Abstract
Background
EphA3, a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinases, plays important roles in tumor angiogenesis and progression. However, the function of EphA3 in solid tumors has not been widely studied. We aimed to explore EphA3 expression in gastric carcinoma and analyze its role as a potential prognostic factor.
Methods
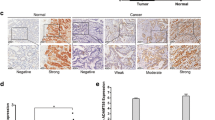
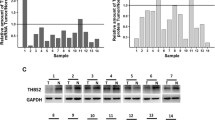
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to assess EphA3 mRNA in a normal gastric mucosa cell line and carcinoma cell lines. Immunohistochemistry for EphA3 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was performed in 318 cases of gastric carcinoma. CD34 immunohistochemical staining was used for microvessel density (MVD) counting. Western blotting was used to analyze EphA3 expression in the cell lines and to determine the expression of EphA3 and VEGF in 75 cases of gastric carcinoma and matched normal mucosa.
Results
EphA3 mRNA and protein expression was significantly higher in gastric cancer than that in normal mucosa (all P < 0.001). EphA3 was significantly correlated with TNM stage and poor prognosis (all P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that EphA3 had an independent effect on survival (P = 0.037). EphA3 was positively correlated with VEGF (P < 0.001), and MVD (P < 0.001). According to Western blot analysis, both EphA3 and VEGF expression were significantly higher in carcinoma than that in normal mucosa (all P < 0.001). A positive correlation was observed between EphA3 and VEGF expression in cancer (P < 0.001, r = 0.513).
Conclusions
EphA3 may play important roles in the angiogenesis and prognosis of gastric carcinoma, and thus may become a useful target for therapeutic intervention and a potential indicator for clinical assessment of tumor prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Partial regression coefficient
- Ephs:
-
Eph receptors
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- MVD:
-
Microvessel density
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- SE:
-
Standard error
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Wikkinson DG. Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:155–64.
Himanen JP, Nikolov DB. Eph receptors and ephrins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35:130–4.
Clifford N, Smith LM, Powell J, Gattenlöhner S, Marx A, O’Connor R. The EphA3 receptor is expressed in a subset of rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines and suppresses cell adhesion and migration. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105:1250–9.
Anon. Unified nomenclature for Eph family receptors and their ligands, the ephrins. Eph Nomenclature Committee. Cell. 1997;90:403–4.
Wang J, Dong Y, Wang X, Ma H, Sheng Z, Li G, et al. Expression of EphA1 in gastric carcinomas is associated with metastasis and survival. Oncol Rep. 2010;24:1577–84.
Nakamura R, Kataoka H, Sato N, Kanamori M, Ihara M, Igarashi H, et al. EPHA2/EFNA1 expression in human gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2005;96:42–7.
Yuan W, Chen Z, Wu S, Ge J, Chang S, Wang X, et al. Expression of EphA2 and E-cadherin in gastric cancer: correlated with tumor progression and lymphogenous metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009;15:473–8.
Wang J, Li G, Ma H, Bao Y, Wang X, Zhou H, et al. Differential expression of EphA7 receptor tyrosine kinase in gastric carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2007;38:1649–56.
Yu G, Gao Y, Ni C, Chen Y, Pan J, Wang X, et al. Reduced expression of EphB2 is significantly associated with nodal metastasis in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:73–80.
Holder N, Klein R. Eph receptors and ephrins: effectors of morphogenesis. Development. 1999;126:2033–44.
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R. The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:419–33.
Heroult M, Schaffner F, Augustin HG. Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:642–50.
Pejovic T. Genetic changes in ovarian cancer. Ann Med. 1995;27:73–8.
Smith LM, Walsh PT, Rüdiger T, Cotter TG, Mc Carthy TV, Marx A, et al. EphA3 is induced by CD28 and IGF-1 and regulates cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res. 2004;292:295–303.
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, et al. Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem. 2004;50:490–9.
Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Lackmann M. Eph-modulated cell morphology, adhesion and motility in carcinogenesis. IUBMB Life. 2005;57:421–31.
Bae HJ, Song JH, Noh JH, Kim JK, Jung KH, Eun JW, et al. Low frequency mutation of the ephrin receptor A3 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2009;56:331–4.
Xi HQ, Zhao P. Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of EphA3 and CD133 expression in colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:498–503.
Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:4–6.
Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD. Growth factors acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases: VEGFs, angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1055–66.
de Vries C, Escobedo JA, Ueno H, Houck K, Ferrara N, Williams LT. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992;255:989–91.
Lazăr D, Tăban S, Raica M, Sporea I, Cornianu M, Goldiş A, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of the tumor neoangiogenesis as a prognostic factor for gastric cancers. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2008;49:137–48.
Tsutsui S, Kume M, Era S. Prognostic value of microvessel density in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer. 2003;10:312–9.
Lackner C, Jukic Z, Tsybrovskyy O, Jatzko G, Wette V, Hoefler G, et al. Prognostic relevance of tumour-associated macrophages and von Willebrand factor-positive microvessels in colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:160–7.
Raspollini MR, Amunni G, Villanucci A, Baroni G, Boddi V, Taddei GL. Prognostic significance of microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in advanced ovarian serous carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2004;14:815–23.
Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R. Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood. Lung Cancer. 2006;51:143–58.
Tanigawa N, Amaya H, Matsumura M, Shimomatsuya T, Horiuchi T, Muraoka R, et al. Extent of tumor vascularization correlates with prognosis and hematogenous metastasis in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2671–6.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Xi HQ, Zhao P, Han WD. Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of LRP16 expression in colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1644–8.
Matsubara J, Yamada Y, Nakajima TE, Kato K, Hamaguchi T, Shirao K, et al. Clinical significance of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Oncology. 2008;74:76–83.
Wood LD, Calhoun ES, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Powell SM, et al. Somatic mutations of GUCY2F, EPHA3, and NTRK3 in human cancers. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:1060–1.
Hansen S, Grabau DA, Sørensen FB, Bak M, Vach W, Rose C. Vascular grading of angiogenesis: prognostic significance in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2000;82:339–47.
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua P, Allred EN, Moore DH, et al. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992;84:1875–87.
Dodelet VC, Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2000;19:5614–9.
Clevers H, Batlle E. EphB/EphrinB receptors and Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2–5.
Boyd AW, Ward LD, Wicks IP, Simpson RJ, Salvaris E, Wilks A, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel receptor-type protein tyrosine kinase (hek) from a human pre-B cell line. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3262–7.
Wicks IP, Wilkinson D, Salvaris E, Boyd AW. Molecular cloning of HEK, the gene encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed by human lymphoid tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:1611–5.
Dottori M, Down M, Huttmann A, Fitzpatrick DR, Boyd AW. Cloning and characterization of EphA3 (Hek) gene promoter: DNA methylation regulates expression in hematopoietic tumor cells. Blood. 1999;94:2477–86.
Fox BP, Tabone CJ, Kandpal RP. Potential clinical relevance of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands expressed in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;342:1263–72.
Tomoda M, Maehara Y, Kakeji Y, Ohno S, Ichiyoshi Y, Sugimachi K. Intratumoral neovascularization and growth pattern in early gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1999;85:2340–6.
Senger DR, Connolly DT, Van de Water L, Feder J, Dvorak HF. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of guinea pig tumor-secreted vascular permeability factors. Cancer Res. 1990;50:1774–8.
Connolly DT, Heuvelman DM, Nelson R, Olander JV, Eppley BL, Delfino JJ. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1989;84:1470–8.
Zhang H, Wu J, Meng L, Shou CC. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:994–8.
Iordache S, Saftoiu A, Georgescu CV, Ramboiu S, Gheonea DI, Filip M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and microvessel density–two useful tools for the assessment of prognosis and survival in gastric cancer patients. J Gastrointest Liver Dis. 2010;19:135–9.
Lee SA, Choi SR, Jang JS, Lee JH, Roh MH, Kim SO, et al. Expression of VEGF, EGFR, and IL-6 in gastric adenomas and adenocarcinomas by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:1955–63.
Chen CN, Cheng YM, Lin MT, Hsieh FJ, Lee PH, Chang KJ. Association of color Doppler vascularity index and microvessel density with survival in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg. 2002;235:512–8.
Zheng H, Tsuneyama K, Cheng C, Takahashi H, Cui Z, Nomoto K, Murai Y, Takano Y. Expression of KAI1 and tenascin, and microvessel density are closely correlated with liver metastasis of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60:50–6.
Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD. Diverse roles for the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases in carcinogenesis. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;59:58–67.
Brantley-Sieders D, Parker M, Chen J. Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor and tumor microenvironment. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3431–42.
Cheng N, Brantley D, Fang WB, Liu H, Fanslow W, Cerretti DP, et al. Inhibition of VEGF-dependent multistage carcinogenesis by soluble EphA receptors. Neoplasia. 2003;5:445–56.
Brantley DM, Cheng N, Thompson EJ, Lin Q, Brekken RA, Thorpe PE, et al. Soluble Eph A receptors inhibit tumor angiogenesis and progression in vivo. Oncogene. 2002;21:7011–26.
Dobrzanski P, Hunter K, Jones-Bolin S, Chang H, Robinson C, Pritchard S, et al. Antiangiogenic and antitumor efficacy of EphA2 receptor antagonist. Cancer Res. 2004;64:910–9.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Po Zhao and Dr. Yazhuo Li, Department of Pathology, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, for their excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by a Grant from the Committee of Science and Technology of Beijing, China, No. Z111107058811047.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H.-Q. Xi and X.-S. Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, HQ., Wu, XS., Wei, B. et al. Aberrant expression of EphA3 in gastric carcinoma: correlation with tumor angiogenesis and survival. J Gastroenterol 47, 785–794 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0549-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0549-4