Abstract
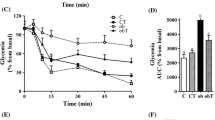
Nesfatin-1 is a novel anorexigenic regulatory peptide. The peptide is the N-terminal part of nucleobindin 2 (NUCB2) and is expressed in brain areas regulating feeding. Outside the brain, nesfatin-1 expression has been reported in adipocytes, gastric endocrine cells and islet cells. We studied NUCB2 expression in human and rodent islets using immunocytochemistry, in situ hybridization and western blot. Furthermore, we investigated the potential influence of nesfatin-1 on secretion of insulin and glucagon in vitro and in vivo in mice and in INS-1 (832/13) cells. The impact of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and glucolipotoxicity on NUCB2 gene expression in human islets and its relationship to insulin secretory capacity and islet gene expression was studied using microarray. Nesfatin-1 immunoreactivity (IR) was abundant in human and rodent beta cells but absent in alpha, delta, PP and ghrelin cells. Importantly, in situ hybridization showed that NUCB2 mRNA is expressed in human and rat islets. Western blot analysis showed that nesfatin-1 IR represented full length NUCB2 in rodent islets. Human islet NUCB2 mRNA was reduced in T2D subjects but upregulated after culture in glucolipotoxic conditions. Furthermore, a positive correlation between NUCB2 and glucagon and insulin gene expression, as well as insulin secretory capacity, was evident. Nesfatin-1 enhanced glucagon secretion but had no effect on insulin secretion from mouse islets or INS-1 (832/13) cells. On the other hand, nesfatin-1 caused a small increase in insulin secretion and reduced glucose during IVGTT in mice. We conclude that nesfatin-1 is a novel glucagon-stimulatory peptide expressed in the beta cell and that its expression is decreased in T2D islets.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brailoiu GC, Dun SL, Brailoiu E, Inan S, Yang J, Chang JK, Dun NJ (2007) Nesfatin-1: distribution and interaction with a G protein-coupled receptor in the rat brain. Endocrinology 148:5088–5094
Foo KS, Brauner H, Ostenson CG, Broberger C (2010) Nucleobindin-2/nesfatin in the endocrine pancreas: distribution and relationship to glycaemic state. J Endocrinol 204:255–263
Gonzalez R, Perry RL, Gao X, Gaidhu MP, Tsushima RG, Ceddia RB, Unniappan S (2011a) Nutrient responsive nesfatin-1 regulates energy balance and induces glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rats. Endocrinology 152:3628–3637
Gonzalez R, Reingold BK, Gao X, Gaidhu MP, Tsushima RG, Unniappan S (2011b) Nesfatin-1 exerts a direct, glucose-dependent insulinotropic action on mouse islet beta- and MIN6 cells. J Endocrinol 208:R9–R16
Gonzalez R, Tiwari A, Unniappan S (2009) Pancreatic beta cells colocalize insulin and pronesfatin immunoreactivity in rodents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:643–648
Gromada J, Franklin I, Wollheim CB (2007) Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr Rev 28:84–116
Hohmeier HE, Mulder H, Chen G, Henkel-Rieger R, Prentki M, Newgard CB (2000) Isolation of INS-1-derived cell lines with robust ATP-sensitive K + channel-dependent and -independent glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 49:424–430
Iwasaki Y, Nakabayashi H, Kakei M, Shimizu H, Mori M, Yada T (2009) Nesfatin-1 evokes Ca(2+) signaling in isolated vagal afferent neurons via Ca(2+) influx through N-type channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:958–962
Li QC, Wang HY, Chen X, Guan HZ, Jiang ZY (2010) Fasting plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and the nutrient-related fluctuation of nesfatin-1 level in normal humans. Regul Pept 159:72–77
Lyssenko V, Nagorny CL, Erdos MR, Wierup N, Jonsson A, Spegel P, Bugliani M, Saxena R, Fex M, Pulizzi N, Isomaa B, Tuomi T, Nilsson P, Kuusisto J, Tuomilehto J, Boehnke M, Altshuler D, Sundler F, Eriksson JG, Jackson AU, Laakso M, Marchetti P, Watanabe RM, Mulder H, Groop L (2009) Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion. Nat Genet 41:82–88
Maejima Y, Sedbazar U, Suyama S, Kohno D, Onaka T, Takano E, Yoshida N, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Fujiwara K, Yashiro T, Horvath TL, Dietrich MO, Tanaka S, Dezaki K, Oh IS, Hashimoto K, Shimizu H, Nakata M, Mori M, Yada T (2009) Nesfatin-1-regulated oxytocinergic signaling in the paraventricular nucleus causes anorexia through a leptin-independent melanocortin pathway. Cell Metab 10:355–365
Mulder H, Lindh AC, Sundler F (1993) Islet amyloid polypeptide gene expression in the endocrine pancreas of the rat: a combined in situ hybridization and immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 274:467–474
Nakata M, Manaka K, Yamamoto S, Mori M, Yada T (2011) Nesfatin-1 enhances glucose-induced insulin secretion by promoting Ca(2+) influx through L-type channels in mouse islet beta-cells. Endocr J (in press)
Oh IS, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi S, Inoue K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto M, Imaki T, Hashimoto K, Tsuchiya T, Monden T, Horiguchi K, Yamada M, Mori M (2006) Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 443:709–712
Pan W, Hsuchou H, Kastin AJ (2007) Nesfatin-1 crosses the blood-brain barrier without saturation. Peptides 28:2223–2228
Price TO, Samson WK, Niehoff ML, Banks WA (2007) Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to a novel satiety molecule nesfatin-1. Peptides 28:2372–2381
Ramanjaneya M, Chen J, Brown JE, Tripathi G, Hallschmid M, Patel S, Kern W, Hillhouse EW, Lehnert H, Tan BK, Randeva HS (2010) Identification of nesfatin-1 in human and murine adipose tissue: a novel depot-specific adipokine with increased levels in obesity. Endocrinology 151:3169–3180
Rosengren AH, Jokubka R, Tojjar D, Granhall C, Hansson O, Li DQ, Nagaraj V, Reinbothe TM, Tuncel J, Eliasson L, Groop L, Rorsman P, Salehi A, Lyssenko V, Luthman H, Renstrom E (2010) Overexpression of alpha2A-adrenergic receptors contributes to type 2 diabetes. Science 327:217–220
Shimizu H, Oh IS, Hashimoto K, Nakata M, Yamamoto S, Yoshida N, Eguchi H, Kato I, Inoue K, Satoh T, Okada S, Yamada M, Yada T, Mori M (2009a) Peripheral administration of nesfatin-1 reduces food intake in mice: the leptin-independent mechanism. Endocrinology 150:662–671
Shimizu H, Oh IS, Okada S, Mori M (2009b) Nesfatin-1: an overview and future clinical application. Endocr J 56:537–543
Stengel A, Goebel M, Wang L, Tache Y (2010) Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in gastric X/A-like cells: role as regulators of food intake and body weight. Peptides 31:357–369
Stengel A, Goebel M, Yakubov I, Wang L, Witcher D, Coskun T, Tache Y, Sachs G, Lambrecht NW (2009) Identification and characterization of nesfatin-1 immunoreactivity in endocrine cell types of the rat gastric oxyntic mucosa. Endocrinology 150:232–238
Wierup N, Björkqvist M, Weström B, Pierzynowski S, Sundler F, Sjölund K (2007) Ghrelin and motilin are cosecreted from a prominent endocrine cell population in the small intestine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3573–3581
Wierup N, Richards WG, Bannon AW, Kuhar MJ, Ahren B, Sundler F (2005) CART knock out mice have impaired insulin secretion and glucose intolerance, altered beta cell morphology and increased body weight. Regul Pept 129:203–211
Wierup N, Svensson H, Mulder H, Sundler F (2002) The ghrelin cell: a novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul Pept 107:63–69
Wierup N, Yang S, McEvilly RJ, Mulder H, Sundler F (2004) Ghrelin is expressed in a novel endocrine cell type in developing rat islets and inhibits insulin secretion from INS-1 (832/13) cells. J Histochem Cytochem 52:301–310
Voss U, Riva M, Nitert M, Ling C, Lindqvist A, Wierup N (2010) Nesfatin-1 stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon secretion and is expressed in human and rodent beta cells. 46th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Stockholm, Sweden, Sep 20–24, 2010
Acknowledgments
Grants support from: Swedish Medical Research Council (Projects No. 522-2008-4216 and K2009-55X 21111-01-4), The Novo Nordisk Foundation, The Royal Physiographic Society in Lund, The Medical Faculty at Lund University, The Gyllenstiernska Krapperup, Fredrik and Ingrid Thuring, Magnus Bergwall, Albert Påhlsson Foundations. Ann-Helen Thorén Fischer, Doris Persson and Britt-Marie Nilsson for excellent technical assistance.
Author contributions
M.R. performed experiments, drew figures and drafted the MS, U.V. performed experiments, M.D.N. performed experiments, analysis and edited the MS, C.L. performed analysis and edited the MS, R.S. performed experiments and drew figures, A.L. performed experiments and drew figures, N.W. conceived the study, performed experiments, drew figures, drafted and edited the MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riva, M., Nitert, M.D., Voss, U. et al. Nesfatin-1 stimulates glucagon and insulin secretion and beta cell NUCB2 is reduced in human type 2 diabetic subjects. Cell Tissue Res 346, 393–405 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1268-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1268-5