Abstract
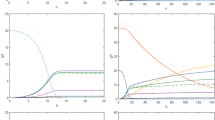
A kinetic model for glucose and xylose co-substrate uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is presented. The model couples the enzyme kinetics with the glucose-dependent genetic expression of the individual transport proteins. This novel approach implies several options for optimizing the co-substrate utilization. Interestingly, the simulations predict a maximum xylose uptake rate at a glucose concentration >0 g/L, which suggests that the genetic expressions of the considered transport proteins are of importance when optimizing the xylose uptake. This was also evident in fed-batch simulations, where a distinct optimal glucose addition rate >0 g/L·h was found. Strategies for improving the co-substrate utilization by genetic engineering of the transport systems are furthermore suggested based on simulations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynd LR, Cushman JH, Nichols RJ, Wyman CE (1991) Fuel ethanol from cellulosic biomass. Science 251:1318–1323
Wingren A, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2003) Techno-economic evaluation of producing ethanol from softwood: comparison of SSF and SHF and identification of bottlenecks. Biotechnol Prog 19:1109–1117
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Carrying XYL1, XYL2 and XKS1 in Mineral Medium Chemostat Cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Kuyper M, Hartog MMP, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJH, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 5:399–409
Saloheimo A, Rauta J, Stasyyk OV, Sibirny AA, Penttilä M, Ruohonen L (2007) Xylose transport studies with xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing heterologous and homologous permeases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1041–1052
Lee WJ, Kim MD, Ryu YW, Bisson LF (2002) Kinetic studies on glucose and xylose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:186–191
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gárdonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiol 148:2783–2788
Bisson LF, Fraenkel DG (1983) Involvement of kinases in glucose and fructose uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80(6):1730–1734
Coons DM, Boulton RB, Bisson LF (1995) Computer-assisted nonlinear regression analysis of the multicomponent glucose uptake kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 1177:3251–3258
Boles E, Hollenberg CP (1997) The molecular genetics of hexose transport in yeast. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:85–111
Kruckeberg AL (1996) The hexose transporter family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 166:283–292
Özcan S, Johnston M (1995) Three different regulatory mechanisms enable yeast hexose transporter (HXT) genes to be induced by different levels of glucose. Mol Cell Biol 15:1564–1572
Diderich JA, Schepper M, van Hoek P, Luttik MAH, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT, Klaassen P, Boelens HFM, de Mattos MJT, van Dam K, Kruckeberg AL (1999) Glucose uptake kinetics and transcription of HXT genes in chemostat cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 274:15350–15359
Liang H, Gaber RF (1996) A novel signal transduction pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae defined by snf3-regulated expression of HXT6. Mol Biol Cell 7:1953–1966
Johnston M, Flick JS, Pexton T (1994) Multiple mechanisms provide rapid and stringent glucose repression of GAL gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 14:3834–3841
Buziol S, Becker J, Baumeister A, Jung S, Mauch K, Reuss M, Boles E (2002) Determination of in vivo kinetics of the starvation-induced Hxt5 glucose transporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 2:283–291
Reifenberger E, Boles E, Ciriacy M (1997) Kinetic characterization of individual hexose transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their relation to the triggering mechanisms of glucose repression. Eur J Biochem 245:324–333
Maier A, Völker B, Boles E, Fuhrmann GF (2002) Characterization of glucose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with plasma membrane vesicles (countertransport) and intact cells (initial uptake) with single Hxt1, Hxt2, Hxt3, Hxt4, Hxt6, Hxt7 or Gal2 transporters. FEMS Yeast Res 2:539–550
Sedlak M, Ho NWY (2004) Characterization of the effectiveness of hexose transporters for transporting xylose during glucose and xylose co-fermentation by a recombinant Saccharomyces yeast. Yeast 21:671–684
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1992) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Özcan S, Johnston M (1999) Function, regulation of yeast hexose transporters. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:554–569
Reifenberger E, Freidel K, Ciriacy M (1995) Identification of novel HXT genes in reveals the impact of individual hexose transporters on glycolytic flux. Mol Microbiol 16:157–167
Diderich JA, Schuurmans JM, van Gaalen MC, Kruckeberg AL, van Dam K (2001) Functional analysis of the hexose transporter homologue HXT5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 18:1515–1524
Adams BG (1972) Induction of galactokinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: kinetics of induction and glucose effects. J Bacteriol 111:308–315
Sonnleitnert B, Käppeli O (1985) Growth of is controlled by its limited respiratory capacity: formulation and verification of a hypothesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:927–937
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2002) A review of the production of ethanol from softwood. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:618–628
Meinander NQ, Boels I, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1999) Fermentation of xylose/glucose mixtures by metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing XYL1 and XYL2 from Pichia stipitis with and without overexpression of TAL1. Bioresour Technol 68:79–87
Pitkänen JP, Aristidou A, Salusjärvi L, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2003) Metabolic flux analysis of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using continuous culture. Metab Eng 5:16–31
Öhgren K, Bengtsson O, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Galbe M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Zacchi G (2006) Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of glucose and xylose in steam-pretreated corn stover at high fiber content with Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB3400. J Biotechnol 126:488–498
Senac T, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1990) Intermediary metabolite concentrations in xylulose- and glucose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:120–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Magnus Bertilsson and Jonas Andersson contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertilsson, M., Andersson, J. & Lidén, G. Modeling simultaneous glucose and xylose uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from kinetics and gene expression of sugar transporters. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31, 369–377 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-007-0169-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-007-0169-1