Abstract
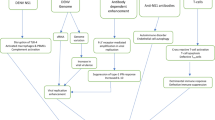
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is an important disease globally. Chronic HBV infection may result in serious complications. Its transmission may be either perinatal or horizontal. Perinatal transmission is particularly important after the implementation of a universal vaccination program. Through either route, chronic carrier status is usually established in early childhood. The course of the disease course is determined by the host–virus interaction. The host’s immune system initially tolerates the virus, and then gradually attempts to clear it. The virus, on the other hand, tries to avoid host immune system attack by a strategy involving targeted epitope mutations. By generating mutants, the virus can survive attacks from the host’s immune system, enabling the infection to persist. Different individuals have different responses to HBV infection; genetic polymorphisms in cytokines, hormones, and other immune modulators may affect the final outcome of chronic HBV infection. Due to the implementation of a universal infant HBV vaccination program, HBV infection is now under control. Unfortunately, there still are some cases of vaccination failure. Very high maternal viremia, in utero infection, or escape mutants are possible reasons for vaccination failure. Immunocompromised hosts also risk vaccination failure. Blood or organ donors with occult HBV infection are possible sources for immunocompromised hosts. These victims of vaccination failure may exhibit a different disease course due to chronic HBV infection from those who acquired the infection before the universal vaccination era. The achievement of our ultimate goal of HBV elimination depends on a globally effective universal vaccination program, as well as the application of some novel successful medications to control those who are already infected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beasley RP, Stevens CE. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan. In: Sung JL, Yu JY, Wang TH, editors. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Hepatitis in Taipei. Taipei: Gastroenterologic Society of the Republic of China, pp. 1–10.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Chen DS, Lee CY, Sung JL. Baseline seroepidemiology of hepatitis B virus in children in Taipei, 1984: a study just before mass hepatitis B vaccination program in Taiwan. J Med Virol. 1986;18:301–7.
Stevens CE, Beasley RP, Tsui J, Lee WC. Vertical transmission of hepatitis B antigen in Taiwan. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:771–4.
Chang MH. Chronic hepatitis virus infection in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:541–8.
Chu CM. Toward control of hepatitis B in the Asia-Pacific Region—natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection adults with emphasis on the occurrence of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:E25–30.
Yuen MF, Lai CL. Toward control of hepatitis B in the Asia–Pacific region—natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:E20–4.
Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B: natural history and treatment. Semin Liver Dis. 2006;26:130–41.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Chen PJ, Tsai KS, Hsu HY, Chen HL, et al. Viremia profiles in children with chronic hepatitis B infection and spontaneous e antigen seroconversion. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2340–5.
Chang MH, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Tsai KS, Lee PI, Chen PJ, et al. Precore stop codon mutant in chronic hepatitis B virus infection in children: its relation to hepatitis B seroconversion and maternal hepatitis B surface antigen. J Hepatol. 1998;28:915–22.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Tsuei DJ. Longitudinal study on mutation profiles of core promoter and precore regions of hepatitis B virus genome in children. Pediatr Res. 2004;56:396–9.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Chen HL. Long-term follow-up study of core gene deletion mutants in children with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2000;32:124–8.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Tung YC, Chen HL, Wang KJ, et al. Mutations of T cell epitopes on the hepatitis B virus surface gene in children with chronic infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:1004–9.
Wu JF, Wu TC, Chen CH, Ni YH, Chen HL, Hsu HY, et al. Serum levels of interleukin 10 and 12 predict early, spontaneous hepatitis B virus e antigen seroconversion. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:165–72.
Wu JF, Tsai WY, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Chen HL, Tsuei DJ, et al. The effect of puberty onset on spontaneous hepatitis B virus e antigen seroconversion in men. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:942–8.
Liu CJ, Lo SC, Kao JH, Tseng PT, Lai MY, Ni YH, et al. Transmission of occult hepatitis B virus by transfusion to adult and pediatric recipients in Taiwan. J Hepatol. 2006;44:39–46.
Su WJ, Ho MC, Ni YH, Chen HL, Hu RH, Wu YM, et al. High-titer antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen before liver transplantation can prevent de novo hepatitis B infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;48:203–8.
Hsu C, Hsiung CA, Su IJ, Hwang WS, Wang MC, Lin SF, et al. A revisit of prophylactic lamivudine for chemotherapy-associated hepatitis B reactivation in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2008;47:844–53.
Loomba R, Rowley A, Wesley R, Liang TJ, Hoofnagle JH, Pucino F, et al. Systematic review: the effect of preventive lamivudine on hepatitis B reactivation during chemotherapy. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:519–28.
Chang MH, Chen THH, Hsu HM, Wu TC, Kong MS, Liang DC, et al. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma by universal vaccination against hepatitis B virus: the effect and problems. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7953–7.
Beasley RP. Rocks along the road to the control of HBV and HCC. Ann Epidemiol. 2009;19:231–4.
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007;45:507–39.
Tang JR, Hsu HY, Lin HH, Ni YH, Chang MH. Hepatitis B surface antigenemia at birth: a long-term follow up study. J Pediatr. 1998;133:374–7.
Milich D, Liang TJ. Exploring the biological basis of hepatitis B e antigen in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2003;38:1075–86.
Milich DR, Jones JE, Hughes JL, Price J, Raney AK, McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:6599–603.
Hsu SC, Chang MH, Ni YH, Hsu HY, Lee CY. Horizontal transmission of hepatitis B virus in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1993;16:66–9.
Weinbaum CM, Williams I, Mast EE, Wang SA, Finelli L, Wasley A, et al. Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. MMWR. 2008;57(RR08):1–20.
Mast EE, Weinbaum CM, Fiore AE, Alter MJ, Bell BP, Finelli L, et al. A comprehensive immunization strategy to eliminate transmission of hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Part II: immunization of adults. MMWR. 2006;55(RR16):1–25.
Chang MH, Lee CY, Chen DS, Hsu HC, Lai MY. Fulminant hepatitis in children in Taiwan: the important role of hepatitis B virus. J Pediatr. 1987;111:34–9.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Lee CY, Hsieh KH, Ni YH, Chen PJ, et al. Precore mutant of hepatitis B virus in childhood fulminant hepatitis B: an infrequent association. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:776–81.
Chang MH, Hwang LY, Hsu HC, Lee CY, Beasley RP. Prospective study of asymptomatic HBsAg carrier children infected in the perinatal period: clinical and liver histologic studies. Hepatology. 1988;8:374–7.
Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373:582–92.
Ni YH, Huang LM, Chang MH, Yen CJ, Lu CY, You SL, et al. Two decades of universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan: impact and implication for future strategies. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1287–93.
Chang MH, Hsu HY, Hsu HC, Ni YH, Chen JS, Chen DS. The significance of spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen sero-conversion in childhood: with special emphasis on the clearance of hepatitis B e antigen before 3 years of age. Hepatology. 1995;22:1387–92.
Chang MH, Sung JL, Lee CY, Chen CJ, Chen JS, Hsu HY, et al. Factors affecting clearance of hepatitis B e antigen in hepatitis B surface antigen carrier children. J Pediatr. 1989;115:385–90.
Chen YC, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Age-specific prognosis following spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;51:435–44.
Bortolotti F, Guido M, Bartolacci S, Cadrobbi P, Crivellaro C, Noventa F, et al. Chronic hepatitis B in children after e antigen seroclearance: final report of a 29-year longitudinal study. Hepatology. 2006;43:556–62.
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lu SN, Jen CL, Wang LY, et al. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:474–82.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73.
Wen WH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Chen HL. The development of hepatocellular carcinoma among prospectively followed children with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Pediatr. 2004;144:397–9.
Chang MH, Chen PJ, Chen JY, Lai MY, Hsu HC, Lian DC, et al. Hepatitis B virus integration in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in childhood. Hepatology. 1991;13:316–20.
Liaw YF, Leung N, Kao JH, Piratvisuth T, Gane E, Han KH, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2008 update. Hepatol Int. 2008;2:263–83.
Kao JH. Hepatitis B viral genotypes: clinical relevance and molecular characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:643–50.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Wang KJ, Hsu HY, Chen HL, Kao JH, et al. Clinical relevance of hepatitis B virus genotype in children with chronic infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1733–8.
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Hepatitis B virus genotypes and spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in Taiwanese hepatitis B carriers. J Med Virol. 2004;72:363–9.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Hsieh KH, Lee CY, Lin HH, Hwang LH, et al. Cellular immune response to HBcAg in mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1992;15:770–6.
Rehermann B. Chronic infections with hepatotropic viruses: mechanisms of impairment of cellular immune responses. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:152–60.
Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1118–29.
Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. New Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–45.
Carman WF, Fagan EA, Hadziyannis S, Karayiannis P, Tassopoulos NC, Williams R, et al. Association of a precore genomic variant of hepatitis B virus with fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology. 1991;14:219–22.
Nakahori S, Yokosuka O, Ehata T, Chuang WL, Imazeki F, Ito Y, et al. Detection of hepatitis B virus precore stop codon mutants by selective amplification method: frequent detection of precore mutants in hepatitis B e antigen positive healthy carriers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995;10:419–25.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Tsuei DJ. Different hepatitis B virus core gene mutations in children with chronic infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2003;52:122–5.
Tordjeman M, Fontan G, Rabillon V, Martin J, Trepo C, Hoffenbach A, et al. Characterization of minor and major antigenic regions within the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids. J Med Virol. 1993;41:221–9.
Raimondo G, Burk RD, Lieberman HM, Muschel J, Hadziyannis SJ, Will H, et al. Interrupted replication of hepatitis B virus in liver tissue of HBsAg carriers with hepatocellular carcinoma. Virology. 1988;166:103–12.
Liu CJ, Jeng YM, Chen CL, Cheng HR, Chen PJ, Chen TC, et al. Hepatitis B virus basal core promoter mutation and DNA load correlate with expression of hepatitis B core antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:742–9.
Chan HL, Hussain M, Lok AS. Different hepatitis B virus genotypes are associated with different mutations in the core promoter and precore regions during hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. Hepatology. 1999;29:976–84.
Tai PC, Banik D, Lin GI, Pai S, Pai K, Lin MH, et al. Novel and frequent mutation of HBV coincide with a major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T-cell epitope of the surface antigen. J Virol. 1997;71:4852–6.
Kamatani Y, Wattanapokayakit S, Ochi H, Kawaguchi T, Takahashi A, Hosono N, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies variants in the HLA-DP locus associated with chronic hepatitis B in Asians. Nat Genet. 2009;41:591–5.
Yeh SH, Chiu CM, Chen CL, Lu SF, Hsu HC, Chen DS, et al. Somatic mutations at the trinucleotide repeats of androgen receptor gene in male hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1610–7.
Yu MW, Cheng SW, Lin MW, Yang SY, Liaw YF, Chang HC, et al. Androgen-receptor gene CAG repeats, plasma testosterone levels, and risk of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:2023–8.
Paz-y-Miño C, Witte T, Robles P, Llumipanta W, Díaz M, Arévalo M. Association among polymorphisms in the steroid 5alpha-reductase type II (SRD5A2) gene, prostate cancer risk, and pathologic characteristics of prostate tumors in an Ecuadorian population. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2009;189:71–6.
Yu MW, Yang YC, Yang SY, Cheng SW, Liaw YF, Lin SM, et al. Hormonal markers and hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a nested case-control study among men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1644–51.
Yeh SH, Chen PJ. Gender disparity of hepatocellular carcinoma: the roles of sex hormones. Oncology. 2010;78(Suppl 1):172–9.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Hsu HY, Hsu HC, Chen CC, Chen WJ, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in childhood. Cancer. 1991;68:1737–41.
Tsuei DJ, Hsu HC, Lee PH, Jeng YM, Pu YS, Chen CN, et al. RBMY, a male germ cell-specific RNA-binding protein, activated in human liver cancers and transforms rodent fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2004;23:5815–22.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Ni YH, Lee PI. Cytokine release of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in children with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29:540–5.
Hoofnagle JH. Reactivation of hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49:S156–65.
Saab S, Waterman B, Chi AC, Tong MJ. Comparison of different immuno- prophylaxis regimens after liver transplantation with hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors: a systematic review. Liver Transplant. 2010;16:300–7.
Otte JB. History of pediatric liver transplantation. Where are we coming from? Where do we stand? Pediatr Transplant. 2002;6:378–87.
Su WJ, Ho MC, Ni YH, Wu JF, Jeng YM, Chen HL, et al. Clinical course of de novo hepatitis B infection after pediatric liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2010;16:215–21.
Marshall DA, Kleinman SH, Wong JB, AuBuchon JP, Grima DT, Kulin NA, et al. Cost-effectiveness of nucleic acid test screening of volunteer blood donations for hepatitis B, hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus in the United States. Vox Sang. 2004;86:28–40.
Ni YH, Chang MH, Huang LM, Chen HL, Hsu HY, Chiu TY, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection in children and adolescents in a hyperendemic area: 15 years after universal hepatitis B vaccination. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:796–800.
Carman WF, Zanetti AR, Karayiannis P, Waters J, Manzillo G, Tanzi E, et al. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1990;336:325–9.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Ni YH, Chen HL. Survey of hepatitis B surface variant infection in children 15 years after nationwide vaccination program in Taiwan. Gut. 2004;53:1499–503.
Hsu HY, Chang MH, Ni YH, Chiang CL, Chen HL, Wu JF, et al. No increase in prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen mutant in a population of children and adolescents who were fully covered by universal infant immunization. J Infect Dis. 2010;201:1192–200.
Chasela CS, Hudgens MG, Jamieson DJ, Kayira D, Hosseinipour MC, Kourtis AP, et al. Maternal or infant antiretroviral drugs to reduce HIV-1 transmission. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2271–81.
van Zonneveld M, van Nunen AB, Niesters HG, de Man RA, Schalm SW, Janssen HL. Lamivudine treatment during pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat. 2003;10:294–7.
Xu WM, Cui YT, Wang L, Yang H, Liang ZQ, Li XM, et al. Lamivudine in late pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Viral Hepat. 2009;16:94–103.
Chang MH, Shau WY, Chen CJ, Wu TC, Kong MS, Liang DC, et al. Hepatitis B vaccination and hepatocellular carcinoma rates in boys and girls. JAMA. 2000;284:3040–2.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Prof. Mei-Hwei Chang for her critical review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, YH. Natural history of hepatitis B virus infection: pediatric perspective. J Gastroenterol 46, 1–8 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0304-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0304-7