Abstract
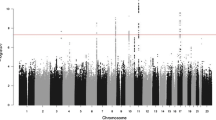
While it is widely appreciated that prostate cancers vary substantially in their propensity to progress to a life-threatening stage, the molecular events responsible for this progression have not been identified. Understanding these molecular mechanisms could provide important prognostic information relevant to more effective clinical management of this heterogeneous cancer. Hence, through genetic linkage analyses, we examined the hypothesis that the tendency to develop aggressive prostate cancer may have an important genetic component. Starting with 1,233 familial prostate cancer families with genome scan data available from the International Consortium for Prostate Cancer Genetics, we selected those that had at least three members with the phenotype of clinically aggressive prostate cancer, as defined by either high tumor grade and/or stage, resulting in 166 pedigrees (13%). Genome-wide linkage data were then pooled to perform a combined linkage analysis for these families. Linkage signals reaching a suggestive level of significance were found on chromosomes 6p22.3 (LOD = 3.0), 11q14.1–14.3 (LOD = 2.4), and 20p11.21–q11.21 (LOD = 2.5). For chromosome 11, stronger evidence of linkage (LOD = 3.3) was observed among pedigrees with an average at diagnosis of 65 years or younger. Other chromosomes that showed evidence for heterogeneity in linkage across strata were chromosome 7, with the strongest linkage signal among pedigrees without male-to-male disease transmission (7q21.11, LOD = 4.1), and chromosome 21, with the strongest linkage signal among pedigrees that had African American ancestry (21q22.13–22.3; LOD = 3.2). Our findings suggest several regions that may contain genes which, when mutated, predispose men to develop a more aggressive prostate cancer phenotype. This provides a basis for attempts to identify these genes, with potential clinical utility for men with aggressive prostate cancer and their relatives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Berry R, Schroeder J, French A, McDonnell S, Peterson B, Cunningham J, Thibodeau S, Schaid D (2000) Evidence for a prostate cancer-susceptibility locus on chromosome 20. Am J Hum Genet 67:82–91
Berthon P, Valeri A, Cohen-Akenine A, Drelon E, Paiss T, Wohr G, Latil A, Millasseau P, Mellah I, Cohen N, Blanche H, Bellane-Chantelot C, Demenais F, Teillac P, Le Duc A, de Petriconi R, Hautmann R, Chumakov I, Bachner L, Maitland NJ, Lindereeau R, Vogel W, Fournier G, Mangin P, Cussenot O (1998) Predisposing gene for early-onset prostate cancer, localized on chromosome 1q42.2–43. Am J Hum Genet 62:1416–1424
Camp NJ, Farnham JM, Cannon-Albright LA (2005) Genomic search for prostate cancer predisposition loci in Utah pedigrees. Prostate 65:365–374
Carpten J, Nupponen N, Isaacs S, Sood R, Robbins C, Xu J, Faruque M, et al (2002) Germline mutations in the ribonuclease L gene in families showing linkage with HPC1. Nat Genet 30:181–184
Carter B, Bova G, Beaty T, Steinberg G, Childs B, Isaacs W, Walsh P (1993) Hereditary prostate cancer: epidemiologic and clinical features. J Urol 150:797–802
Chang BL, Isaacs SD, Wiley KE, Gillanders EM, Zheng SL, Meyers DA, Walsh PC, Trent JM, Xu J, Isaacs WB (2005) Genome-wide screen for prostate cancer susceptibility genes in men with clinically significant disease. Prostate 64:356–361
Cunningham JM, McDonnell SK, Marks A, Hebbring S, Anderson SA, Peterson BJ, Slager S, French A, Blute ML, Schaid DJ, Thibodeau SN (2003) Genome linkage screen for prostate cancer susceptibility loci: results from the Mayo Clinic Familial Prostate Cancer Study. Prostate 57:335–346
Easton DF, Schaid DJ, Whittemore AS, Isaacs WJ (2003) Where are the prostate cancer genes?—A summary of eight genome wide searches. Prostate 57:261–269
Edwards S, Meitz J, Eeles R, Evans C, Easton D, Hopper J, Giles G, Foulkes WD, Narod S, Simard J, Badzioch M, Mahle L (2003) Results of a genome-wide linkage analysis in prostate cancer families ascertained through the ACTANE consortium. Prostate 57:270–279
Etzioni R, Penson DF, Legler JM, di Tommaso D, Boer R, Gann PH, Feuer EJ (2002) Overdiagnosis due to prostate-specific antigen screening: lessons from U.S. prostate cancer incidence trends. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:981–990
Feingold E, Brown PO, Siegmund D (1993) Gaussian models for genetic linkage analysis using complete high-resolution maps of identity by descent. Am J Hum Genet 53:234–251
Gibbs M, Stanford JL, McIndoe RA, Jarvik GP, Kolb S, Goode EL, Chakrabarti L, Schuster EF, Buckley VA, Miller EL, Brandzel S, Li S, Hood L, Ostrander EA (1999) Evidence for a rare prostate cancer-susceptibility locus at chromosome 1p36. Am J Hum Genet 64:776–787
Gillanders EM, Xu J, Chang BL, Lange EM, Wiklund F, Bailey-Wilson JE, Baffoe-Bonnie A, et al (2004) Combined genome-wide scan for prostate cancer susceptibility genes. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1240–1247
Goddard KA, Witte JS, Suarez BK, Catalona WJ, Olson JM (2001) Model-free linkage analysis with covariates confirms linkage of prostate cancer to chromosomes 1 and 4. Am J Hum Genet 68:1197–1206
Grönberg H (2003) Prostate cancer epidemiology. Lancet 361:859–864
Hsieh C-L, Oakley-Girvan I, Balise RR, Halpern J, Gallagher RP, Wu AH, Kolonel LN, O’Brien LE, Lin IG, Van Den Berg DJ, Teh CZ, West DW, Whittemore AS (2001) A genome screen of families with multiple cases of prostate cancer: evidence of genetic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet 69:148–158
Janer M, Friedrichsen DM, Stanford JL, Badzioch MD, Kolb S, Deutsch K, Peters MA, Goode EL, Welti R, DeFrance HB, Iwasaki L, Li S, Hood L, Ostrander EA, Jarvik GP (2003) Genomic scan of 254 hereditary prostate cancer families. Prostate 57:309–319
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ (2004) Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin 54:8–29
Johns LE, Houlston RS (2003) A systematic review and meta-analysis of familial prostate cancer risk. BJU Int 91:789–794
Kong A, Cox NJ (1997) Allele-sharing models: LOD scores and accurate linkage tests. Am J Hum Genet 61:1179–1188
Kong A, Gudbjartsson D, Sainz J, Jonsdottir G, Gudjonsson S, Richardsson B, Sigurdardottir S, Barnard B, Hallbeck B, Masson M, Shlien A, Palsson S, Frigge M, Thorgeirsson T, Gulcher J, Stefansson K (2002) A high-resolution recombination map of the human genome. Nat Genet 31:241–247
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES (1996) Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet 58:1347–1363
Lander E, Kruglyak L (1995) Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting results. Nature Genet 11:241–247
Lange EM, Gillanders EM, Davis CC, Brown WM, Campbell JK, Jones M, Gildea D, Riedesel E, Albertus J, Freas-Lutz D, Markey C, Giri V, Dimmer JB, Montie JE, Trent JM, Cooney KA (2003) Genome-wide scan for prostate cancer susceptibility genes using families from the University of Michigan prostate cancer genetics project finds evidence for linkage on chromosome 17 near BRCA1. Prostate 57:326–334
Lange EM, Ho LA, Beebe-Dimmer JL, Wang Y, Gillanders EM, Trent JM, Lange LA, Wood DP, Cooney KA (2006) Genome-wide linkage scan for prostate cancer susceptibility genes in men with aggressive disease: significant evidence for linkage at chromosome 15q12. Hum Genet 119:400–407
Lin DY (2005) An efficient Monte Carlo approach to assessing statistical significance in genomic studies. Bioinformatics 21:781–787
Lindor NM, Greene MH, Program tMFC (1998) The concise handbook of family cancer syndromes. J Natl Cancer Inst 14:1039–1071
Matsui H, Suzuki K, Ohtake N, Nakata S, Takeuchi T, Yamanaka H, Inoue I (2004) Genomewide linkage analysis of familial prostate cancer in the Japanese population. J Hum Genet 49:9–15
Nelson WG, De Marzo AM, DeWeese TL, Isaacs WB (2004) The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. J Urol 172:S6–S11; discussion S11–S12
Neville PJ, Conti DV, Paris PL, Levin H, Catalona WJ, Suarez BK, Witte JS, Casey G (2002) Prostate cancer aggressiveness locus on chromosome 7q32–q33 identified by linkage and allelic imbalance studies. Neoplasia 4:424–431
Neville PJ, Conti DV, Krumroy LM, Catalona WJ, Suarez BK, Witte JS, Casey G (2003) Prostate cancer aggressiveness locus on chromosome segment 19q12–q13.1 identified by linkage and allelic imbalance studies. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 36:332–339
Ostrander EA, Stanford JL (2000) Genetics of prostate cancer: too many loci, too few genes. Am J Hum Genet 67:1367–1375
Paiss T, Worner S, Kurtz F, Haeussler J, Hautmann RE, Gschwend JE, Herkommer K, Vogel W (2003) Linkage of aggressive prostate cancer to chromosome 7q31–33 in German prostate cancer families. Eur J Hum Genet 11:17–22
Schaid D (2004) The complex genetic epidemiology of prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet 13(Review Issue):R103–R121
Schaid DJ, Chang BL (2005) Description of the International Consortium For Prostate Cancer Genetics, and failure to replicate linkage of hereditary prostate cancer to 20q13. Prostate 63:276–290
Schleutker J, Baffoe-Bonnie AB, Gillanders E, Kainu T, Jones MP, Freas-Lutz D, Markey C, Gildea D, Riedesel E, Albertus J, Gibbs KD Jr, Matikainen M, Koivisto PA, Tammela T, Bailey-Wilson JE, Trent JM, Kallioniemi OP (2003) Genome-wide scan for linkage in Finnish hereditary prostate cancer (HPC) families identifies novel susceptibility loci at 11q14 and 3p25–26. Prostate 57:280–289
Slager S, Schaid D, Cunningham J, McDonnell S, Marks A, Peterson B, Hebbring S, Anderson S, French A, Thibodeau S (2003) Confirmation of linkage of prostate cancer aggressiveness with chromosome 19q. Am J Hum Genet 72:759–762
Slager SL, Zarfas KE, Brown WM, Lange EM, McDonnell SK, Wojno KJ, Cooney KA (2006) Genome-wide linkage scan for prostate cancer aggressiveness loci using families from the University of Michigan Prostate Cancer Genetics Project. Prostate 66:173–179
Smith JR, Freije D, Carpten JD, Grönberg H, Xu J, Isaacs SD, Brownstein MJ, Bova GS, Guo H, Bujinovszky P, Nusskern DR, Damber JE, Bergh A, Emanuelsson M, Kallioniemi OP, Walker-Daniels J, Bailey-Wilson JE, Beaty TH, Meyers DA, Walsh PC, Collins FS, Trent JM, Isaacs WB (1996) Major susceptibility locus for prostate cancer on chromosome 1 suggested by a genome-wide search. Science 274:1371–1374
Stanford J, McDonnell S, Friedrichsen D, Carlson E, Kolb S, Deutsch K, Janer M, Hood L, Ostrander E, Schaid D (2006) Prostate cancer and genetic susceptibility: a genome scan incorporating disease aggressiveness. Prostate 66:317–325
Suarez BK, Lin J, Burmester JK, Broman KW, Weber JL, Banerjee TK, Goddard KAB, Witte JS, Elston RC, Catalona WJ (2000) A genome screen of multiplex prostate cancer sibships. Am J Hum Genet 66:933–944
Tavtigian S, Simard J, Teng D, Abtin V, Baumgard M, Beck A, Camp N, et al (2001) A strong candidate prostate cancer susceptibility gene at chromosome 17p. Nat Genet 27:172–180
Whittemore AS, Halpern J (2001) Problems in the definition, interpretation, and evaluation of genetic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet 68:457–465
Wiklund F, Gillanders EM, Albertus JA, Bergh A, Damber JE, Emanuelsson M, Freas-Lutz DL, Gildea DE, Goransson I, Jones MS, Jonsson BA, Lindmark F, Markey CJ, Riedesel EL, Stenman E, Trent JM, Grönberg H (2003) Genome-wide scan of Swedish families with hereditary prostate cancer: suggestive evidence of linkage at 5q11.2 and 19p13.3. Prostate 57:290–297
Witte J, Goddard K, Conti D, Elston R, Lin J, Suarez B, Broman K, Burmester J, Weber J, Catalona W (2000) Genomewide scan for prostate cancer-aggressiveness loci. Am J Hum Genet 67:92–99
Witte JS, Suarez BK, Thiel B, Lin J, Yu A, Banerjee TK, Burmester JK, Casey G, Catalona WJ (2003) Genome-wide scan of brothers: replication and fine mapping of prostate cancer susceptibility and aggressiveness loci. Prostate 57:298–308
Xu J (2000) Combined analysis of hereditary prostate cancer linkage to 1q24–25: results from 772 hereditary prostate cancer families from the International Consortium for Prostate Cancer Genetics. Am J Hum Genet 66:945–957
Xu J, Meyers D, Freije D, Isaacs S, Wiley K, Nusskern D, Ewing C, et al (1998) Evidence for a prostate cancer susceptibility locus on the X chromosome. Nat Genet 20:175–179
Xu J, Zheng SL, Hawkins GA, Faith DA, Kelly B, Isaacs SD, Wiley KE, Chang B, Ewing CM, Bujinovszky P, Carpten JD, Bleecker ER, Walsh PC, Trent JM, Meyers DA, Isaacs WB (2001) Linkage and association studies of prostate cancer susceptibility: evidence for linkage at 8p22–23. Am J Hum Genet 69:341–350
Xu J, Zheng SL, Komiya A, Mychaleckyj JC, Isaacs SD, Hu JJ, Sterling D, et al (2002) Germline mutations and sequence variants of the macrophage scavenger receptor 1 gene are associated with prostate cancer risk. Nat Genet 32:321–325
Xu J, Gillanders EM, Isaacs SD, Chang BL, Wiley KE, Zheng SL, Jones M, Gildea D, Riedesel E, Albertus J, Freas-Lutz D, Markey C, Meyers DA, Walsh PC, Trent JM, Isaacs WB (2003) Genome-wide scan for prostate cancer susceptibility genes in the Johns Hopkins hereditary prostate cancer families. Prostate 57:320–325
Xu J, Dimitrov L, Chang BL, Adams TS, Turner AR, Meyers DA, Eeles RA, et al (2005) A combined genomewide linkage scan of 1,233 families for prostate cancer-susceptibility genes conducted by the international consortium for prostate cancer genetics. Am J Hum Genet 77:219–229
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the many families who participated in this study and to the many urologists who kindly assisted us by providing information and access to their patients. All members of the ICPCG are supported by the U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS), National Institutes of Health (CA89600). Additional support to participating groups, or members within groups, follows. ACTANE Group: Genotyping and statistical analysis for this study and recruitment of U.K. families was supported by Cancer Research U.K. Additional support was provided by the Prostate Cancer Charitable Trust (now Prostate Cancer Research Foundation), The Times Christmas Appeal, and the Institute of Cancer Research. Genotyping was conducted in the Jean Rook Gene Cloning Laboratory, which is supported by BREAKTHROUGH Breast Cancer-Charity 328323. The funds for the ABI 377 used in this study were generously provided by the legacy of the late Marion Silcock. We thank Mrs Sheila Seal and Mrs Anita Hall for kindly storing and logging the samples that were provided. D.F.E. is a principal research fellow of Cancer Research U.K. Recruitment of Australian PC-affected families was funded by National Health and Medical Research Council grant 940934 and was further supported by Tattersall’s and the Whitten Foundation; infrastructure was provided by the Cancer Council Victoria. We acknowledge the work of study coordinator Margaret Staples; the research team of Bernadette McCudden, John Connal, Richard Thorowgood, Chris Costa, Melodie Kevan, and Sue Palmer; and Jolanta Karpowicz, for DNA extractions. The Texas study of familial PC was initiated by the Department of Epidemiology, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. M.B. was supported by NCI post-doctoral fellowship in Cancer Prevention R25. Additional support to W.D.F. was supplied by grant DAMD-17-00-10033. BC/CA/HI Group: USPHS CA67044. JHU Group: USPHS CA58236 (W.B.I.), CA95052-01 (J.X.), CA106523-01A1 (J.X.). Genotyping for the JHU, Michigan, Tampere, and Umeå groups were performed by Elizabeth Gillanders, MaryPat Jones, Derk Gildea, Erica Riedesel, Julie Albertus, Diana Freas-Lutz, Carol Markey, John Carpten, and Jeff Trent at the National Human Genome Research Institute, NIH. Mayo Clinic Group: USPHS CA72818. Michigan Group: USPHS CA079596. Fred Hutchinson/ISB Group: USPHS CA78835 (E.A.O.), CA080122 (J.L.S.), and from the Prostate Cancer Foundation and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. Tampere Group: Medical Research Fund of Tampere University Hospital, Reino Lahtikari Foundation, Finnish Cancer Organizations, Sigrid Juselius Foundation and Academy of Finland (grant number 201480). Ulm Group: Deutsche Krebshilfe, grant number 70-3111-V03. Umeå Group: Grants from the Swedish Cancer Society (Cancerfonden) and Stiftelsen för Strategisk Forskning. Utah Group: NIH National Cancer Institute grant number R01 CA90752 (to L.A.C.). National Institutes of Health grant number K07 CA98364 (to N.J.C.). Data collected for this publication was assisted by the Utah Cancer Registry supported by National Institutes of Health Contract NO1-PC-35141, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program, with additional support from the Utah Department of Health and the University of Utah. Partial support for all datasets within the Utah Population Database (UPDB) was provided by the University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute. Public Health Services research grant number M01-RR00064 from the National Center for Research Resources. Genotyping services were provided by the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR). CIDR is fully funded through a federal contract from the National Institutes of Health to The Johns Hopkins University, contract number N01-HG-65403. Washington University Group: Urological Research Foundation.
Mayo Clinic
Authors: Daniel J. Schaid, Shannon K. McDonnell, Katherine E. Zarfas, Julie M. Cunningham, Scott Hebbring, Stephen N. Thibodeau
Affiliations: Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA (D.J.S., S.K.M, K.E.Z, J.M.C., S.H., and S.N.T.)
ACTANE
Authors: Rosalind A. Eeles, Douglas F. Easton, William D. Foulkes, Jacques Simard, Graham G. Giles, John L. Hopper, Lovise Mahle, Pal Moller, Michael Badzioch, D. Timothy Bishop, Chris Evans, Steve Edwards, Julia Meitz, Sarah Bullock, Questa Hope, Michelle Guy, The ACTANE Consortium
Affiliations: Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden National Health Service Trust Foundation Hospital, Sutton, UK (R.A.E., S.E., J.M., S.B., Q.H., and M.G.); Cancer Research U.K. Genetic Epidemiology Unit, Strangeways Research Labs, Cambridge, UK (D.F.E. and C.E.); Program in Cancer Genetics, Departments of Oncology and Human Genetics, McGill University, Montreal, Canada (W.D.F.); Cancer Genomics Laboratory, Centre hospitalier de l’Universite Laval Research Centre, Sainte-Foy, QC, Canada (J. Simard); Cancer Epidemiology Centre, Cancer Council Victoria (G.G.G.), and Centre for Genetic Epidemiology, University of Melbourne, Carlton, Australia (J.L.H.); Unit of Medical Genetics, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo, Norway (L.M. and P.M.); Cancer Research U.K. Genetic Epidemiology Laboratory, St. James’ University Hospital, Leeds, UK (T.B.); MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA (M.B)
BC/CA/HI
Authors: Chih-lin Hsieh, Jerry Halpern, Raymond R. Balise, Ingrid Oakley-Girvan, Alice S. Whittemore
Affiliations: University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA (C.-l.H.); Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, USA (J.H., R.N.B., and A.S.W.); Northern California Cancer Center, Union City and Stanford, USA (I.O.-G.)
Data Coordinating Center
Authors: Jianfeng Xu, Latchezar Dimitrov, Bao-Li Chang, Tamara S. Adams, Aubrey R. Turner, Deborah A. Meyers
Affiliations: Center for Human Genomics, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC, USA (J.X., L.D., B.-L.C., T.S.A., A.R.T., and D.A.M.)
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/Institute for Systems Biology
Authors: Danielle M. Friedrichsen, Kerry Deutsch, Suzanne Kolb, Marta Janer, Leroy Hood, Elaine A. Ostrander, Janet L. Stanford
Affiliations: Divisions of Human Biology (D.M.F.) and Public Health Sciences (S.K. and J.L.S.), Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, and Institute for Systems Biology (K.D., M.J., and L.H.), Seattle, USA
Johns Hopkins University
Authors: Charles M. Ewing, Marta Gielzak, Sarah D. Isaacs, Patrick C. Walsh, Kathleen E. Wiley, William B. Isaacs
Affiliations: Department of Urology, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions (C.M.E., M.G., S.D.I. P.C.W., K.E.W., and W.B.I), and Inherited Disease Research Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, NIH (J.B.-W.), Baltimore, USA
University of Michigan
Authors: Ethan M. Lange, Lindsey A. Ho, Jennifer L. Beebe-Dimmer, David P. Wood, Kathleen A. Cooney
Affiliations: Departments of Genetics and Biostatistics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA (E.M.L. and L.A.H); Departments of Internal Medicine and Urology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA (J.L.B.-D., D.P.W, and K.A.C.)
National Institutes of Health
Authors: Daniela Seminara
Affiliations: Cancer Genetics Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, (E.A.O.), National Cancer Institute (NCI) (D.S.), and Inherited Disease Research Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, (J.B-W.), National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA
University of Tampere and Tampere University Hospital
Authors: Tarja Ikonen, Agnes Baffoe-Bonnie, Henna Fredriksson, Mika P. Matikainen, Teuvo LJ Tammela, Joan Bailey-Wilson, Johanna Schleutker
Affiliations: University of Tampere and Tampere University Hospital, Tampere, Finland (T.I., H.F., M.P.M. T.L.T., and J. Schleutker); Fox Chase Cancer Center, Division of Population Science, Philadelphia, USA (A.B.-B.)
University of Ulm
Authors: Christiane Maier, Kathleen Herkommer, Josef J. Hoegel, Walther Vogel, Thomas Paiss
Affiliations: Abteilung Humangenetik, Universität Ulm, Ulm, Germany (C.M., J.J.H., and W.V.), and Urologische Universitätsklinik und Poliklinik, Abteilung für Urologie und Kinderurologie (K.H. and T.P.), Ulm, Germany
University of Umeå
Authors: Fredrik Wiklund, Monica Emanuelsson, Elisabeth Stenman, Björn-Anders Jonsson, Henrik Grönberg
Affiliations: Department of Radiation Sciences, Oncology, University of Umeå, Umeå, Sweden (F.W., M.E., E.S., B.-A.J., and H.G.)
University of Utah
Authors: Nicola J. Camp, James Farnham, Lisa A. Cannon-Albright
Affiliations: Division of Genetic Epidemiology, Department of Biomedical Informatics, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, USA (N.J.C., J.F., and L.C.A)
Washington University
Authors: William J. Catalona, Brian K. Suarez, and Kimberly A. Roehl
Affiliations: Department of Urology and the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA (W.J.C.); Department of Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA (B.K.S and K.A.R.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
The names of all authors and their affiliations are listed in the Acknowledgements. The fact that Dr Schaid’s name is given here for purposes of correspondence should not be taken to imply that he played the sole leading part in writing this article.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0287-x
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaid, D.J., Investigators of the International Consortium for Prostate Cancer Genetics. Pooled genome linkage scan of aggressive prostate cancer: results from the International Consortium for Prostate Cancer Genetics. Hum Genet 120, 471–485 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0219-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0219-9