Abstract
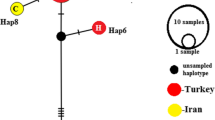
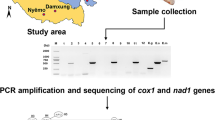
The definitive identification of Echinococcus species is currently carried out by sequencing and phylogenetic strategies. However, the application of polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) patterns is not broadly used as a result of heterogeneity traits of Echinococcus genome in different regions of the world. Therefore, designing and conducting a standardized pattern should indigenously be considered in under-studied areas. In this investigation, an in silico mapping was designed and developed for eight Echinococcus spp. on the basis of regional sequences in Iran and the world. The numbers of 60 Echinococcus isolates were collected from the liver and lungs of 15 human, 15 sheep, 15 cattle, and 15 camel cases in Semnan province, Central Iran. DNA samples were extracted and examined by polymerase chain reaction of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) and PCR-RFLP via Rsa1 endonuclease enzyme. Moreover, 15 amplicons of cytochrome oxidase 1 (Cox1) were directly sequenced in order to identify the strains/haplotypes. PCR-RFLP and phylogenetic analyses revealed firmly the presence of the G1 and G6 genotypes with heterogeneity (three novel haplotypes) of Cox1 gene although no other expected genotypes were found in the region. Finding shows that the identification of novel haplotypes along with discrimination of Echinococcus spp. through regional patterns can unambiguously illustrate the real taxonomic status of parasite in Central Iran.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirmajdi MM, Sankian M, Mashhadi IE, Varasteh A, Vahedi F, Sadrizadeh A, Spotin A (2011) Apoptosis of human lymphocytes after exposure to hydatid fluid. Iran J Parasitol 6:9–16
Alvarez Rojas CA, Romig T, Lightowlers MW (2014) Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes infecting humans–review of current knowledge. Int J Parasitol 44(1):9–18
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus D (1995) A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus. Parasitology 110:317–328
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus D (1992) Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:165–173
Bowles J, McManus D (1993) NADH dehydrogenase 1 gene sequences compared for species and strains of the genus Echinococcus. Int J Parasitol 23:969–972
Bowles J, McManus D, Donald P (1993a) Molecular variation in Echinococcus. Acta Trop 53:291–305
Bowles J, McManus D, Donald P (1993b) Rapid discrimination of Echinococcus species and strains using a polymerase chain reaction-based RFLP method. Mol Biochem Parasitol 57:231–239
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9(10):1657–1659
Eckert J, Thompson RCA (1997) Intraspecific variation of Echinococcus granulosus and related species with emphasis on their infectivity to humans. Acta Trop 64:19–34
Fasihi Harandi M, Hobbs RP, Adams PJ, Mobedi I, Morgan-Ryan UM, Thompson RCA (2002) Molecular and morphological characterization of Echinococcus granulosus of human and animal origin in Iran. Parasitology 125:367–373
Gerbi SA (1986) The evolution of eukaryotic ribosomal DNA. BioSystems 19:247–258
Gholami S, Sosari M, Fakhar M, Sharif M, Daryani A, Hashemi MB, Vahadi M (2012) Molecular Characterization of Echinococcus granulosus from Hydatid Cysts Isolated from Human and Animals in Golestan Province, North of Iran. Iran J Parasitol 7:8
Hobbs RP, Lymbery AJ, Thompson RCA (1990) Rostellar hook morphology of Echinococcus granulosus (Batsch, 1786) from natural and experimental Australian hosts, and its implications for strain recognition. Parasitology 101:273–281
Huson DH, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol Biol Evol 23:254–267
Ito A, Dorjsuren T, Davaasuren A, Yanagida T, Sako Y, Nakaya K, Chuluunbaatar G (2014) Cystic echinococcoses in Mongolia: molecular identification, serology and risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(6):e2937
Jamali R, Ghazanchaei A, Asgharzadeh M (2004) Identification and characterization of Echinococcus granulosus by PCR-RFLP technique in Tabriz district. J Parasit Dis 28:69–72
McManus DP, Bryant C (1995) Biochemistry, physiology and molecular biology of Echinococcus. Echinococcus and hydatid disease. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 135–181
McManus DP, Rishi AK (1989) Genetic heterogeneity within Echinococcus granulosus: isolates from different hosts and geographical areas characterized with DNA probes. Parasitology 99:17–29
Nakao M, Yanagida T, Okamoto M, Knapp J, Nkouawa A, SakoY IA (2010) State-of-the-art Echinococcus and Taenia: phylogenetic taxonomy of human-pathogenic tapeworms and its application to molecular diagnosis. Infect Genet Evol 10:444–452
Nakao M, Lavikainen A, Yanagida T, Ito A (2013) Phylogenetic systematics of thegenus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae). Int J Parasitol 43:1017–1029
Okamoto M, Bessho Y, Kamiya M, Kurosawa T, Horii T (1995) Phylogenetic relationships withinTaenia taeniaeformis variants and other taeniid cestodes inferred from the nucleotide sequence of the cytochromec oxidase subunit I gene. Parasitol Res 81:451–458
Pour AA, Hosseini SH, Shayan P (2011) Comparative genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus infecting buffalo in Iran using cox1 gene. Parasitol Res 108:1229–1234
Rokni MB (2009) Echinococcosis/hydatidosis in Iran. Iran J Parasitol 4:1–16
Rosenzvit MC, Zhang LH, Kamenetzky L, Canova SG, Guarnera EA, McManusDP DP (1999) Genetic variation and epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus in Argentina. Parasitology 118:523–530
Schantz PM, Colli C, Cruz-Reyes A, Prezioso U (1976) sylvatic echinococcosis in Argentina. II. Susceptibility of wild carnivores to Echinococcus granulosus (Batsch, 1786) and host-induced morphological variation. Trop Med Parasitol 27:70–78
Sharafi SM, Rostami nejad M, Moazeni M, Yousefi M, Saneie B, Hosseinisafa A, Yousofi-Darani H (2014) Echinococcus granulosus genotypes in Iran. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 7:82
Sharbatkhori M, Harandi MF, Mirhendi H, Hajialilo E, Kia EB (2011) Sequence analysis of cox1 and nad1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus G3 genotype in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from central Iran. Parasitol Res 108:521–527
Smyth JD, McManus DP, Barrett NJ, Bryceson A, Cowie AGA (1980) In vitro culture of human hydatid material. Lancet 1:202–203
Spotin A, Majdi MMA, Sankian M, Varasteh A (2012) The study of apoptotic bifunctional effects in relationship between host and parasite in cystic echinococcosis: a new approach to suppression and survival of hydatid cyst. Parasitol Res 110:1979–1984
Thompson RCAJ, Jenkins DJ (2014) Echinococcus as a model system: biology and epidemiology. Int J Parasitol 44:865–877
Thompson RCA (2013) Parasite zoonoses and wildlife: one health, spillover andhuman activity. Int J Parasitol 43:1079–1088
Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ (1988) The Nature, Extent and Significance of Variation within the Genus Echinococcus. Adv Parasitol 27:209–258
Umhang G, Chihai O, Boué F (2014) Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in a hyperendemic European focus, the Republic of Moldova. Parasitol Res 113(12):4371–4376
Van Herwerden L, Gasser RB, Blair D (2000) ITS-1 ribosomal DNA sequence variants are maintained in different species and strains of Echinococcus. Int J Parasitol 30:157–169
Villalobos N, González L, Morales J, De Aluja A, Jiménez M, Blanco M, Harrison L, Parkhouse R, Gárate T (2007) Molecular identification ofEchinococcus granulosus genotypes (G1 and G7) isolated from pigs in Mexico. Vet Parasitol 147:185–189
Wachira TM, Bowles J, Zeyhle E, McManus DP (1993) Molecular examination of the sympatry and distribution of sheep and camel strains of Echinococcus granulosus in Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg 48:473–479
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Youssefi MR, Tabaripour R, Omrani VF, Spotin A, Esfandiari B (2013) Genotypic characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in Iranian goats. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 3:362–366
Zhang L, Eslami A, Hosseini SH, McManus DP (1998) Indication of the presence of two distinct strains of Echinococcus granulosus in Iran by mitochondrial DNA markers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 59:171–174
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran. This article is derived from the master’s thesis of the third author (Thesis No. 92/1-4/7). We should thank all staff of Parasitology Department of Mazandaran, Semnan, and Shahrood Universities of Medical Sciences for their collaboration
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spotin, A., Gholami, S., Najafi Nasab, A. et al. Designing and conducting in silico analysis for identifying of Echinococcus spp. with discrimination of novel haplotypes: an approach to better understanding of parasite taxonomic. Parasitol Res 114, 1503–1509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4334-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4334-1