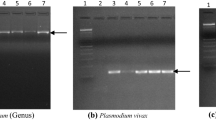
Abstract
Malaria is a complex disease that varies widely in epidemiology and clinical manifestation in the southeastern part of Turkey. In many regions of the world, chloroquine (CQ) has been the standard treatment for Plasmodium vivax. However, the resistance of the Plasmodium species to antimalarial drugs has become an increasing problem and a concern worldwide. Our target was to determine the Plasmodium species in the southeast region of Turkey and the therapeutic efficacy of CQ used in the treatment of malaria. Blood samples were collected from 180 patients infected with malaria before and after CQ treatment and were subjected to DNA isolation. The isolated DNA was amplified by a seminested multiplex polymerase chain reaction (SnM-PCR) including primers selected on Plasmodium small subunit ribosomal RNA (ssrRNA) genes for identification of the malaria species. The SnM-PCR results showed that only P. vivax exists in this province. It was also determined that there is a therapeutic failure to CQ in 9.5% of patients. These were the second report on identification of P. vivax and the third report on determination of the therapeutic failure in patients who used CQ to cure human malaria in the southeastern region of Turkey. Our results demonstrate that the SnM-PCR is a sensitive, specific, and a rapid tool for the differentiation of malaria species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkafa F, Simsek Z, Dilmec F, Baytak S (2002) Epidemiology of malaria in Sanliurfa. Acta Parasitologica Turcica 26:143–146
Aslan G, Seyrek A, Kocagoz T, Ulukanligil M, Erguven S, Gunalp A (2007) The diagnosis of malaria and identification of Plasmodium species by polymerase chain reaction in Turkey. Parasitol Int 56:217–220
Boonma P, Christensen PR, Suwanarusk R, Price RN, Russell B, Lek-Uthai U (2007) Comparison of three molecular methods for the detection and speciation of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum. Malar J 15(6):124
Fryauff DJ, Tuti S, Mardi A, Masbar S, Patipelohi R, Leksana B, Kain KC, Bangs MJ, Richie TL, Baird JK (1998) Chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium vivax in transmigration settlements of West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Am J Trop Med Hyg 59:513–518
Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Grüner AC, Rénia L, Letourneur F, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, Snounou G (2005) Practical PCR genotyping protocols for Plasmodium vivax using Pvcs and Pvmsp1. Malar J 4:1–13
Kho WG, Chung JY, Sim EJ, Kim MY, Kim DW, Jongwutiwes S, Tanabe K (2003) A multiplex polymerase chain reaction for a differential diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Parasitol Int 52:229–236
Kimura M, Kaneko O, Liu Q, Zhou M, Kawamoto F, Wataya Y, Otani S, Yamaguchi Y, Tanabe K (1997) Identification of the four species of human malaria parasites by nested PCR that targets variant sequences in the small subunit rRNA gene. Parasitol Int 46:91–95
Kurcer MA, Simsek Z, Zeyrek FY, Atay S, Celik H, Kat I, Topluoglu S (2004) Efficacy of chloroquine in the treatment of Plasmodium vivax malaria in Turkey. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 98:447–451
Kurcer MA, Simsek Z, Kurcer Z (2006) The decreasing efficacy of chloroquine in the treatment of Plasmodium vivax malaria, in Sanliurfa, south-eastern Turkey. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 100:109–113
Mehlotra RK, Kasehagen LJ, Baisor M, Lorry K, Kazura JW, Bockarie MJ, Zimmerman PA (2002) Malaria infections are randomly distributed in diverse holoendemic areas of Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 67:555–562
Mert A, Ozaras R, Tabak F, Bilir M, Ozturk R, Aktuglu Y (2003) Malaria in Turkey: a review of 33 cases. Eur J Epidemiol 18:579–582
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Ratcliff A, Siswantoro H, Kenangalem E, Wuwung M, Brockman A, Edstein MD, Laihad F, Ebsworth EP, Anstey NM, Tjitra E, Price RN (2007) Therapeutic response of multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax to chloroquine and sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine in southern Papua, Indonesia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 101:351–359
Rubio JM, Benito A, Berzosa PJ, Roche J, Puente S, Subirats M, López-Vélez R, García L, Alvar J (1999a) Usefulness of seminested multiplex PCR in surveillance of imported malaria in Spain. J Clin Microbiol 37:3260–3264
Rubio JM, Benito A, Roche J, Berzosa PJ, García ML, Micó M, Edú M, Alvar J (1999b) Semi-nested, multiplex polymerase chain reaction for detection of human malaria parasites and evidence of Plasmodium vivax infection in Equatorial Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 60:183–187
Rubio JM, Roche J, Berzosa PJ, Moyano E, Benito A (2000) The potential utility of the semi-nested multiplex PCR technique for the diagnosis and investigation of congenital malaria. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 38:233–236
Sa JM, Nomura T, Neves J, Baird JK, Wellems TE, del Portillo HA (2005) Plasmodium vivax: allele variants of the mdr1 gene do not associate with chloroquine resistance among isolates from Brazil, Papua, and monkey-adapted strains. Exp Parasitol 109:256–259
Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh J, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA (1999) A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 60:687–692
Tabuk TC, Ulger S (2000) The malaria situation in Turkey. Med Parazitol (Mosk) 2:26–27
The Ministry of Health of Turkey (2002). Turkey Health Report
World Health Organization (2002). A general guide for the assessment of therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine for vivax malaria. URL: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/searo/2002/SEA_MAL_231.pdf
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr JM Rubio (Spain), for providing the sequences of the primers, and the Commission of Scientific Research Projects of Harran University for financial assistance (HÜBAK-371, Turkey).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilmec, F., Kurcer, M.A., Akkafa, F. et al. Monitoring of failure of chloroquine treatment for Plasmodium vivax using polymerase chain reaction in Sanliurfa province, Turkey. Parasitol Res 106, 783–788 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1710-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1710-8