Abstract
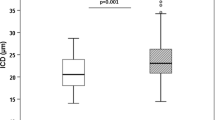
Recent studies have shown a close correlation between advanced diabetic retinopathy and the late stages of atherosclerosis. The purpose of this study was to analyse the association between diabetic retinopathy and early atherosclerotic changes in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. We studied 28 adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Eight patients with nonproliferative retinopathy were compared with the remaining 20 patients, and with 11 healthy controls. The function of endothelium was assessed by measuring flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), the intima-media thickness (IMT) of the common carotid arteries and adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, sE-selectin). In the group with retinopathy FMD equalled 7.8±4.1% vs. 12.1±5.1% in the control group (p=0.04), and in the group without retinopathy, 7.6±5.5% (p=0.04 compared to controls). Higher IMT was found in all patients with diabetes in comparison with healthy controls: 0.49±0.06 mm vs. 0.42±0.03 mm (p=0.001). Patients with retinopathy had a significantly higher value of IMT in comparison not only with controls but also with patients without complications: 0.56±0.06 mm vs. 0.47±0.03 mm (p=0.0001). Adhesion molecule levels were not changed in patients with retinopathy. Higher IMT was found in adolescents with diabetic retinopathy in comparison with patients without complications, which may suggest that macrovascular changes are more advanced in these patients than in their diabetic peers without retinopathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciulla TA, Amador AG, Zinman B (2003) Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care 26:2653–2664
Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, Ferris FL 3rd, King GL, Klein R (2004) Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 27[Suppl 1]:S84–S87
Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL (1984) The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. II. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol 102:520–526
— (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. N Engl J Med 329:977–986
— (1995) The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbAlc) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 44:968–983
Zhang L, Krzentowski G, Albert A, Lefebvre PJ (2001) Risk of developing retinopathy in Diabetes Control and Complications Trial type 1 diabetic patients with good or poor metabolic control. Diabetes Care 24:1275–1279
Sacha E (2005) Diabetic retinopathy. Current opinion on pathophysiology, diagnostics and therapy. Przegl Lek 62:238–242
Gordon PA (2004) Effects of diabetes on the vascular system: current research evidence and best practice recommendations. J Vasc Nurs 22:2–11, quiz 12–13
Romundstad S, Holmen J, Kvenild K, Hallan H, Ellekjaer H (2003) Microalbuminuria and all-cause mortality in 2,089 apparently healthy individuals: a 4.4-year follow-up study. The Nord-Trondelag Health Study (HUNT), Norway. Am J Kidney Dis 42:466–473
Arroyo JG (2002) Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 86:3–4
Fuller JH, Stevens LK, Wang SL (2001) Risk factors for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity: the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia 44[Suppl 2]:S54–S64
Kim YH, Hong MK, Song JM, Han KH, Kang DH, Song JK, Kim JJ, Park SW, Park SJ (2002) Diabetic retinopathy as a predictor of late clinical events following percutaneous coronary intervention. J Invasive Cardiol 14:599–602
Visona A, Lusiani L, Bonanome A, Beltramello G, Confortin L, Papesso B, Costa F, Pagnan A (1995) Wall thickening of common carotid arteries in patients affected by noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: relationship to microvascular complications. Angiology 46:793–799
Klein R, Marino EK, Kuller LH, Polak JF, Tracy RP, Gottdiener JS, Burke GL, Hubbard LD, Boineau R (2002) The relation of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease to retinopathy in people with diabetes in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Br J Ophthalmol 86:84–90
Norgaz T, Hobikoglu G, Aksu H, Guveli A, Aksoy S, Ozer O, Bolca O, Narin A (2005) Retinopathy is related to the angiographically detected severity and extent of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int Heart J 46:639–646
Rajala U, Pajunpaa H, Koskela P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S (2000) High cardiovascular disease mortality in subjects with visual impairment caused by diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 23:957–961
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM Spiegelhalter DJ, Miller OI, Sullivan ID, Lloyd JK, Deanfield JE (1992) Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet 340:1111–1115
Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R (1986) Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation 74:1399–1406
Blankenberg S, Barbaux S, Tiret L (2003) Adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 170:191–203
Blann AD, Lip GY (1998) The endothelium in atherothrombotic disease: assessment of function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 9:297–306
Jarvisalo MJ, Raitakari M, Toikka JO, Putto-Laurila A, Rontu R, Laine S, Lehtimaki T, Ronnemaa T, Viikari J, Raitakari OT (2004) Endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial intimamedia thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Circulation 109:1750–1755
Singh TP, Groehn H, Kazmers A (2003) Vascular function and carotid intimal-medial thickness in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:661–665
Jarvisalo MJ, Putto-Laurila A, Jartti L, Lehtimaki T, Solakivi T, Ronnemaa T, Raitakari OT (2002) Carotid artery intimamedia thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 51:493–498
Krantz JS, Mack WJ, Hodis HN, Liu CR, Liu CH, Kaufman FR (2004) Early onset of subclinical atherosclerosis in young persons with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 145:452–457
Nathan DM, Lachin J, Cleary P, Orchard T, Brillon DJ, Backlund JY, O’Leary DH, Genuth S (2003) Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group: Intensive diabetes therapy and carotid intima-media thickness in type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 348:2294–2303
Gibney J, Turner B, Weis U, Meeking DR, Cansfield J, Watts GF, Shaw KM, Cummings MH (2004) Reduced forearm reactive hyperaemia in normoalbuminuric subjects with Type 1 diabetes and retinopathy. Diabet Med 21:931–935
Rema M, Mohan V, Deepa R, Ravikumar R (2004) Association of carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness with diabetic retinopathy: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-2). Diabetes Care 27:1962–1967
Klein R, Sharrett AR, Klein BE, Moss SE, Folsom AR, Wong TY, Brancati FL, Hubbard LD, Couper D (2002) The association of atherosclerosis, vascular risk factors, and retinopathy in adults with diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Ophthalmology 109:1225–1234
Fairchild JM, Hing SJ, Donaghue KC, Bonney MA, Fung AT, Stephens MM, Mitchell P, Howard NJ, Silink M (1994) Prevalence and risk factors for retinopathy in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Med J Aust 160:757–762
— (1998) Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. BMJ 317:703–713
Donaghue KC, Fairchild JM, Chan A, Hing SJ, Howard NJ, Silink M (1999) Diabetes complication screening in 937 children and adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 12:185–192
Klein BE, Klein R, Moss SE, Palta M (1995) A cohort study of the relationship of diabetic retinopathy to blood pressure. Arch Ophthalmol 113:601–606
Parving HH (1991) Impact of blood pressure and antihypertensive treatment on incipient and overt nephropathy, retinopathy, and endothelial permeability in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 14:260–269
Lloyd CE, Klein R, Maser RE, Kuller LH, Becker DJ, Orchard TJ (1995) The progression of retinopathy over 2 years: the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) Study. J Diabetes Complications 9:140–148
Frost D, Friedl A, Beischer W (2002) Determinants of early carotid atherosclerosis progression in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 110:92–94
Elhadd TA, Kennedy G, Hill A, McLaren M, Newton RW, Greene SA, Belch JJ (1999) Abnormal markers of endothelial cell activation and oxidative stress in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes with no clinical vascular disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:405–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Głowińska-Olszewska, B., Urban, M., Urban, B. et al. The association of early atherosclerosis and retinopathy in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: preliminary report. Acta Diabetol 44, 131–137 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-007-0253-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-007-0253-7