Abstract
Background
Pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) plus ribavirin (RBV) therapy is the current standard of care for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Determining precisely the risk of serious adverse events (SAEs) and mortality from a single study is rather difficult because of the infrequency of such events. The aim of this systematic review was to assess the rates of SAEs and the mortality of PEG-IFN/RBV therapy in a pooled large sample, and to assess the relationship between SAEs and mortality rates and therapeutic characteristics.
Methods
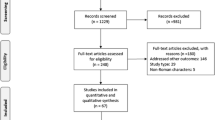
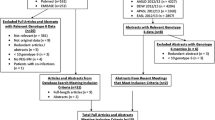
A literature search was conducted using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library to identify randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of PEG-IFN/RBV therapy. We calculated the crude mortality and SAE rates with 95 % confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
Eighty studies with 153 treatment arms that included 27569 patients were enrolled (14401 patients treated with Peg-IFN alpha-2a/RBV and 13168 with Peg-IFN alpha-2b/RBV). All-cause and treatment-related deaths were observed in 50 (0.18 %; 95 % confidence interval [CI] 0.13–0.24 %) and sixteen (0.058 %; 95 % CI 0.033–0.094 %) patients, respectively. The crude SAE rate was 7.08 % (95 % CI 6.75–7.41 %). Subgroup analysis revealed higher SAE rates in patients receiving PEG-IFN alpha-2a than in those with PEG-IFN alpha-2b (7.45 vs. 6.74 %), and higher SAE rates with higher doses than with the lower doses in PEG-IFN-2a and 2b (11.94 vs. 6.99 %, 7.10 vs. 5.05 %, respectively), and with extended duration (>48 weeks) than with standard duration (48 weeks) (15.5 vs. 6.67 %) in PEG-IFN alpha-2a.
Conclusion
The mortality rate during PEG-IFN/RBV therapy was acceptably low, but the rate of SAEs was not negligible in a treatment for a benign disease, and the rate was affected by treatment regimens.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- PEG-IFN:
-
Pegylated interferon
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- RBV:
-
Ribavirin
- SAE:
-
Serious adverse event
- SVR:
-
Sustained virological response
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, Hutin YJ, Bell BP. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J Hepatol. 2006;45(4):529–38.
Yvan H, Mary EK, Gregory JD, Joseph FP, Gregory LA, Geoffrey D, et al. Global burden of disease (GBD) for hepatitis C. J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;44(1):20–9.
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358(9286):958–65.
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL Jr, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(13):975–82.
Bruno S, Camma C, Di Marco V, Rumi M, Vinci M, Camozzi M, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for naive patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2004;41(3):474–81.
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, et al. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(5):346–55.
Mangia A, Santoro R, Minerva N, Ricci GL, Carretta V, Persico M, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b and ribavirin for 12 vs. 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(25):2609–17.
Brok J, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Meta-analysis: ribavirin plus interferon vs. interferon monotherapy for chronic hepatitic C—an updated Cochrane review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(7):840–50.
Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Moriyama M, Arakawa Y, Ide T, Sata M, et al. Interferon therapy reduces the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma: national surveillance program of cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C in Japan. IHIT Study Group. Inhibition of Hepatocarcinogenesis by Interferon Therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131(3):174–81.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
World Health Organization. Available at: http://apps.who.int/ghodata/?vid=720 (2011). Accessed 24 Oct 2011.
Bruno R, Sacchi P, Ciappina V, Zochetti C, Patruno S, Maiocchi L, et al. Viral dynamics and pharmacokinetics of peginterferon alpha-2a and peginterferon alpha-2b in naive patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized, controlled study. Antivir Ther. 2004;9(4):491–7.
Awad T, Thorlund K, Hauser G, Stimac D, Mabrouk M, Gluud C. Peginterferon alpha-2a is associated with higher sustained virological response than peginterferon alpha-2b in chronic hepatitis C: systematic review of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2010;51(4):1176–84.
Ascione A, De Luca M, Tartaglione MT, Lampasi F, Di Costanzo GG, Lanza AG, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin is more effective than peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for treating chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(1):116–22.
McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, Muir AJ, Galler GW, McCone J, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b or alpha-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6):580–93.
Rumi MG, Aghemo A, Prati GM, D’Ambrosio R, Donato MF, Soffredini R, et al. Randomized study of peginterferon-alpha2a plus ribavirin vs peginterferon-alpha2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(1):108–15.
Scotto G, Fazio V, Fornabaio C, Tartaglia A, Di Tullio R, Saracino A, et al. Peg-interferon alpha-2a versus Peg-interferon alpha-2b in nonresponders with HCV active chronic hepatitis: a pilot study. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008;28(10):623–9.
Yenice N, Mehtap O, Gumrah M, Arican N. The efficacy of pegylated interferon alpha 2a or 2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2006;17(2):94–8.
Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Ge D, Gumbs CE, Urban TJ, Shianna KV, et al. ITPA gene variants protect against anaemia in patients treated for chronic hepatitis C. Nature. 2010;464(7287):405–8.
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ, et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature. 2009;461(7262):399–401.
Hung CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Wang JH, Chen CH, Hu TH, et al. Anemia associated with antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C: incidence, risk factors, and impact on treatment response. Liver Int. 2006;26(9):1079–86.
Iwasaki Y, Ikeda H, Araki Y, Osawa T, Kita K, Ando M, et al. Limitation of combination therapy of interferon and ribavirin for older patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2006;43(1):54–63.
Oze T, Hiramatsu N, Yakushijin T, Mochizuki K, Oshita M, Hagiwara H, et al. Indications and limitations for aged patients with chronic hepatitis C in pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy. J Hepatol. 2011;54(4):604–11.
McHutchison JG, Everson GT, Gordon SC, Jacobson IM, Sulkowski M, Kauffman R, et al. Telaprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(18):1827–38.
Poordad F, McCone J Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S, Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, et al. Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(13):1195–206.
Abergel A, Hezode C, Leroy V, Barange K, Bronowicki JP, Tran A, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for treatment of chronic hepatitis C with severe fibrosis: a multicentre randomized controlled trial comparing two doses of peginterferon alpha-2b. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13(12):811–20.
Alfaleh FZ, Hadad Q, Khuroo MS, Aljumah A, Algamedi A, Alashgar H, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C in Saudi patients commonly infected with genotype 4. Liver Int. 2004;24(6):568–74.
Andriulli A, Cursaro C, Cozzolongo R, Iacobellis A, Valvano MR, Mangia A, et al. Early discontinuation of ribavirin in HCV-2 and HCV-3 patients responding to Peg-interferon alpha-2a and ribavirin. J Viral Hepat. 2009;16(1):28–35.
Angelico M, Koehler-Horst B, Piccolo P, Angelico F, Gentile S, Francioso S, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin versus peginterferon alpha-2a monotherapy in early virological responders and peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin versus peginterferon alpha-2a, ribavirin and amantadine triple therapy in early virological nonresponders: the SMIEC II trial in naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20(7):680–7.
Benhamou Y, Afdhal NH, Nelson DR, Shiffman ML, Halliman DG, Heise J, et al. A phase III study of the safety and efficacy of viramidine versus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C: ViSER1 results. Hepatology. 2009;50(3):717–26.
Berg C, Goncales FL Jr, Bernstein DE, Sette H Jr, Rasenack J, Diago M, et al. Re-treatment of chronic hepatitis C patients after relapse: efficacy of peginterferon-alpha-2a (40 kDa) and ribavirin. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13(7):435–40.
Berg T, von Wagner M, Nasser S, Sarrazin C, Heintges T, Gerlach T, et al. Extended treatment duration for hepatitis C virus type 1: comparing 48 versus 72 weeks of peginterferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(4):1086–97.
Berg T, Weich V, Teuber G, Klinker H, Moller B, Rasenack J, et al. Individualized treatment strategy according to early viral kinetics in hepatitis C virus type 1-infected patients. Hepatology. 2009;50(2):369–77.
Bosques-Padilla F, Trejo-Estrada R, Campollo-Rivas O, Cortez-Hernandez C, Dehesa-Violante M, Maldonado-Garza H, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin for treating chronic hepatitis C virus infection: analysis of Mexican patients included in a multicenter international clinical trial. Ann Hepatol. 2003;2(3):135–9.
Brady DE, Torres DM, An JW, Ward JA, Lawitz E,Harrison SA. Induction pegylated interferon alpha-2b in combination with ribavirin in patients with genotypes 1 and 4 chronic hepatitis C: a prospective, randomized, multicenter, open-label study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8(1):66–71e1.
Brandao C, Barone A, Carrilho F, Silva A, Patelli M, Caramori C, et al. The results of a randomized trial looking at 24 weeks vs. 48 weeks of treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kDa) and ribavirin combination therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13(8):552–9.
Bressler B, Wang K, Grippo JF, Heathcote EJ. Pharmacokinetics and response of obese patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with different doses of PEG-IFN alpha-2a (40 kD) (PEGASYS). Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;67(3):280–7.
Bronowicki JP, Ouzan D, Asselah T, Desmorat H, Zarski JP, Foucher J, et al. Effect of ribavirin in genotype 1 patients with hepatitis C responding to pegylated interferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin. Gastroenterology. 2006;131(4):1040–8.
Carr C, Hollinger FB, Yoffe B, Wakil A, Phillips J, Bzowej N, et al. Efficacy of interferon alpha-2b induction therapy before retreatment for chronic hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2007;27(8):1111–8.
Ciancio A, Picciotto A, Giordanino C, Smedile A, Tabone M, Manca A, et al. A randomized trial of pegylated-interferon-alpha2a plus ribavirin with or without amantadine in the re-treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C not responding to standard interferon and ribavirin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(7):1079–86.
Dalgard O, Bjoro K, Ring-Larsen H, Bjornsson E, Holberg-Petersen M, Skovlund E, et al. Pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin for 14 versus 24 weeks in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3 and rapid virological response. Hepatology. 2008;47(1):35–42.
Diago M, Crespo J, Olveira A, Perez R, Barcena R, Sanchez-Tapias JM, et al. Clinical trial: pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of re-treatment with fixed-dose induction of peginterferon alpha-2a in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 true non-responder patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26(8):1131–8.
Ferenci P, Formann E, Laferl H, Gschwantler M, Hackl F, Brunner H, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kD) plus ribavirin with or without amantadine in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. J Hepatol. 2006;44(2):275–82.
Ferenci P, Brunner H, Laferl H, Scherzer TM, Maieron A, Strasser M, et al. A randomized, prospective trial of ribavirin 400 mg/day versus 800 mg/day in combination with peginterferon alpha-2a in hepatitis C virus genotypes 2 and 3. Hepatology. 2008;47(6):1816–23.
Ferenci P, Laferl H, Scherzer TM, Maieron A, Hofer H, Stauber R, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a/ribavirin for 48 or 72 weeks in hepatitis C genotypes 1 and 4 patients with slow virologic response. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(2):503–12e1.
Fried MW, Jensen DM, Rodriguez-Torres M, Nyberg LM, Di Bisceglie AM, Morgan TR, et al. Improved outcomes in patients with hepatitis C with difficult-to-treat characteristics: randomized study of higher doses of peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin. Hepatology. 2008;48(4):1033–43.
Gish RG, Arora S, Rajender Reddy K, Nelson DR, O’Brien C, Xu Y, et al. Virological response and safety outcomes in therapy-naive patients treated for chronic hepatitis C with taribavirin or ribavirin in combination with pegylated interferon alpha-2a: a randomized, phase 2 study. J Hepatol. 2007;47(1):51–9.
Glue P, Rouzier-Panis R, Raffanel C, Sabo R, Gupta SK, Salfi M, et al. A dose-ranging study of pegylated interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. The Hepatitis C Intervention Therapy Group. Hepatology. 2000;32(3):647–53.
Hasan F, Al-Khaldi J, Asker H, Al-Ajmi M, Owayed S, Varghese R, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin with or without amantadine [correction of amantidine] for the treatment of non-responders to standard interferon and ribavirin. Antivir Ther. 2004;9(4):499–503.
Helbling B, Jochum W, Stamenic I, Knopfli M, Cerny A, Borovicka J, et al. HCV-related advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis: randomized controlled trial of pegylated interferon alpha-2a and ribavirin. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13(11):762–9.
Herrine SK, Brown RS Jr, Bernstein DE, Ondovik MS, Lentz E, Te H. Peginterferon alpha-2a combination therapies in chronic hepatitis C patients who relapsed after or had a viral breakthrough on therapy with standard interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin: a pilot study of efficacy and safety. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50(4):719–26.
Hezode C, Forestier N, Dusheiko G, Ferenci P, Pol S, Goeser T, et al. Telaprevir and peginterferon with or without ribavirin for chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(18):1839–50.
Ide T, Hino T, Ogata K, Miyajima I, Kuwahara R, Kuhara K, et al. A randomized study of extended treatment with peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin based on time to HCV RNA negative-status in patients with genotype 1b chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(1):70–5.
Jacobson IM, Gonzalez SA, Ahmed F, Lebovics E, Min AD, Bodenheimer HC Jr, et al. A randomized trial of pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in the retreatment of chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(11):2453–62.
Jacobson IM, Brown RS Jr, Freilich B, Afdhal N, Kwo PY, Santoro J, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b and weight-based or flat-dose ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients: a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2007;46(4):971–81.
Jensen DM, Marcellin P, Freilich B, Andreone P, Di Bisceglie A, Brandao-Mello CE, et al. Re-treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C who do not respond to peginterferon-alpha2b: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(8):528–40.
Kamal SM, El Tawil AA, Nakano T, He Q, Rasenack J, Hakam SA, et al. Peginterferon {alpha}-2b and ribavirin therapy in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4: impact of treatment duration and viral kinetics on sustained virological response. Gut. 2005;54(6):858–66.
Kamal SM, El Kamary SS, Shardell MD, Hashem M, Ahmed IN, Muhammadi M, et al. Pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in patients with genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C: the role of rapid and early virologic response. Hepatology. 2007;46(6):1732–40.
Kawaoka T, Kawakami Y, Tsuji K, Ito H, Kitamoto M, Aimitsu S, et al. Dose comparison study of pegylated interferon-alpha-2b plus ribavirin in naive Japanese patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 2: a randomized clinical trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(3):366–71.
Khattab M, Emad M, Abdelaleem A, Eslam M, Atef R, Shaker Y, et al. Pioglitazone improves virological response to peginterferon alpha-2b/ribavirin combination therapy in hepatitis C genotype 4 patients with insulin resistance. Liver Int. 2010;30(3):447–54.
Kuboki M, Iino S, Okuno T, Omata M, Kiyosawa K, Kumada H, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kD) plus ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in Japanese patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22(5):645–52.
Lagging M, Langeland N, Pedersen C, Farkkila M, Buhl MR, Morch K, et al. Randomized comparison of 12 or 24 weeks of peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 2/3 infection. Hepatology. 2008;47(6):1837–45.
Langlet P, D’Heygere F, Henrion J, Adler M, Delwaide J, Van Vlierberghe H, et al. Clinical trial: a randomized trial of pegylated-interferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin with or without amantadine in treatment-naive or relapsing chronic hepatitis C patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;30(4):352–63.
Lee SD, Yu ML, Cheng PN, Lai MY, Chao YC, Hwang SJ, et al. Comparison of a 6-month course peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin and interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in treating Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C in Taiwan. J Viral Hepat. 2005;12(3):283–91.
Liu CH, Liu CJ, Lin CL, Liang CC, Hsu SJ, Yang SS, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin for treatment-naive Asian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(10):1260–9.
Lodato F, Azzaroli F, Brillanti S, Colecchia A, Tame MR, Montagnani M, et al. Higher doses of peginterferon alpha-2b administered twice weekly improve sustained virological response in difficult-to-treat patients with chronic hepatitis C: results of a pilot randomized study. J Viral Hepat. 2005;12(5):536–42.
Marcellin P, Horsmans Y, Nevens F, Grange JD, Bronowicki JP, Vetter D, et al. Phase 2 study of the combination of merimepodib with peginterferon-alpha2b, and ribavirin in nonresponders to previous therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2007;47(4):476–83.
Marcellin P, Gish RG, Gitlin N, Heise J, Halliman DG, Chun E, et al. Safety and efficacy of viramidine versus ribavirin in ViSER2: randomized, double-blind study in therapy-naive hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol. 2010;52(1):32–8.
McHutchison JG, Manns MP, Muir AJ, Terrault NA, Jacobson IM, Afdhal NH, et al. Telaprevir for previously treated chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(14):1292–303.
Mecenate F, Pellicelli AM, Barbaro G, Romano M, Barlattani A, Mazzoni E, et al. Short versus standard treatment with pegylated interferon alpha-2A plus ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3: the cleo trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:21.
Mendez-Navarro J, Chirino RA, Corey KE, Gorospe EC, Zheng H, Moran S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of double versus triple therapy with amantadine for genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C in Latino patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55(9):2629–35.
Meyer-Wyss B, Rich P, Egger H, Helbling B, Mullhaupt B, Rammert C, et al. Comparison of two PEG-interferon alpha-2b doses (1.0 or 1.5 μg/kg) combined with ribavirin in interferon-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C and up to moderate fibrosis. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13(7):457–65.
Napoli N, Giannelli G, Antonaci A, Antonaci S. The use of different peg-interferon alpha-2b regimens plus ribavirin in HCV-1b-infected patients after rapid virological response does not affect the achievement of sustained virological response. J Viral Hepat. 2008;15(4):300–4.
Pearlman BL, Ehleben C, Saifee S. Treatment extension to 72 weeks of peginterferon and ribavirin in hepatitis c genotype 1-infected slow responders. Hepatology. 2007;46(6):1688–94.
Roberts SK, Weltman MD, Crawford DH, McCaughan GW, Sievert W, Cheng WS, et al. Impact of high-dose peginterferon alpha-2A on virological response rates in patients with hepatitis C genotype 1: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2009;50(4):1045–55.
Roffi L, Colloredo G, Pioltelli P, Bellati G, Pozzpi M, Parravicini P, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha2b plus ribavirin: an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment regimen for patients with hepatitis C virus related histologically proven cirrhosis. Antivir Ther. 2008;13(5):663–73.
Rossignol JF, Elfert A, El-Gohary Y, Keeffe EB. Improved virologic response in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4 treated with nitazoxanide, peginterferon, and ribavirin. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):856–62.
Rustgi VK, Lee WM, Lawitz E, Gordon SC, Afdhal N, Poordad F, et al. Merimepodib, pegylated interferon, and ribavirin in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C pegylated interferon and ribavirin nonresponders. Hepatology. 2009;50(6):1719–26.
Sanchez-Tapias JM, Diago M, Escartin P, Enriquez J, Romero-Gomez M, Barcena R, et al. Peginterferon-alpha2a plus ribavirin for 48 versus 72 weeks in patients with detectable hepatitis C virus RNA at week 4 of treatment. Gastroenterology. 2006;131(2):451–60.
Shiffman ML, Salvatore J, Hubbard S, Price A, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 with peginterferon, ribavirin, and epoetin alpha. Hepatology. 2007;46(2):371–9.
Shiffman ML, Suter F, Bacon BR, Nelson D, Harley H, Sola R, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin for 16 or 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(2):124–34.
Shiffman ML, Ghany MG, Morgan TR, Wright EC, Everson GT, Lindsay KL, et al. Impact of reducing peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin dose during retreatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(1):103–12.
Sjogren MH, Sjogren R Jr, Lyons MF, Ryan M, Santoro J, Smith C, et al. Antiviral response of HCV genotype 1 to consensus interferon and ribavirin versus pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52(6):1540–7.
Sood A, Midha V, Hissar S, Kumar M, Suneetha PV, Bansal M, et al. Comparison of low-dose pegylated interferon versus standard high-dose pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C with genotype 3: an Indian experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(2):203–7.
Tang KH, Herrmann E, Pachiadakis I, Paulon E, Tatman N, Zeuzem S, et al. Clinical trial: individualized treatment duration for hepatitis C virus genotype 1 with peginterferon-alpha 2a plus ribavirin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(9):810–9.
Toyoda H, Kumada T, Kiriyama S, Sone Y, Tanikawa M, Hisanaga Y, et al. Eight-week regimen of antiviral combination therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin for patients with chronic hepatitis C with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 and a rapid virological response. Liver Int. 2009;29(1):120–5.
von Wagner M, Huber M, Berg T, Hinrichsen H, Rasenack J, Heintges T, et al. Peginterferon-alpha-2a (40 kD) and ribavirin for 16 or 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 or 3 chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(2):522–7.
von Wagner M, Hofmann WP, Teuber G, Berg T, Goeser T, Spengler U, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of 400 mg amantadine combined with peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin for 48 weeks in chronic hepatitis C virus-1 infection. Hepatology. 2008;48(5):1404–11.
Yu ML, Dai CY, Lin ZY, Lee LP, Hou NJ, Hsieh MY, et al. A randomized trial of 24- vs. 48-week courses of PEG interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for genotype-1b-infected chronic hepatitis C patients: a pilot study in Taiwan. Liver Int. 2006;26(1):73–81.
Yu ML, Dai CY, Huang JF, Hou NJ, Lee LP, Hsieh MY, et al. A randomised study of peginterferon and ribavirin for 16 versus 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 2007;56(4):553–9.
Yu ML, Dai CY, Huang JF, Chiu CF, Yang YH, Hou NJ, et al. Rapid virological response and treatment duration for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 patients: a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2008;47(6):1884–93.
Zeuzem S, Diago M, Gane E, Reddy KR, Pockros P, Prati D, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kD) and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C and normal aminotransferase levels. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(6):1724–32.
Zeuzem S, Pawlotsky JM, Lukasiewicz E, von Wagner M, Goulis I, Lurie Y, et al. International, multicenter, randomized, controlled study comparing dynamically individualized versus standard treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2005;43(2):250–7.
Zeuzem S, Buti M, Ferenci P, Sperl J, Horsmans Y, Cianciara J, et al. Efficacy of 24 weeks treatment with peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C infected with genotype 1 and low pretreatment viremia. J Hepatol. 2006;44(1):97–103.
Zeuzem S, Yoshida EM, Benhamou Y, Pianko S, Bain VG, Shouval D, et al. Albinterferon alpha-2b dosed every two or four weeks in interferon-naive patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2008;48(2):407–17.
Conflict of interest
Kazuhiko Koike has served as a speaker for MSD and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and has received research funding from MSD and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, T., Kishikawa, T., Sato, M. et al. Meta-analysis: mortality and serious adverse events of peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol 48, 254–268 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0631-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0631-y