Abstract
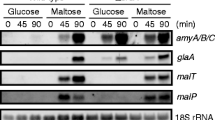
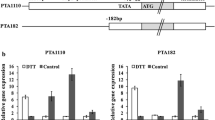
We have cloned a regulatory gene for amylase synthesis in Aspergillus oryzae. This gene, amyR, encodes a 604-amino acid transcriptional activator with a Cys6 zinc cluster, that shows extensive homology to the DNA binding domain of GAL4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The DNA binding domain of amyR binds to two types of sequences found in a number of promoters from Aspergillus genes coding for starch-degrading enzymes. One type of binding site is characterized by two CGG triplets separated by eight nucleotides. The other type has only one CGG triplet, which is followed by the sequence AAATTTAA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 March 1999 / Accepted: 24 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petersen, K., Lehmbeck, J. & Christensen, T. A new transcriptional activator for amylase genes in Aspergillus . Mol Gen Genet 262, 668–676 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380051129
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380051129