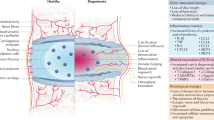
Abstract
The homeostasis of intervertebral disc (IVD) tissues is accomplished through a complex and precise coordination of a variety of substances, including cytokines, growth factors, enzymes and enzyme inhibitors. Recent biological therapeutic strategies for disc degeneration have included attempts to up-regulate the production of key matrix proteins or to down-regulate the catabolic events induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Several approaches to deliver these therapeutic biologic agents have been proposed and tested in a preclinical setting. One of the most advanced biological therapeutic approaches to regenerate or repair a degenerated disc is the injection of a recombinant growth factor. Abundant evidence for the efficacy of growth factor injection therapy for the treatment of IVD degeneration can be found in preclinical animal studies. Recent data obtained from animal studies on changes in cytokine expression following growth factor injection illustrate the great potential for patients with chronic discogenic low back pain. The first clinical trial for growth factor injection has been initiated and the results of that study may prove the usefulness of growth factor injection for treating the symptoms of patients with degenerative disc diseases. The focus of this review article is the effects of an in vivo injection of growth factors on the biological repair of the degenerated intervertebral disc in animal models. The effects of growth factor injection on the symptoms of patients with low back pain, the therapeutic target of growth factor injection and the limitations of the efficacy of growth factor therapy are also reviewed. Further quantitative studies on the effect of growth factor injection on pain generation and the long term effects on the endplate and cell survival after an injection using large animals are needed. An international academic-industrial consortium addressing these aims, such as was achieved for osteoarthritis (The Osteoarthritis Initiative), may further the development of biological therapies for degenerative disc diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuda K, Oegema TR Jr, An HS (2004) Growth factors and treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 29:2757–2769
Masuda K, An HS (2004) Growth factors and the intervertebral disc. Spine J 4:330S–340S
Ahn SH, Cho YW, Ahn MW, Jang SH, Sohn YK, Kim HS (2002) mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines in herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine 27:911–917
Burke JG, Watson RW, Conhyea D, McCormack D, Dowling FE, Walsh MG, Fitzpatrick JM (2003) Human nucleus pulposus can respond to a pro-inflammatory stimulus. Spine 28:2685–2693
Kang JD, Georgescu HI, McIntyre-Larkin L, Stefanovic-Racic M, Donaldson WF 3rd, Evans CH (1996) Herniated lumbar intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2. Spine 21:271–277
Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, Boos N (2005) Expression and distribution of tumor necrosis factor alpha in human lumbar intervertebral discs: a study in surgical specimen and autopsy controls. Spine 30:44–53; discussion 54
Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V, Myers RR (2000) 2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies: exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine 25:2975–2980
Olmarker K, Larsson K (1998) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and nucleus-pulposus-induced nerve root injury. Spine 23:2538–2544
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA (2005) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R732–R745
Seguin CA, Pilliar RM, Roughley PJ, Kandel RA (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates matrix production and catabolism in nucleus pulposus tissue. Spine 30:1940–1948
Masuda K, An HS (2006) Prevention of disc degeneration with growth factors. Eur Spine J 15(Suppl 15):422–432
Setton LA, Bonassar LJ, Masuda K (2007) Regeneration and replacement of the intervertebral disc. In: Robert L, Robert L, Joseph V (eds) Principles of tissue engineering, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 877–896
Masuda K, An H (2008) Growth factors for intervertebral disc regeneration. In: Yue J, Bertagnoli R, McAfee P, An H (eds) Motion preservation surgery of the spine—advanced techniques and controversies. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Masuda K, Imai Y, Okuma M, Muehleman C, Nakagawa K, Akeda K, Thonar E, Andersson G, An HS (2006) Osteogenic protein-1 injection into a degenerated disc induces the restoration of disc height and structural changes in the rabbit anular puncture model. Spine 31:742–754
Thompson JP, Oegema TJ, Bradford DS (1991) Stimulation of mature canine intervertebral disc by growth factors. Spine 16:253–260
Gruber HE, Fisher EC Jr, Desai B, Stasky AA, Hoelscher G, Hanley EN Jr (1997) Human intervertebral disc cells from the annulus: three-dimensional culture in agarose or alginate and responsiveness to TGF-beta1. Exp Cell Res 235:13–21
Osada R, Ohshima H, Ishihara H, Yudoh K, Sakai K, Matsui H, Tsuji H (1996) Autocrine/paracrine mechanism of insulin-like growth factor-1 secretion, and the effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 on proteoglycan synthesis in bovine intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res 14:690–699
Gruber HE, Norton HJ, Hanley EN Jr (2000) Anti-apoptotic effects of IGF-1 and PDGF on human intervertebral disc cells in vitro. Spine 25:2153–2157
Masuda K, Takegami K, An H, Kumano F, Chiba K, Andersson GB, Schmid T, Thonar E (2003) Recombinant osteogenic protein-1 upregulates extracellular matrix metabolism by rabbit annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells cultured in alginate beads. J Orthop Res 21:922–930
Yoon TS, Su Kim K, Li J, Soo Park J, Akamaru T, Elmer WA, Hutton WC (2003) The effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on rat intervertebral disc cells in vitro. Spine 28:1773–1780
Imai Y, Miyamoto K, An HS, Thonar EJ, Andersson GB, Masuda K (2007) Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 upregulates proteoglycan metabolism of human anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells. Spine 32:1303–1309; discussion 1310
Takegami K, Thonar EJ, An HS, Kamada H, Masuda K (2002) Osteogenic protein-1 enhances matrix replenishment by intervertebral disc cells previously exposed to interleukin-1. Spine 27:1318–1325
Takegami K, An HS, Kumano F, Chiba K, Thonar EJ, Singh K, Masuda K (2005) Osteogenic protein-1 is most effective in stimulating nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells to repair their matrix after chondroitinase ABC-induced in vitro chemonucleolysis. Spine J 5:231–238
Kim DJ, Moon SH, Kim H, Kwon UH, Park MS, Han KJ, Hahn SB, Lee HM (2003) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 facilitates expression of chondrogenic, not osteogenic, phenotype of human intervertebral disc cells. Spine 28:2679–2684
Gilbertson L, Ahn SH, Teng PN, Studer RK, Niyibizi C, Kang JD (2008) The effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2, recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-12, and adenoviral bone morphogenetic protein-12 on matrix synthesis in human annulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus cells. Spine J 8:449–456. doi:S1529-9430(06)01068-0[pii]10.1016/j.spinee.2006.11.006
Li X, Leo BM, Beck G, Balian G, Anderson GD (2004) Collagen and proteoglycan abnormalities in the GDF-5-deficient mice and molecular changes when treating disk cells with recombinant growth factor. Spine 29:2229–2234
Chujo T, An HS, Akeda K, Miyamoto K, Muehleman C, Attawia M, Andersson G, Masuda K (2006) Effects of growth differentiation factor-5 on the intervertebral disc—in vitro bovine study and in vivo rabbit disc degeneration model study. Spine 31:2909–2917
Wehling P (2002) Antiapoptotic and antidegenerative effect of an autologous IL-1ra/IGF-1/PDGF combination on human intervertebral disc cells in vivo. In: Proceeding of the international society for the study of the lumbar spine, 29th Annual Meeting,Cleveland, OH, p 24
Akeda K, An HS, Pichika R, Attawia M, Thonar EJ, Lenz ME, Uchida A, Masuda K (2006) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) stimulates the extracellular matrix metabolism of porcine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus cells cultured in alginate beads. Spine 31:959–966
Chen WH, Lo WC, Lee JJ, Su CH, Lin CT, Liu HY, Lin TW, Lin WC, Huang TY, Deng WP (2006) Tissue-engineered intervertebral disc and chondrogenesis using human nucleus pulposus regulated through TGF-beta1 in platelet-rich plasma. J Cell Physiol 209:744–754. doi:10.1002/jcp.20765
Walsh AJ, Bradford DS, Lotz JC (2004) In vivo growth factor treatment of degenerated intervertebral discs. Spine 29:156–163
An HS, Takegami K, Kamada H, Nguyen CM, Thonar EJ, Singh K, Andersson GB, Masuda K (2005) Intradiscal administration of osteogenic protein-1 increases intervertebral disc height and proteoglycan content in the nucleus pulposus in normal adolescent rabbits. Spine 30:25–31
Miyamoto K, Masuda K, Kim JG, Inoue N, Akeda K, Andersson GB, An HS (2006) Intradiscal injections of osteogenic protein-1 restore the viscoelastic properties of degenerated intervertebral discs. Spine J 6:692–703
Eurell JA, Brown MD, Ramos M (1990) The effects of chondroitinase ABC on the rabbit intervertebral disc. A roentgenographic and histologic study. Clin Orthop 256:238–243
Fry TR, Eurell JC, Johnson AL, Brown MD, Losonsky JM, Schaeffer DJ (1991) Radiographic and histologic effects of chondroitinase ABC on normal canine lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine 16:816–819
Henderson N, Stanescu V, Cauchoix J (1991) Nucleolysis of the rabbit intervertebral disc using chondroitinase ABC. Spine 16:203–208
Kato F, Mimatsu K, Kawakami N, Iwata H, Miura T (1992) Serial changes observed by magnetic resonance imaging in the intervertebral disc after chemonucleolysis. A consideration of the mechanism of chemonucleolysis. Spine 17:934–939
Ando T, Kato F, Mimatsu K, Iwata H (1995) Effects of chondroitinase ABC on degenerative intervertebral discs. Clin Orthop 318:214–221
Sugimura T, Kato F, Mimatsu K, Takenaka O, Iwata H (1996) Experimental chemonucleolysis with chondroitinase ABC in monkeys. Spine 21:161–165
Takahashi T, Kurihara H, Nakajima S, Kato T, Matsuzaka S, Sekiguchi T, Onaya M, Miyauchi S, Mizuno S, Horie K, Fujita Y, Hirose T (1996) Chemonucleolytic effects of chondroitinase ABC on normal rabbit intervertebral discs. Course of action up to 10 days postinjection and minimum effective dose. Spine 21:2405–2411
Yamada K, Tanabe S, Ueno H, Oinuma A, Takahashi T, Miyauchi S, Shigeno S, Hirose T, Miyahara K, Sato M (2001) Investigation of the short-term effect of chemonucleolysis with chondroitinase ABC. J Vet Med Sci 63:521–525
Lu DS, Shono Y, Oda I, Abumi K, Kaneda K (1997) Effects of chondroitinase ABC and chymopapain on spinal motion segment biomechanics. An in vivo biomechanical, radiologic, and histologic canine study. Spine 22:1828–1834
Norcross JP, Lester GE, Weinhold P, Dahners LE (2003) An in vivo model of degenerative disc disease. J Orthop Res 21:183–188
Boxberger JI, Auerbach JD, Sen S, Elliott DM (2008) An in vivo model of reduced nucleus pulposus glycosaminoglycan content in the rat lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine 33:146–154. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816054f800007632-200801150-00005[pii]
Hoogendoorn RJ, Helder MN, Kroeze RJ, Bank RA, Smit TH, Wuisman PI (2008) Reproducible long-term disc degeneration in a large animal model. Spine 33:949–954. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816c90f000007632-200804200-00004[pii]
Hoogendoorn RJ, Wuisman PI, Smit TH, Everts VE, Helder MN (2007) Experimental intervertebral disc degeneration induced by chondroitinase ABC in the goat. Spine 32:1816–1825. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31811ebac500007632-200708010-00004[pii]
Imai Y, Okuma M, An H, Nakagawa K, Yamada M, Thonar E, Muehleman C, Masuda K (2007) Restoration of disc height loss by recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 injection into intervertebral discs undergoing degeneration induced by an intradiscal injection of chondroitinase ABC. Spine 32:1197–1205
Kim KW, Lim TH, Kim JG, Jeong ST, Masuda K, An HS (2003) The origin of chondrocytes in the nucleus pulposus and histologic findings associated with the transition of a notochordal nucleus pulposus to a fibrocartilaginous nucleus pulposus in intact rabbit intervertebral discs. Spine 28:982–990
Scott NA, Harris PF, Bagnall KM (1980) A morphological and histological study of the postnatal development of intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine of the rabbit. J Anat 130:75–81
Yoon S, Kim K, Li J, Boden S, Hutton W (2005) Age related intervertebral disc degeneration in the rabbit. Trans Orthop Res Soc:888
Chujo T, An H, Asanuma K, Takatori R, Inoue N, Attawia M, Lee C, Muehleman C, Masuda K (2007) A single injection of recombinant human GDF-5 effectively restores mature rabbit of intervertebral discs degenerated by anular puncture. Trans Orthop Res Soc 32:267
Larson JW 3rd, Levicoff EA, Gilbertson LG, Kang JD (2006) Biologic modification of animal models of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 2):83–87
Reddi AH (2000) Morphogenetic messages are in the extracellular matrix: biotechnology from bench to bedside. Biochem Soc Trans 28:345–349
Huang KY, Yan JJ, Hsieh CC, Chang MS, Lin RM (2007) The in vivo biological effects of intradiscal recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on the injured intervertebral disc: an animal experiment. Spine 32:1174–1180
Nagae M, Ikeda T, Mikami Y, Hase H, Ozawa H, Matsuda K, Sakamoto H, Tabata Y, Kawata M, Kubo T (2007) Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng 13:147–158
Kawakami M, Matsumoto T, Hashizume H, Kuribayashi K, Chubinskaya S, Yoshida M (2005) Osteogenic protein-1 (osteogenic protein-1/bone morphogenetic protein-7) inhibits degeneration and pain-related behavior induced by chronically compressed nucleus pulposus in the rat. Spine 30:1933–1939
Chubinskaya S, Kawakami M, Rappoport L, Matsumoto T, Migita N, Rueger DC (2007) Anti-catabolic effect of OP-1 in chronically compressed intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res 25:517–530
Pichika R, An H, Asanuma K, Tonomura H, Lenz M, Masuda K (2008) Intradiscal injection of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-7 significantly suppressed the expression of cytokines and catabolic enzymes in the rabbit anular puncture model. Ortho Res Soc Trans 33:1389
Pichika R, An H, Miyamoto K, Chujo T, Abe Y, Lenz M, Masuda K (2007) Suppressive effect of bone morphogenetic protein-7 on interleukin-1β mediated gene expression of cytokines and catabolic enzymes in human intervertebral disc cells. Ortho Res Soc Trans 32:243
Gruber HE, Hanley EN Jr (1998) Analysis of aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Comparison of surgical specimens with normal controls. Spine 23:751–757
Nishimura K, Mochida J (1998) Percutaneous reinsertion of the nucleus pulposus. An experimental study. Spine 23:1531–1538
Okuma M, Mochida J, Nishimura K, Sakabe K, Seiki K (2000) Reinsertion of stimulated nucleus pulposus cells retards intervertebral disc degeneration: an in vitro and in vivo experimental study. J Orthop Res 18:988–997
Anderson DG, Albert TJ, Fraser JK, Risbud M, Wuisman P, Meisel HJ, Tannoury C, Shapiro I, Vaccaro AR (2005) Cellular therapy for disc degeneration. Spine 30:S14–S19
Gruber HE, Johnson TL, Leslie K, Ingram JA, Martin D, Hoelscher G, Banks D, Phieffer L, Coldham G, Hanley EN Jr (2002) Autologous intervertebral disc cell implantation: a model using Psammomys obesus, the sand rat. Spine 27:1626–1633
Ganey T, Libera J, Moos V, Alasevic O, Fritsch KG, Meisel HJ, Hutton WC (2003) Disc chondrocyte transplantation in a canine model: a treatment for degenerated or damaged intervertebral disc. Spine 28:2609–2620
Urban JP, Smith S, Fairbank JC (2004) Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine 29:2700–2709
Rajasekaran S, Venkatadass K, Naresh Babu J, Ganesh K, Shetty AP (2008) Pharmacological enhancement of disc diffusion and differentiation of healthy, ageing and degenerated discs: results from in-vivo serial post-contrast MRI studies in 365 human lumbar discs. Eur Spine J 17:626–643
Rajasekaran S, Babu JN, Arun R, Armstrong BR, Shetty AP, Murugan S (2004) ISSLS prize winner: A study of diffusion in human lumbar discs: a serial magnetic resonance imaging study documenting the influence of the endplate on diffusion in normal and degenerate discs. Spine 29:2654–2667
Walsh AL, Lotz J, Bradford D (2002) Single and multiple injections of GDF-5, IGF-1, or TGF beta into degenerated intervertebral discs. Ortho Res Soc Trans 27
Imai Y, An H, Thonar E, Muehleman C, Okuma M, Matsumoto T, Andersson G, Masuda K (2003) Co-injected recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 minimizes chondroitinase ABC-induced intervertebral disc degeneration: an in vivo study using a rabbit model. Trans Orthop Res Soc 1143
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuda, K. Biological repair of the degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors. Eur Spine J 17 (Suppl 4), 441–451 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0749-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0749-z