and selegiline against lactacystin-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic degeneration. J Neurochem 105:1970–1978
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of Teva Pharmaceutical Co. (Netanya, Israel), the Technion-Research and Development and Rappaport Family Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology (Haifa, Israel) and Goldings Fund for Parkinson’s Research (USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the special issue "Jerusalem".
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinreb, O., Amit, T., Sagi, Y. et al. Genomic and proteomic study to survey the mechanism of action of the anti-Parkinson’s disease drug, rasagiline compared with selegiline, in the rat midbrain. J Neural Transm 116, 1457–1472 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0225-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0225-x