Abstract
Purpose
Dexmedetomidine, a selective α2-adrenoceptor agonist, has analgesic and sedative effects. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of small, single-dose intravenous dexmedetomidine administration after hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia.
Methods
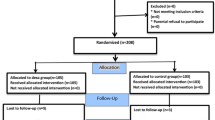
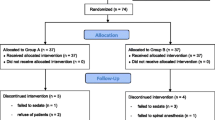
Sixty adult patients classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status 1 or 2 and scheduled for lower extremity surgery under spinal anesthesia were studied. Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups and administered hyperbaric intrathecal bupivacaine 12 mg. 5 min after spinal anesthesia, patients in groups 1, 2, and 3 received normal saline 10 ml, dexmedetomidine 0.25 μg/kg, and dexmedetomidine 0.5 μg/kg, respectively, over 10-min intravenous administration. The onset time, maximum block level, two-dermatome sensory regression time, duration of motor and sensory anesthesia, and side effects were assessed.
Results
The two-dermatome sensory regression time was significantly increased in groups 2 and 3. The duration of motor and sensory anesthesia was significantly increased in group 3. Onset time, maximum block level, level of sedation, and incidence of hypotension and treatment-needed bradycardia were no different among the groups.
Conclusion
Single-dose intravenous dexmedetomidine 0.25–0.5 μg/kg, administered 5 min after intrathecal injection of hyperbaric bupivacaine, improved the duration of spinal anesthesia without significant side effects. This method may be useful for increasing the duration of spinal anesthesia, even after intrathecal injection of local anesthetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson JO, Grecu L, Lawson NW. Antonomic nervous system. In: Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK, Cahalan MK, Stock MC, editors. Clinical anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009. p. 355.
Basar N, Akpinar S, Doganci N. Buyukkocak U, Kaymak C, Sert O, Apan A. The effects of preanesthetic, single-dose dexmedetomidine on induction, hemodynamic, and cardiovascular parameters. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:431–6.
Kanazi GE, Aouad MT, Jabbour-Khoury SI, Al Jazzar MD, Alameddine MM, Al-Yaman R, Bulbul M, Baraka AS. Effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine or clonidine on the characteristics of bupivacaine spinal block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006;50:222–7.
Kaya FN, Yavascaoglu B, Turker G, Yildirim A, Gurbet A, Mogol EB, Ozcan B. Intravenous dexmedetomidine, but not midazolam, prolongs bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. Can J Anaesth. 2010;57:39–45.
Al-Mustafa MM, Badran IZ, Abu-Ali HM, Al-Barazangi BA, Massad IM, Al-Ghanem SM. Intravenous dexmedetomidine prolongs bupivacaine spinal analgesia. Middle East J Anesthesiol. 2009;20:225–31.
Elcicek K, Tekin M, Kati I. The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on spinal hyperbaric ropivacaine anesthesia. J Anesth. 2010;24:544–8.
Grant SA, Breslin DS, Macleod DB, Gleason D, Martin G. Dexmedetomidine infusion for sedation during fiberoptic intubation: a report of three cases. J Clin Anesth. 2004;16:124–6.
Bloor BC, Ward DS, Belleville JP, Maze M. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans. II. Hemodynamic changes. Anesthesiology. 1992;77:1134–42.
Chernik DA, Gilling D, Laine H, Hendler J, Siler JM, Davidson AB, Schwam EM, Siegel JL. Validity and reliability of the Observer’s Assessment of Alertness/Sedation scale: study with intravenous midazolam. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10(244–51):126.
Kaabachi O, Zarghouni A, Ouezini R, Abdelaziz AB, Chattaoui O, Kokki H. Clonidine 1 microg/kg is a safe and effective adjuvant to plain bupivacaine in spinal anesthesia in adolescents. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:516–9.
Coskuner I, Tekin M, Kati I, Yagmur C, Elcicek K. Effects of dexmedetomidine on the duration of anaesthesia and wakefulness in bupivacaine epidural block. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007;24:535–40.
Kallio A, Scheinin M, Koulu M, Ponkilainen R, Ruskoaho H, Viinamäki O, Scheinin H. Effects of dexmedetomidine, a selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, on hemodynamic control mechanisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989;46:33–42.
Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:382–94.
Jaakola ML, Salonen M, Lehtinen R, Scheinin H. The analgesia action of dexmedetomidine -a novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist-in healthy volunteer. Pain. 1991;46:281–5.
Jorm CM, Stamford JA. Actions of the hypnotic anaesthetic, dexmedetomidine, on noradrenaline release and cell firing in rat locus coeruleus slices. Br J Anaesth. 1993;71:447–9.
Calasans-Maia JA, Zapata-Sudo G, Sudo RT. Dexmedetomidine prolongs spinal anaesthesia induced by levobupivacaine 0.5% in guinea-pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57:1415–20.
Strahlendorf JC, Strahlendorf HK, Kingsley RE, Gintautas J, Barnes CD. Facilitation of lumbar monosynaptic reflexes by locus coeruleus stimulation. Neuropharmacology. 1980;19:225–300.
Brummett CM, Padda AK, Amodeo FS, Welch KB, Lydic R. Perineural dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine causes a dose-dependent increase in the duration of thermal antinociception in sciatic nerve block in rat. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:1111–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, S.H., Lee, S.K., Lim, K.J. et al. The effects of single-dose intravenous dexmedetomidine on hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. J Anesth 27, 380–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1541-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1541-0