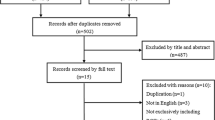
Abstract
Purpose
This systematic review summarises the literature on patient selection, decision-making, effectiveness and outcomes in the surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis (LDS).
Introduction
In daily practice, decision-making in the treatment of LDS is challenging. There is little consensus on either the precise indications or prognostic factors for any specific therapy (operative or non-operative).
Methods
We searched for LDS trials published between 01.01.1990 and 16.11.2011 in Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library and Cinahl. Two independent reviewers selected studies according to the inclusion criteria. Data were then extracted by two of the authors. Quality assessment was performed using the Downs and Black list for the clinical trials/studies and AMSTAR for the reviews.
Results
Data synthesis: 21 papers met the inclusion criteria (2 studies comprising both a RCT and a concurrent observational analysis, 1 RCT, 6 prospective studies, 8 retrospective studies, 3 reviews, 1 review guideline). The quality of the clinical studies was on average “fair” [mean score 15.6 points (range 10–19) out of 24 points (Downs and Black)]. The quality of the reviews ranged from 1 to 7 out of 11 points with an average of 5 points (AMSTAR). The study outcomes could not be subject to meta-analysis due to heterogeneity of study design and variable measure used.
Conclusions
Despite there being many articles describing and/or comparing different surgical options for LDS, there was insufficient evidence to draw conclusions concerning clear indications for specific types of surgical treatment, predictors of outcome or complication rates. There remains a need to establish a decision-making tool to facilitate daily clinical practice and to assure appropriate treatment for patients with LDS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newman PH (1955) Spondylolisthesis, its cause and effect. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 16(5):305–323
O’Rourke MR, Grobler LJ (1998) L4–L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis: indications and technique for operative management. Iowa Orthop J 18:76–86
Farfan HF, Osteria V, Lamy C (1976) The mechanical etiology of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 117:40–55
Farfan HF (1980) The pathological anatomy of degenerative spondylolisthesis. A cadaver study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 5(5):412–418
Chen IR, Wei TS (2009) Disc height and lumbar index as independent predictors of degenerative spondylolisthesis in middle-aged women with low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(13):1402–1409
Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN (2003) Lumbar spinal stenosis. Treatment strategies and indications for surgery. Orthop Clin N Am 34(2):281–295
Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN (2005) Degenerative spondylolisthesis: Review of current trends and controversies. Spine 30(6):S71–S81
Kalichman L, Hunter DJ (2008) Diagnosis and conservative management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17(3):327–335
Faldini C et al (2007) Surgical treatment of symptomatic degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis by decompression and instrumented fusion. J Orthop Traumatol 8(3):128–133
Weinstein JN et al (2009) Surgical compared with nonoperative treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Four-year results in the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) randomized and observational cohorts. J Bone Jt Surg Am 91(6):1295–1304
Weinstein JN et al (2007) Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med 356(22):2257–2270
Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S (1994) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. A meta-analysis of literature 1970–1993. Spine 19(Suppl 20):2256S–2265S
Bridwell KH et al (1993) The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 6(6):461–472
Downs SH, Black N (1998) The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health 52(6):377–384
Shea BJ et al (2007) External validation of a measurement tool to assess systematic reviews (AMSTAR). PLoS ONE 2(12):e1350
Sears W (2005) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: restoration of sagittal balance using insert-and-rotate interbody spacers. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 5(2):170–179
Okuda S et al (2006) Surgical outcomes of posterior lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients. [Reprint in J Bone Jt Surg Am. 2007 Sep; 89 Suppl 2 Pt.2:310–20; PMID: 17768224]. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88 (12): 2714–2720
Abdul QR et al (2011) Clinico-radiological profile of indirect neural decompression using cage or auto graft as interbody construct in posterior lumbar interbody fusion in spondylolisthesis: Which is better? J Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2(1):12–16
Adogwa O et al (2011) Cost-effectiveness of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for Grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis.[Erratum appears in J Neurosurg Spine. 2011 Aug; 15(2):211; PMID: 21682560]. J Neurosurg Spine 15(2):138–143
Kristof RA et al (2002) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis-induced radicular compression: nonfusion-related decompression in selected patients without hypermobility on flexion-extension radiographs. J Neurosurg 97(3 Suppl):281–286
Kornblum MB et al (2004) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine 29(7):726–733 discussion 733–4
Abdu WA et al (2009) Degenerative spondylolisthesis: does fusion method influence outcome? Four-year results of the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(21):2351–2360
Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 73(6):802–808
Fischgrund JS et al (1997) 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine 22(24):2807–2812
Tormenti MJ et al (2012) Perioperative surgical complications of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a single-center experience. J Neurosurg Spine 16(1):44–50
Fischgrund JS (2004) The argument for instrumented decompressive posterolateral fusion for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis. Spine 29(2):173–174
Watters WC 3rd et al (2009) An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 9(7):609–614
Yan D-L et al (2008) Comparative study of PILF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17(10):1311–1316
Boden SD et al (1996) Orientation of the lumbar facet joints: association with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Jt Surg Am 78(3):403–411
Xu H, Tang H, Li Z (2009) Surgical treatment of adult degenerative spondylolisthesis by instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the Han nationality. J Neurosurg Spine 10(5):496–499
Martin CR et al (2007) The surgical management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Spine 32(16):1791–1798
Ghogawala Z et al (2004) Prospective outcomes evaluation after decompression with or without instrumented fusion for lumbar stenosis and degenerative Grade I spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 1(3):267–272
Carreon LY et al (2003) Perioperative complications of posterior lumbar decompression and arthrodesis in older adults. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A 85(11):2089–2092
Acknowledgments
SNF Swiss National Science Foundation (grant number IZ32Z0_141535): Wildhainweg 3, 3001 Bern. Eurospine, the Spine Society of Europe: Seefeldstrasse 16, 8610 Uster, (Administrative Office). Schulthess Klinik Research Funds: Lengghalde 8, 8008 Zürich.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest. The authors have no financial or personal relationships that might potentially influence their reporting or interpretation of studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Steiger and H.-J. Becker contributed equally to this work.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Search strategy and results




Appendix 2
See Table 5.
Appendix 3: Excluded studies after full text consultation
Adachi K, Futami T et al (2003) Spinal canal enlargement procedure by restorative laminoplasty for the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 3(6):471–478
Al-Mukhtar M, Kazzaz S et al (2009) Results of an observational cohort of 100 consecutive patients undergoing transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Br J Neurosurg 23(2):134
Alexander DI, Manson NA et al (2001) Efficacy of calcium sulfate plus decompression bone in lumbar and lumbosacral spinal fusion: preliminary results in 40 patients. Can J Surg 44(4):262–266
Altaf F, Jalgaonkar A et al (2011) Prospective study of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J 11(10):112S–113S
Anderson PA, Tribus CB et al (2006) Treatment of neurogenic claudication by interspinous decompression: application of the X STOP device in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 4(6):463–471
Aono H, Iwasaki M et al (2007) Surgical outcome of drop foot caused by degenerative lumbar diseases. Spine 32(8):E262–E266
Asazuma T, Yamugishi M et al (2004) Posterior spinal fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases using the Crock-Yamagishi (C-Y) spinal fixation system. J Spinal Disord Tech 17(3):174–177
Aubin M, Drew J et al (2010) Clinical and radiological fusion rates following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) with silicate substituted calcium-phosphate bone graft substitute without ICBG for the surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease. Spine
Auerbach J, Davis R (2011) Direct versus indirect decompression and stabilization: a comparison of clinical outcomes with coflex interlaminar stabilization, laminectomy and spinal fusion, and X-STOP to treat spinal stenosis and low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J 11(10):104S–105S
Auerbach J, Davis R et al (2011) Direct decompression and Coflex (registered trademark) interlaminar stabilization compared with laminectomy and posterior spinal fusion with pedicle screw instrumentation for spinal stenosis with back pain or degenerative spondylolisthesis: 2-year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter FDA IDE trial. Spine J 11(10):86S–87S
Azzazi A, Elhawary Y (2010) Dynamic stabilization using X-stop versus transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis; Comparative study of the clinical outcome. Neurosurg Q 20(3):165–169
Barrey C, Belliard H et al (2011) One-step combined anterior and posterior lumbosacral fusion. Eur Spine J 20(7):1204
Beaman DN, Graziano GP et al (1993) Substance P innervation of lumbar spine facet joints. Spine 18(8):1044–1049
Bednar DA (2002) Surgical management of lumbar degenerative spinal stenosis with spondylolisthesis via posterior reduction with minimal laminectomy. J Spinal Disord Tech 15(2):105–109
Blondel B, Adetchessi T et al (2011) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion through a unilateral approach and percutaneous osteosynthesis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(6):595–601
Bohnen IM, Schaafsma J et al (1997) Results and complications after posterior lumbar spondylodesis with the “variable screw placement spinal fixation system”. Acta Orthop Belg 63(2):67–73
Booth KC, Bridwell KH et al (1999) Minimum 5-year results of degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and instrumented posterior fusion. Spine 24(16):1721–1727
Brantigan JW, Neidre A (2003) Achievement of normal sagittal plane alignment using a wedged carbon fiber reinforced polymer fusion cage in treatment of spondylolisthesis. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 3(3):186–196
Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA et al (1993) The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 6(6):461–472
Brotis AG, Paterakis KN et al (2010) Instrumented posterior lumbar fusion outcomes for lumbar degenerative disorders in a southern European, semirural population. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(7):444–450
Burkus JK, Gornet MF et al (2009) Six-year outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis with use of interbody fusion cages and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Bone Jt Surg Am 91(5):1181–1189
Buttermann GR, Garvey TA et al (1998) Lumbar fusion results related to diagnosis. Spine 23(1):116–127
Caputy AJ, Luessenhop AJ (1992) Long-term evaluation of decompressive surgery for degenerative lumbar stenosis. J Neurosurg 77(5):669–676
Caserta S, La Maida GA et al (2002) Elastic stabilization alone or combined with rigid fusion in spinal surgery: a biomechanical study and clinical experience based on 82 cases. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S192–S197
Cavu O et al (2007) Efficacy of unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis. Turkish Neurosurg: 100–108
Cavusoglu H, Turkmenoglu O et al (2007) Efficacy of unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis. Turkish Neurosurg 17(2):100–108
Chaloupka R, Krbec M et al (2006) Two year clinical results of 360 degree fusion of lumbar spondylolisthesis managed by transpedicular fixation and PLIF or ALIF technique EuroSpine 2006. 8th Annual Meeting of the European Spine Society, 25–28 October 2006, Istanbul, Turkey-Abstracts P11. Eur Spine J: S506–S507
Chang M, Crandall D et al (2011) Iliac screw fixation: radiographic and clinical outcomes of unilateral versus bilateral placement. Spine J 11(10):142S
Chang P, Seow KH et al (1993) Comparison of the results of spinal fusion for spondylolisthesis in patients who are instrumented with patients who are not. Singapore Med J 34(6):511–514
Cheh G, Bridwell KH et al (2007) Adjacent segment disease following lumbar/thoracolumbar fusion with pedicle screw instrumentation: a minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine 32(20):2253–2257
Chen KX, Yang QY et al (2010) Treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis through posterolateral fusion and fixation with pedicle screws. Zhongguo gu shang (China J Orthop Traumatol): 254–256
Christensen FB, Thomsen K et al (1999) The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on posterolateral spinal fusion. A prospective, randomized study with a two-year follow-up. Ugeskrift for laeger: 1920–1925
Chu G, Aikenmu K et al (2011) Unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res 15(35):6540–6545
Costa F, Cardia A et al (2011) Spinal navigation: standard preoperative versus intraoperative computed tomography data set acquisition for computer-guidance system: Radiological and clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Spine 36(24):2094–2098
Crandall D, Gebhardt M et al (2011) Tlif with an obliquely placed rectangular cage: does cage position or level effect lumbar lordosis? Spine J 11(10):134S
Crandall D, Patterson J et al (2011) RhBMP-2 in TLIF: dose related complications from a large series. Spine J 11(10):61S
Crandall D, Schmidt K et al (2011) Primary versus revision spine surgery: long-term work status and outcomes. Spine J 11(10):48S–49S
Crawford CH, Smail J et al (2011) Health-related quality of life after posterolateral lumbar arthrodesis in patients 75 years of age and older. Spine 36(13):1065–1068
Csecsei G, Klekner A et al (1997) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) using the bony elements of the dorsal spinal segment. Acta Chir Hung 36(1–4):54–56
Dantas FLR, Prandini MN et al (2007) Comparison between posterior lumbar fusion with pedicle screws and posterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screws in adult spondylolisthesis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 65(3B):764–770
Deinsberger R, Kinn E et al (2006) Microsurgical treatment of juxta facet cysts of the lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord Tech 19(3):155–160
Derincek A, Mehbod A et al (2008) Degeneration of non-fused segments after floating lumbar fusion. Acta Orthop Belg 74(4):507–511
Devkota P, Shrestha SK et al (2011) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the management of spondylolisthesis. Nepal Medical College J NMCJ 13(1):46–49
Dhall SS, Wang MY et al (2008) Clinical and radiographic comparison of mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in 42 patients with long-term follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine 9(6):560–565
Dimar Ii JR, Glassman SD et al (2009) Clinical and radiographic analysis of an optimized rhBMP-2 formulation as an autograft replacement in posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A 91(6):1377–1386
Elhawary Y, Azzazi A (2010) Dynamic stabilization using X-stop vs. trans-pedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis: comparative study of the clinical outcome. Spine J 10(9):130S
Epstein NE (1998) Primary fusion for the management of ‘unstable’ degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neuro-Orthopedics 23(1–2):45–52
Epstein NE (2004) Lumbar laminectomy for the resection of synovial cysts and coexisting lumbar spinal stenosis or degenerative spondylolisthesis: an outcome study. Spine 29(9):1049–1055 discussion 1056
Epstein NE (2008) An analysis of noninstrumented posterolateral lumbar fusions performed in predominantly geriatric patients using lamina autograft and beta tricalcium phosphate. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 8(6):882–887
Fernandez-Fairen M, Sala P et al (2007) A prospective randomized study of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 32(4):395–401
Fras C, Fras M (2010) MRI utility in diagnosing lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J 10(9):22S
Frazier DD, Lipson SJ et al (1997) Associations between spinal deformity and outcomes after decompression for spinal stenosis. Spine 22(17):2025–2029
Fujiya M, Saita M et al (1990) Clinical study on stability of combined distraction and compression rod instrumentation with posterolateral fusion for unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 15(11):1216–1222
Gaetani P, Aimar E et al (2006) Functional disability after instrumented stabilization in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: a follow-up study. Funct Neurol 21(1):31–37
Gavaskar AS, Achimuthu R (2010) Transfacetal fusion for low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine: results of a prospective single center study. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(3):162–165
Gelalis ID, Arnaoutoglou C et al (2010) Prospective analysis of surgical outcomes in patients undergoing decompressive laminectomy and posterior instrumentation for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Orthopaedica et Traumatologica Turcica 44(3):235–240
Ghogawala Z, Benzel EC et al (2010) Lumbar spinal fusion reduces risk of re-operation after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis associated with grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis: initial results from the slip trial. Neurosurgery 67(2):542–543
Glassman SD, Carreon LY et al (2009) Lumbar fusion outcomes stratified by specific diagnostic indication. Spine J 9(1):13–21
Grob D, Humke T et al (1993) Significance of simultaneous fusion and surgical decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthopade 22(4):243–249
Grob D, Humke T et al (1996) Direct pediculo-body fixation in cases of spondylolisthesis with advanced intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J 5(4):281–285
Grobler LJ, Robertson PA et al (1993) Decompression for degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis at L4–5. The effects on facet joint morphology. Spine 18(11):1475–1482
Guigui P, Benoist M et al (1998) Motor deficit in lumbar spinal stenosis: a retrospective study of a series of 50 patients. J Spinal Disord 11(4):283–288
Ha K-Y, Na K-H et al (2008) Comparison of posterolateral fusion with and without additional posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 21(4):229–234
Hackenberg L, Halm H et al (2005) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a safe technique with satisfactory three to 5 year results. Eur Spine J 14(6):551–558
Hansraj KK, O’Leary PF et al (2001) Decompression, fusion, and instrumentation surgery for complex lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 384:18–25
Haro H, Maekawa S et al (2008) Prospective analysis of clinical evaluation and self-assessment by patients after decompression surgery for degenerative lumbar canal stenosis. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 8(2):380–384
Hasegewa K, Kitahara K et al (2009) Biomechanical evaluation of segmental instability in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 18(4):465–470
Hashizume H, Yoshida M et al (2010) Does the decompression surgery improve the low back pain in the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis? Spine
Hatta Y, Shiraishi T et al (2009) Muscle-preserving interlaminar decompression for the lumbar spine: a minimally invasive new procedure for lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine 34(8):E276–E280
Hee HT, Wong HK (2003) The long-term results of surgical treatment for spinal stenosis in the elderly. Singapore Med J 44(4):175–180
Hioki A, Miyamoto K et al (2005) Two-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease: improved clinical outcome with restoration of lumbar lordosis. Spine J 5(6):600–607
Ho YK, Lee SH et al (2007) Computed tomography-guided percutaneous facet screw fixation in the lumbar spine: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine 7(1):95–98
Hong S-W, Lee H-Y et al (2010) Interspinous ligamentoplasty in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: midterm clinical results. J Neurosurg Spine 13(1):27–35
Hong SW, Choi KY et al (2011) A comparison of unilateral and bilateral laminotomies for decompression of L4–L5 spinal stenosis. Spine 36(3):E172–E178
Houten JK, Post NH et al (2006) Clinical and radiographically/neuroimaging documented outcome in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus 20(3):E8
Huang K-F, Chen T-Y (2003) Clinical results of a single central interbody fusion cage and transpedicle screws fixation for recurrent herniated lumbar disc and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Chang Gung Med J 26(3):170–177
Hwang CJ, Vaccaro AR et al (2010) Immunogenicity of osteogenic protein 1: results from a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter pivotal study of uninstrumented lumbar posterolateral fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 13(4):484–493
Ido K, Urushidani H (2001) Radiographic evaluation of posterolateral lumbar fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: long-term follow-up of more than 10 years vs. midterm follow-up of 2–5 years. Neurosurg Rev 24(4):195–199
Ikuta K, Tono O et al (2008) Clinical outcome of microendoscopic posterior decompression for spinal stenosis associated with degenerative spondylolisthesis—minimum 2-year outcome of 37 patients. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 51(5):267–271
Ikuta K, Tono O et al (2009) Prevalence and clinical features of intraspinal facet cysts after decompression surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine 10(6):617–622
Ito Y, Oda H et al (2003) Results of surgical treatment for lumbar canal stenosis due to degenerative spondylolisthesis: enlargement of the lumbar spinal canal. J Orthop Sci 8(5):648–656
Ito Z, Matsuyama Y et al (2010) Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 35(21):E1101–E1105
Iwamoto J, Takeda T (2002) Effect of surgical treatment on physical activity and bone resorption in patients with neurogenic intermittent claudication. J Orthop Sci 7(1):84–90
Jang J-S, Lee S-H (2005) Clinical analysis of percutaneous facet screw fixation after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 3(1):40–46
Jang J-S, Lee S-H (2005) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with ipsilateral pedicle screw and contralateral facet screw fixation. J Neurosurg Spine 3(3):218–223
Jin AM, Cao H et al (2002) Treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis by Socon internal fixator: report of 18 cases. Di 1 jun yi da xue xue bao Academic J First Med College PLA 22(3): 230–231
Jin J, Jianxiong S et al (2000) Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis with SOCON instrumentation. Chin Med Sci J 15(2):111–114
Jiya TU, Smit T et al (2011) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using non resorbable poly-ether-ether-ketone versus resorbable poly-L-lactide-co-D, L-lactide fusion devices. Clinical outcome at a minimum of 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 20(4):618–622
Jonsson B, Akesson M et al (1992) Low risk for vertebral slipping after decompression with facet joint preserving technique for lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 1(2):100–104
Kamioka Y, Yamamoto H (1990) Lumbar trapezoid plate for lumbar spondylolisthesis: a clinical study on preoperative and postoperative instability. Spine 15(11):1198–1203
Kanayama M, Hashimoto T et al (2005) Non-fusion surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis using artificial ligament stabilization: surgical indication and clinical results. Spine 30(5):588–592
Kanayama M, Hashimoto T et al (2007) A minimum 10-year follow-up of posterior dynamic stabilization using Graf artificial ligament. Spine 32(18): 1992–1996; discussion 1997
Kaner T, Dalbayrak S et al (2010) Comparison of posterior dynamic and posterior rigid transpedicular stabilization with fusion to treat degenerative spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics 33(5)
Kang B-U, Choi W-C et al (2009) An analysis of general surgery-related complications in a series of 412 minilaparotomic anterior lumbosacral procedures. J Neurosurg Spine 10(1):60–65
Katz JN (2004) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Point of view. Spine 29(7):733–734
Kawaguchi S, Oguma H et al (2010) Fusion status and clinical outcomes of instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with local autogenous bone graft: 2-year results of prospective cohort study. Spine
Kawakami M, Tamaki T et al (2002) Lumbar sagittal balance influences the clinical outcome after decompression and posterolateral spinal fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine 27(1):59–64
Kim DH, Shanti N et al (2010) Association between degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinous process fracture following interspinous process spacer surgery. Spine J 10(9):24S
Kim HS, Park IH et al (2007) Bone cement augmentation of pedicular screwing in severe osteoporotic spondylolisthetic patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 42(1):6–10
Kim KH, Lee SH et al (2010) Adjacent segment disease after interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixations for isolated L4–L5 Spondylolisthesis: a minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine 35(6):625–634
Kim MK, Lee S-H et al (2011) The impact of sagittal balance on clinical results after posterior interbody fusion for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: a pilot study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord 12:69
Kim NH, Kim HK et al (1993) A computed tomographic analysis of changes in the spinal canal after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clinical Orthop Relat Res 286: 180–191
Kim S-Y, Maeng DH et al (2008) Anterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbosacral junction in steep sacral slope. J Spinal Disord Tech 21(1):33–38
Kim S, Mortaz S et al (2011) Cost-utility of lumbar decompression with or without fusion for patients with symptomatic degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J 11(10):26S–27S
Kim SS, Denis F et al (1990) Factors affecting fusion rate in adult spondylolisthesis. Spine 15(9):979–984
Kimura I, Shingu H et al (2001) Lumbar posterolateral fusion alone or with transpedicular instrumentation in L4–L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord 14(4):301–310
Kinoshita T, Ohki I et al (2001) Results of degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with posterior decompression alone via a new surgical approach. J Neurosurg 95(1 Suppl):11–16
Kleeman TJ, Hiscoe AC et al (2000) Patient outcomes after minimally destabilizing lumbar stenosis decompression: the “Port-Hole” technique. Spine 25(7):865–870
Klopfenstein JD, Kim LJ et al (2006) Retroperitoneal approach for lumbar interbody fusion with anterolateral instrumentation for treatment of spondylolisthesis and degenerative foraminal stenosis. Surg Neurol 65(2): 111–116; discussion 116
Konno S, Kikuchi S (2000) Prospective study of surgical treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison between decompression alone and decompression with graf system stabilization. Spine 25(12):1533–1537
Korge A, Siepe C et al (2010) Minimally invasive anterior approaches to the lumbosacral junction. Oper Orthop Traumatol 22(5–6):582–592
Kotani Y, Abumi K et al (2011) Effect of minimally invasive lumbar posterolateral fusion using percutaneous pedicle screw on paravertebral muscle change and postoperative residual low back pain. Spine J 11(10):103S–104S
Kotani Y, Ito M et al (2010) Prospective comparative analysis of minimally invasive lumbar posterolateral fusion with percutaneous pedicle screws vs. conventional approach for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J 10(9):118S
Lattig F, Fekete T et al (2010) Does the fusion level influence the outcome of single-level posterior lumbar fusion for degenerative disease? Spine
Lattig F, Fekete TF et al (2011) Lumbar facet joint effusion in MRI: a sign of instability in degenerative spondylolisthesis? Eur Spine J
Lauber S, Schulte TL et al (2006) Clinical and radiologic 2- to 4-year results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Spine 31(15):1693–1698
Laus M, Tigani D et al (1994) Posterolateral spinal fusion: a study of 123 cases with a long-term follow-up. Chir Organi Mov 79(1):69–79
Lawhorne TW 3rd, Girardi FP et al (2009) Treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: potential impact of dynamic stabilization based on imaging analysis. Eur Spine J 18(6):815–822
Lee DY, Lee SH (2010) Perioperative complications of single-level instrumented mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: analysis of risk factors in consecutive 207 patients. Spine J 10(9):22S–23S
Lee DY, Lee SH et al (2010) Decompression and interspinous dynamic stabilization using the locker for lumbar canal stenosis associated with low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 53(3):117–121
Lee S-C, Chen J-F et al (2009) In situ local autograft for instrumented lower lumbar or lumbosacral posterolateral fusion. J Clin Neurosci 16(1):37–43
Lee S-H, Lee J-H et al (2010) Spinopelvic alignment after interspinous soft stabilization with a tension band system in grade 1 degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine 35(15):E691–E701
Lee SE, Park SB et al (2008) Clinical experience of the dynamic stabilization system for the degenerative spine disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 43(5):221–226
Lee SH, Kang BU et al (2006) Revision surgery of the lumbar spine: anterior lumbar interbody fusion followed by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation. J Neurosurg Spine 5(3):228–233
Lee TC (1994) Reduction and stabilization without laminectomy for unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis: a preliminary report. Neurosurgery 35(6):1072–1076
Lee TC (1995) Complications of transpedicular reduction and stabilization of the thoracolumbar spine. J Formos Med Assoc 94(12):738–741
Lemcke J, Klotzer S et al (2007) PLIF and ALIF for the degenerative spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 145(1):48–54
Li SG, Qiu GX et al (2005) Improving effect of general spine system on the low back pain and intermittent claudication of patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Chin J Clin Rehabil 9(18):225–227
Liao J-C, Chen W-J et al (2009) Outcome of the L5–S1 segment after posterior instrumented spinal surgery in degenerative lumbar diseases. Chang Gung Med J 32(1):81–88
Liao J-C, Chen W-J et al (2011) Surgical outcomes of degenerative spondylolisthesis with L5–S1 disc degeneration: comparison between lumbar floating fusion and lumbosacral fusion at a minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine 36(19):1600–1607
Lin JH, Tsai TH et al (2008) Comparison of outcomes for posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) between spinal block bullet and fusion cages. J Med Sci 28(5):193–198
Liu G, Buchowski JM et al (2009) Revision surgery following cervical laminoplasty: etiology and treatment strategies. Spine 34(25):2760–2768
Lowe TG, Tahernia AD et al (2002) Unilateral transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): indications, technique, and 2-year results. J Spinal Disord Tech 15(1):31–38
Markwalder TM (1993) Surgical management of neurogenic claudication in 100 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis due to degenerative spondylolisthesis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 120(3–4):136–142
Matsudaira K, Yamazaki T et al (2005) Spinal stenosis in grade I degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study of outcomes following laminoplasty and laminectomy with instrumented spinal fusion. J Orthop Sci 10(3):270–276
Matsumura A, Taneichi H et al (2006) Comparative study of radiographic disc height changes using two different interbody devices for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: open box vs. fenestrated tube interbody cage.[Erratum appears in Spine. 2007 Mar 15;32(6):709]. Spine 31(23):E871–E876
Maxwell JH, Davis R et al (2010) 36-Month clinical and radiographic outcomes of instrumented, posterolateral spinal fusion from a prospective, randomized clinical study. Spine J 10(9):73S–74S
McAfee P, Khoo LT et al (2007) Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with a total posterior arthroplasty prosthesis: implant description, surgical technique, and a prospective report on 29 patients. Neurosurg Focus 22(1):E13
McAfee PC, DeVine JG et al (2005) The indications for interbody fusion cages in the treatment of spondylolisthesis: analysis of 120 cases. Spine 30(6 Suppl):S60–S65
McConnell J (2011) A comparison of b-tcpdbmaversus rhBMP-2 in anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective, randomized trial with two-year clinical and radiographic outcomes. Spine J 11(10):64S–65S
McCulloch JA (1998) Microdecompression and uninstrumented single-level fusion for spinal canal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 23(20):2243–2252
Mecs L, Sohar G et al (2010) Biomechanical consequences of adjacent segment lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Osteoarthr Cartilage 18:S230
Mehta S, Goss B et al (2010). Retrospective comparative analysis of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis treated with posterolateral fusion (PLF) with bone morphogenic protein (BMP) 2 with or without additional transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). Spine
Metellus P, Fuentes S et al (2006) Retrospective study of 77 patients harbouring lumbar synovial cysts: functional and neurological outcome. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148(1):47–54
Minamide A, Yoshida M et al (2010) Factors affected to clinical outcomes of decompression surgery without fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine
Miyashita H, Kumano K (1990) Pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. J Western Pacific Orthop Assoc 27(1):117–124
Mochida J, Suzuki K et al (1999) How to stabilize a single level lesion of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 368: 126–134
Mokhtar SA, McCombe PF et al (2010) Health-related quality of life: a comparison of outcomes after lumbar fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis with large joint replacement surgery and population norms. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 10(4):306–312
Montgomery DM, Fischgrund JS (1994) Passive reduction of spondylolisthesis on the operating room table: a prospective study. J Spinal Disord 7(2):167–172
Muresu F, Zachos A et al (2011) The fusion instrumented with percutaneous systems: longitude, sextant and interbody cage for the treatment of the lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Traumatol 12:S43
Naderi S, Ekinci G et al (1999) The role of facet joint angle in spondylolisthesis: a radiologic study. Neuro-Orthopedics 26(2):49–54
Nalbandian MM, Hoashi JS et al (2010) Variations in the iliolumbar vein during the anterior approach for spinal procedures. J Vasc Surg 51(4):1074
Nasca RJ (2002) Lumbar spinal stenosis: surgical considerations. J South Orthop Assoc 11(3):127–134
Nishizawa T, Fujimura Y (1997) A clinical study of anterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg 5(1):21–27
Nojiri K, Matsumoto M et al (2005) Comparative assessment of pedicle morphology of the lumbar spine in various degenerative diseases. Surg Radiol Anat 27(4):317–321
Oishi Y, Murase M et al (2010) Smaller facet effusion in association with restabilization at the time of operation in Japanese patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 12(1):88–95
Okuda S, Oda T et al (2008) Lamina horizontalization and facet tropism as the risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration after PLIF. Spine 33(25):2754–2758
Okuda T, Baba I et al (2004) The pathology of ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar disease. Spine 29(15):1689–1697
Okuyama K, Kido T et al (2007) PLIF with a titanium cage and excised facet joint bone for degenerative spondylolisthesis—in augmentation with a pedicle screw. J Spinal Disord Tech 20(1):53–59
Oliveira L, Marchi L et al (2010) Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) for the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J 10(9):23S
Oliveira L, Marchi L et al (2010) A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion procedure to indirectly decompress the neural elements. Spine 35(26 Suppl):S331–S337
Onda A, Otani K et al (2006) Mid-term and long-term follow-up data after placement of the Graf stabilization system for lumbar degenerative disorders. J Neurosurg Spine 5(1):26–32
Oshtory R, Zucherman J et al (2010) X-stop effectively treats neurogenic claudication caused by lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J 10(9):137S
Ozgur BM, Agarwal V et al (2010) Two-year clinical and radiographic success of minimally invasive lateral transpsoas approach for the treatment of degenerative lumbar conditions. SAS J 4(2):41–46
Palmer S, Turner R et al (2002) Bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis involving a unilateral approach with microscope and tubular retractor system. J Neurosurg 97(2 Suppl):213–217
Park DK, An HS et al (2010) Does multilevel lumbar stenosis lead to poorer outcomes?: a subanalysis of the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) lumbar stenosis study. Spine 35(4):439–446
Park P, Foley KT (2008) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with reduction of spondylolisthesis: technique and outcomes after a minimum of 2 years’ follow-up. Neurosurg Focus 25(2):E16
Park SC, Yoon SH et al (2009) Minimum 2-year follow-up result of degenerative spinal stenosis treated with interspinous U (Coflex(trademark)). J Korean Neurosurg Soc 46(4):292–299
Park Y-K, Kim J-H et al (2002) Facet fusion in the lumbosacral spine: a 2-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery 51(1):88–95; discussion 95–86
Park Y, Ha JW et al (2010) The optimal indications and treatment results of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine
Park YK, Chung HS (1999) Instrumented facet fusion for the degenerative lumbar disorders. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141(9):915–920
Parker SL, Adogwa O et al (2011) Utility of minimum clinically important difference in assessing pain, disability, and health state after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 14(5):598–604
Parker SL, McGirt MJ et al (2011) Accuracy of free-hand pedicle screws in the thoracic and lumbar spine: analysis of 6816 consecutive screws. Neurosurgery 68(1):170–178
Pateder DB, Benzel E (2010) Noninstrumented facet fusion in patients undergoing lumbar laminectomy for degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Surg Orthop Adv 19(3):153–158
Plotz GMJ, Benini A (1998) Lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: review of 106 operated cases with degenerative anterior vertebral translation as the predominant aspect of the spondylosis. Neurosurg Q 8(4):271–287
Plotz GMJ, Kramer M et al (2000) Degenerative spondylolisthesis of the fourth lumbar vertebra—Mid-term results of undercutting decompression and transpedicular fusion in 44 patients. Neuro-Orthopedics 27(1–2):15–36
Podichetty VK, Spears J et al (2006) Complications associated with minimally invasive decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 19(3):161–166
Postacchini F, Cinotti G (1992) Bone regrowth after surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Bone Jt Surg British 74(6):862–869
Potter BK, Freedman BA et al (2005) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiographic results and complications in 100 consecutive patients. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(4):337–346
Putzier M, Schneider SV et al (2004) Application of a dynamic pedicle screw system (DYNESYS) for lumbar segmental degenerations—comparison of clinical and radiological results for different indications. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 142(2):166–173
Radcliff K, Curry E et al (2011) Predictors of reoperation in lumbar stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis surgery: a subgroup analysis of the sport study. Spine J 11(10):68S
Radcliff K, Hwang R et al (2011) Does iliac crest autograft affect the outcome of fusion in the setting of degenerative spondylolisthesis? A subgroup analysis of the SPORT study. Spine J 11(10):60S
Rampersaud YR, Gray R et al (2011) Cost-utility analysis of posterior minimally invasive fusion compared with conventional open fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis. SAS J 5(2):29–35
Rampersaud YR, Wai E et al (2010) Health related quality of life following decompression compared to decompression and fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: a Canadian multicenter study. Spine J 10(9):35S–36S
Rechtine GR, Sutterlin CE et al (1996) The efficacy of pedicle screw/plate fixation on lumbar/lumbosacral autogenous bone graft fusion in adult patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord 9(5):382–391
Robertson PA, Grobler LJ et al (1993) Postoperative spondylolisthesis at L4–5. The role of facet joint morphology. Spine 18(11):1483–1490
Rouben D, Casnellie M et al (2011) Long-term durability of minimal invasive posterior transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a clinical and radiographic follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech 24(5):288–296
Rousseau M-A, Lazennec J-Y et al (2005) Predictors of outcomes after posterior decompression and fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 14(1):55–60
Sanderson PL, Wood PL (1993) Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in old people. J Bone Jt Surg British 75(3):393–397
Sapkas GS, Mavrogenis AF et al (2007) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus circumferential fusion using the B-Twin expandable spinal system. J Long Term Eff Med Implants 17(3):217–227
Sasai K, Umeda M et al (2008) Microsurgical bilateral decompression via a unilateral approach for lumbar spinal canal stenosis including degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 9(6):554–559
Sato K, Kikuchi S (1997) Clinical analysis of two-level compression of the cauda equina and the nerve roots in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine 22(16): 1898–1903; discussion 1904
Satomi K, Hirabayashi K et al (1992) A clinical study of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Radiographic analysis and choice of treatment. Spine 17(11):1329–1336
Schaeren S, Broger I et al (2008) Minimum four-year follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. Spine 33(18):E636–E642
Schnake KJ, Schaeren S et al (2006) Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 31(4):442–449
Schnee CL, Freese A et al (1997) Outcome analysis for adults with spondylolisthesis treated with posterolateral fusion and transpedicular screw fixation. J Neurosurg 86(1):56–63
Schwender JD, Holly LT et al (2005) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(Suppl):S1–S6
Sharma AK, Kepler CK et al (2011) Lateral lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiographic outcomes at 1 year: a preliminary report. J Spinal Disord Tech 24(4):242–250
Silvers HR, Lewis PJ et al (1993) Decompressive lumbar laminectomy for spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg 78(5):695–701
Smith A, Arginteanu M et al (2010) Increased incidence of cage migration and non-union in instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable cages. Spine J 10(9):94S–95S
Soini J, Laine T et al (1993) Spondylodesis augmented by transpedicular fixation in the treatment of olisthetic and degenerative conditions of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 297: 111–116
Speck G, Pike J (2000) Postero-lateral lumbar fusion using OP-1: a model using patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis-preliminary results [Abstract]. J Bone Jt Surg British, 277
Stoll TM, Dubois G et al (2002) The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S170–S178
Sur YJ, Kong CG et al (2011) Survivorship analysis of 150 consecutive patients with DIAM (trademark) implantation for surgery of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Eur Spine J 20(2):280–288
Thalgott JS, Sasso RC et al (1997) Adult spondylolisthesis treated with posterolateral lumbar fusion and pedicular instrumentation with AO DC plates. J Spinal Disord 10(3):204–208
Thomsen K, Christensen FB et al (1997) 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Spine 22(24):2813–2822
Tillich M, Trummer M et al (2001) Symptomatic intraspinal synovial cysts of the lumbar spine: correlation of MR and surgical findings. Neuroradiology 43(12):1070–1075
Toyoda H, Nakamura H et al (2011) Clinical outcome of microsurgical bilateral decompression via unilateral approach for lumbar canal stenosis: minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine 36(5):410–415
Toyone T, Ozawa T et al (2010) Adjacent segment degeneration occured 3-times more 5-years after bilateral instrumented PLIF than unilateral instrumented PLIF. Spine
Tsai RYC, Yang RS et al (1998) Microscopic laminotomies for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 11(5):389–394
Tsuji T, Watanabe K et al (2010) Risk factors for radiological adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar fusion for spondylolisthesis. Spine
Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M et al (2009) Mini-open versus conventional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison of paraspinal muscle damage and slip reduction. Spine 34(18):1923–1928
Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M et al (2008) Union versus nonunion after posterolateral lumbar fusion: a comparison of long-term surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17(8):1107–1112
Unnanantana A (1997) Posterolateral lumbar fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: experiences of a modified technique without instrumentation. J Med Assoc Thai 80(9):570–574
Vaccaro AR, Garfin SR (1997) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis, a prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis: a critical analysis. Spine 22(4):368–369
Vaccaro AR, Lawrence JP et al (2008) The safety and efficacy of OP-1 (rhBMP-7) as a replacement for iliac crest autograft in posterolateral lumbar arthrodesis: a long-term (>4 years) pivotal study. Spine 33(26):2850–2862
Vaccaro AR, Patel T et al (2003) A pilot safety and efficacy study of OP-1 putty (rhBMP-7) as an adjunct to iliac crest autograft in posterolateral lumbar fusions. Eur Spine J 12(5):495–500
Vaccaro AR, Patel T et al (2005) A 2-year follow-up pilot study evaluating the safety and efficacy of op-1 putty (rhbmp-7) as an adjunct to iliac crest autograft in posterolateral lumbar fusions. Eur Spine J 14(7):623–629
Vaccaro AR, Patel T et al (2004) A pilot study evaluating the safety and efficacy of OP-1 Putty (rhBMP-7) as a replacement for iliac crest autograft in posterolateral lumbar arthrodesis for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 29(17):1885–1892
Vanek P, SK (2007) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and instruments. Prospective study with the minimum of 20-month follow-up. [Czech]. Ceska a Slovenska Neurologie a Neurochirurgie, 552–557
Vazquez RM, Gireesan GT (2003) Balloon-assisted endoscopic retroperitoneal gasless (BERG) technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF): the Northwestern experience. Surg Endosc 17(2):268–272
Verhoof OJ, Bron JL et al (2008) High failure rate of the interspinous distraction device (X-Stop) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17(2):188–192
Wang J, Zhou Y et al (2010) Comparison of one-level minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Eur Spine J 19(10):1780–1784
Weiner BK, Torretti J et al (2007) Microdecompression for lumbar synovial cysts: an independent assessment of long term outcomes. J Orthop Surg 2:5
Weisskopf M, Ohnsorge JAK et al (2006) Reduction of spondylolisthesis by temporary adjacent segment distraction. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 144(5):511–515
Welch WC, Cheng BC et al (2007) Clinical outcomes of the Dynesys dynamic neutralization system: 1-year preliminary results. Neurosurg Focus 22(1):E8
Winkler PA, Schroder M et al (1998) Juxta articular cysts of the lumbar facet joint: review of clinicopathologic features and report of 13 cases. Neuro-Orthopedics 22(2):77–84
Yu CH, Chang BS et al (2010) Adjacent segment degeneration after single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion—comparison between spondylolytic spondylolisthesis, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and spinal stenosis. Spine J 10(9):24S–25S
Yu CH, Lee JE et al (2011) Adjacent segment degeneration after single-level PLIF: comparison between spondylolytic spondylolisthesis, degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J 5(2):82–90
Zagra A, Giudici F et al (2009) Long-term results of pediculo-body fixation and posterolateral fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 18(Suppl 1):151–155
Zhang YF, Yang HL et al (2005) Mobilization range of the vertebral bodies after treatment of lumbar instability with titanium-coated fusion cage. Chin J of Clin Rehabil 9(10):204–205
Zhao J, Hou T et al (2003) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using one diagonal fusion cage with transpedicular screw/rod fixation. Eur Spine J 12(2):173–177
Zhao J, Wang X et al (2002) One versus two BAK fusion cages in posterior lumbar interbody fusion to L4-L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis: a randomized, controlled prospective study in 25 patients with minimum two-year follow-up. Spine 27(24):2753–2757
Zhou J, Wang B et al (2011) Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with single cage for the treatment of degenerative lumbar disease. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(9):1239–1245
Zouboulis P, Karageorgos A et al (2006) Functional outcome of surgical treatment for multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis.[Erratum appears in Acta Orthop. 2007 Dec; 78(6):862 Note: Panagiotis, Zouboulis E [corrected to Zouboulis, Panagiotis]; Athanasios, Karageorgos [corrected to Karageorgos, Athanasios]; Panagiotis, Dimakopoulos [corrected to Dimakopoulos, Panagiotis]; Minos, Tyllianakis [corrected to Tyllianakis, Minos]; Charis, Matzaroglou [corrected to Matzaroglou, Charis]; Elias, Lambiris [corrected to Lambiris, Elias]]. Acta Orthopaedica 77(4):670–676
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steiger, F., Becker, HJ., Standaert, C.J. et al. Surgery in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: indications, outcomes and complications. A systematic review. Eur Spine J 23, 945–973 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3144-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3144-3