Abstract
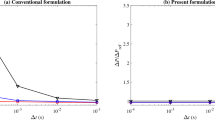
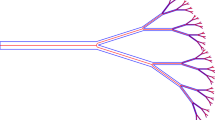
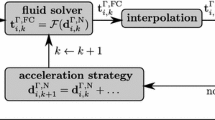
Computation of incompressible flows in arterial fluid mechanics, especially because it involves fluid–structure interaction, poses significant numerical challenges. Iterative solution of the fluid mechanics part of the equation systems involved is one of those challenges, and we address that in this paper, with the added complication of having boundary layer mesh refinement with thin layers of elements near the arterial wall. As test case, we use matrix data from stabilized finite element computation of a bifurcating middle cerebral artery segment with aneurysm. It is well known that solving linear systems that arise in incompressible flow computations consume most of the time required by such simulations. For solving these large sparse nonsymmetric systems, we present effective preconditioning techniques appropriate for different stages of the computation over a cardiac cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2004) Influence of wall elasticity on image-based blood flow simulation. Jpn Soc Mech Eng J Ser A 70: 1224–1231 (in Japanese)
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2006) Computer modeling of cardiovascular fluid–structure interactions with the deforming-spatial-domain/stabilized space–time formulation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 1885–1895
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2006) Fluid–structure interaction modeling of aneurysmal conditions with high and normal blood pressures. Comput Mech 38: 482–490
Bazilevs Y, Calo VM, Zhang Y, Hughes TJR (2006) Isogeometric fluid–structure interaction analysis with applications to arterial blood flow. Comput Mech 38: 310–322
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2007) Influence of wall elasticity in patient-specific hemodynamic simulations. Comput Fluids 36: 160–168
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Cragin T, Nanna B, Conklin BS, Pausewang J, Schwaab M (2007) Modeling of fluid–structure interactions with the space–time finite elements: arterial fluid mechanics. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 54: 901–922
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2007) Numerical investigation of the effect of hypertensive blood pressure on cerebral aneurysm—dependence of the effect on the aneurysm shape. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 54: 995–1009
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Schwaab M, Conklin BS (2008) Arterial fluid mechanics modeling with the stabilized space–time fluid–structure interaction technique. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 57: 601–629
Bazilevs Y, Calo VM, Hughes TJR, Zhang Y (2008) Isogeometric fluid–structure interaction: theory, algorithms, and computations. Comput Mech 43: 3–37
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2008) Fluid–structure interaction modeling of a patient-specific cerebral aneurysm: influence of structural modeling. Comput Mech 43: 151–159
Tezduyar TE, Schwaab M, Sathe S (2008) Sequentially-coupled arterial fluid–structure interaction (SCAFSI) technique. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2008.05.024
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2008) Fluid–structure interaction modeling of blood flow and cerebral aneurysm: significance of artery and aneurysm shapes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2008.08.020
Bazilevs Y, Gohean JR, Hughes TJR, Moser RD, Zhang Y (2009) Patient-specific isogeometric fluid–structure interaction analysis of thoracic aortic blood flow due to implantation of the Jarvik 2000 left ventricular assist device. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2009.04.015
Takizawa K, Christopher J, Tezduyar TE, Sathe S (2009) Space–time finite element computation of arterial fluid–structure interactions with patient-specific data. Commun Numer Methods Eng. doi:10.1002/cnm.1241
Tezduyar TE, Takizawa K, Christopher J (2009) Multiscale sequentially-coupled arterial fluid–structure interaction (SCAFSI) technique”. In: Hartmann S, Meister A, Schaefer M, Turek S (eds) International workshop on fluid–structure interaction—theory, numerics and applications. Kassel University Press, Kassel
Torii R, Oshima M, Kobayashi T, Takagi K, Tezduyar TE (2009) Influence of wall thickness on fluid–structure interaction computations of cerebral aneurysms. Commun Numer Methods Eng. doi:10.1002/cnm.1289
Tezduyar T, Aliabadi S, Behr M, Johnson A, Mittal S (1993) Parallel finite-element computation of 3D flows. Computer 26: 27–36
Tezduyar TE, Aliabadi SK, Behr M, Mittal S (1994) Massively parallel finite element simulation of compressible and incompressible flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 119: 157–177
Mittal S, Tezduyar TE (1994) Massively parallel finite element computation of incompressible flows involving fluid–body interactions. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 112: 253–282
Mittal S, Tezduyar TE (1995) Parallel finite element simulation of 3D incompressible flows—fluid–structure interactions. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 21: 933–953
Johnson AA, Tezduyar TE (1997) Parallel computation of incompressible flows with complex geometries. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 24: 1321–1340
Johnson AA, Tezduyar TE (1999) Advanced mesh generation and update methods for 3D flow simulations. Comput Mech 23: 130–143
Kalro V, Tezduyar TE (2000) A parallel 3D computational method for fluid–structure interactions in parachute systems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190: 321–332
Stein K, Benney R, Kalro V, Tezduyar TE, Leonard J, Accorsi M (2000) Parachute fluid–structure interactions: 3-D computation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190: 373–386
Tezduyar T, Osawa Y (2001) Fluid–structure interactions of a parachute crossing the far wake of an aircraft. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191: 717–726
Ohayon R (2001) Reduced symmetric models for modal analysis of internal structural-acoustic and hydroelastic-sloshing systems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190: 3009–3019
Stein K, Tezduyar T, Benney R (2003) Mesh moving techniques for fluid–structure interactions with large displacements. J Appl Mech 70: 58–63
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Keedy R, Stein K (2004) Space–time techniques for finite element computation of flows with moving boundaries and interfaces. In: Gallegos S, Herrera I, Botello S, Zarate F, Ayala G (eds) Proceedings of the III international congress on numerical methods in engineering and applied science, CD-ROM, Monterrey, Mexico
Stein K, Tezduyar TE, Benney R (2004) Automatic mesh update with the solid-extension mesh moving technique. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 2019–2032
van Brummelen EH, de Borst R (2005) On the nonnormality of subiteration for a fluid–structure interaction problem. SIAM J Sci Comput 27: 599–621
Michler C, van Brummelen EH, de Borst R (2005) An interface Newton–Krylov solver for fluid–structure interaction. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 47: 1189–1195
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Keedy R, Stein K (2006) Space–time finite element techniques for computation of fluid–structure interactions. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 2002–2027
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Stein K (2006) Solution techniques for the fully-discretized equations in computation of fluid–structure interactions with the space–time formulations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 5743–5753
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Stein K, Aureli L (2006) Modeling of fluid–structure interactions with the space–time techniques. In: Bungartz H-J, Schafer M (eds) Fluid–structure interaction. Lecture notes in computational science and engineering, vol 53. Springer, Berlin, pp 50–81
Dettmer W, Peric D (2006) A computational framework for fluid–structure interaction: finite element formulation and applications. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 5754–5779
Khurram RA, Masud A (2006) A multiscale/stabilized formulation of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations for moving boundary flows and fluid–structure interaction. Comput Mech 38: 403–416
Kuttler U, Forster C, Wall WA (2006) A solution for the incompressibility dilemma in partitioned fluid–structure interaction with pure Dirichlet fluid domains. Comput Mech 38: 417–429
Bletzinger K-U, Wuchner R, Kupzok A (2006) Algorithmic treatment of shells and free form-membranes in FSI. In: Bungartz H-J, Schafer M (eds) Fluid–structure interaction. Lecture notes in computational science and engineering, vol 53. Springer, Berlin, pp 336–355
Masud A, Bhanabhagvanwala M, Khurram RA (2007) An adaptive mesh rezoning scheme for moving boundary flows and fluid–structure interaction. Comput Fluids 36: 77–91
Sawada T, Hisada T (2007) Fuid–structure interaction analysis of the two dimensional flag-in-wind problem by an interface tracking ALE finite element method. Comput Fluids 36: 136–146
Wall WA, Genkinger S, Ramm E (2007) A strong coupling partitioned approach for fluid–structure interaction with free surfaces. Comput Fluids 36: 169–183
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S (2007) Modeling of fluid–structure interactions with the space–time finite elements: solution techniques. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 54: 855–900
Kuttler U, Wall WA (2008) Fixed-point fluid–structure interaction solvers with dynamic relaxation. Comput Mech 43: 61–72
Dettmer WG, Peric D (2008) On the coupling between fluid flow and mesh motion in the modelling of fluid–structure interaction. Comput Mech 43: 81–90
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Pausewang J, Schwaab M, Christopher J, Crabtree J (2008) Interface projection techniques for fluid– structure interaction modeling with moving-mesh methods. Comput Mech 43: 39–49
Tezduyar TE, Sathe S, Pausewang J, Schwaab M, Christopher J, Crabtree J (2008) Fluid–structure interaction modeling of ringsail parachutes. Comput Mech 43: 133–142
Sathe S, Tezduyar TE (2008) Modeling of fluid–structure interactions with the space–time finite elements: contact problems. Comput Mech 43: 51–60
Manguoglu M, Sameh AH, Tezduyar TE, Sathe S (2008) A nested iterative scheme for computation of incompressible flows in long domains. Comput Mech 43: 73–80
Tezduyar TE (1992) Stabilized finite element formulations for incompressible flow computations. Adv Appl Mech 28: 1–44
Tezduyar TE, Behr M, Liou J (1992) A new strategy for finite element computations involving moving boundaries and interfaces—the deforming-spatial-domain/space–time procedure: I. The concept and the preliminary numerical tests. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 94: 339–351
Tezduyar TE, Behr M, Mittal S, Liou J (1992) A new strategy for finite element computations involving moving boundaries and interfaces—the deforming-spatial-domain/space–time procedure: II. Computation of free-surface flows, two-liquid flows, and flows with drifting cylinders. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 94: 353–371
Tezduyar TE (2003) Computation of moving boundaries and interfaces and stabilization parameters. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 43: 555–575
Takizawa K, Moorman C, Wright S, Christopher J, Tezduyar TE (2009) Wall shear stress calculations in space–time finite element computation of arterial fluid–structure interactions. Comput Mech (submitted)
Cuthill E, McKee J (1969) Reducing the bandwidth of sparse symmetric matrices. In: Proceedings of the 1969 24th national conference. ACM Press, New York, pp 157–172
Baggag A, Sameh A (2004) A nested iterative scheme for indefinite linear systems in particulate flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 1923–1957
Sameh A, Manguoglu M, Sathe S, Tezduyar TE (2007) A nested iterative scheme for nonsymmetric linear systems. In: Onate E, Papadrakakis M, Schrefler B (eds) Coupled problems 2007. CIMNE, Barcelona
Sameh A, Manguoglu M, Sathe S, Pausewang J, Tezduyar TE (2007) Iterative techniques with banded preconditioners for fluid mechanics computations over long domains. In: Onate E, Garcia J, Bergan P, Kvamsdal T (eds) Marine 2007. CIMNE, Barcelona
Sameh AH, Manguoglu M, Sathe S, Pausewang J, Tezduyar TE (2007) Iterative schemes for time accurate solution of flow in long narrow domains. In: Proceedings of the third Asian-Pacific congress on computational mechanics (CD-ROM), Kyoto, Japan
Manguoglu M, Sameh AH, Saied F, Tezduyar TE, Sathe S (2009) Preconditioning techniques for nonsymmetric linear systems in computation of incompressible flows. J Appl Mech 76: 021204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manguoglu, M., Takizawa, K., Sameh, A.H. et al. Solution of linear systems in arterial fluid mechanics computations with boundary layer mesh refinement. Comput Mech 46, 83–89 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-009-0426-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-009-0426-z