Summary
Temporary occlusion of major cerebral blood vessels occasionally becomes necessary during surgical procedures. Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is an important non-enzymatic scavenger of free radicals and its protective effect on the brain in permanent focal cerebral ischaemia has been proven in a primate model of focal cerebral ischaemia [16]. Additional damage caused by reperfusion of the infarcted area has been shown in the rat model [22].
This study was undertaken to study the efficacy of ascorbic acid in decreasing infarct size in ischaemic reperfused brain.
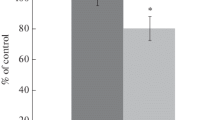
Maccaca radiata monkeys in the treated group were given two grams of ascorbic acid, parentally immediately before clipping the middle cerebral artery and the control group was given placebo. Reperfusion was done after four hours. Mean infarct size in all the three brain slices in the ascorbic acid pretreated group was 7.3%±2.7 and in the placebo group 22.1±6.7 under similar conditions. The mean infarct size in the ascorbic acid pretreated group of monkeys was significantly lower when compared with the placebo group (p=0.0003).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, P., Chandy, M. Effect of Ascorbic Acid on Infarct Size in Experimental Focal Cerebral Ischaemia and Reperfusion in a Primate Model. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140, 977–980 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050201
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050201