Abstract
Purpose
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (BC) is a highly recurrent disease, with the first recurrences arising shortly after transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB). Topical administration of interleukin-2 (IL-2) has been shown as an effective adjuvant therapy for BC; however, predictive biomarkers that may identify suitable subgroups of patients are lacking. In this pilot study we sought to determine the prognostic value of epigenetic and genetic inactivation of tumour suppressor genes (TSGs) among BC patients treated with IL-2.
Methods
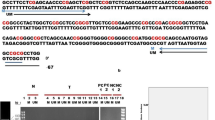
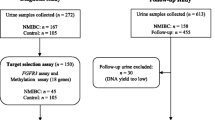
After complete TURB, patients with multifocal superficial BC were treated with five daily intravesical instillations of IL-2. Promoter hypermethylation in six TSGs and the TP53 gene mutations were prospectively assessed by methylation-specific PCR and automated capillary single-strand conformation polymorphism in 21 primary bladder cancer specimens and ten bladder wall biopsies collected during follow-up.
Results
After IL-2 treatment, 9 out of 21 (43%) patients did not develop recurrent tumour within the 1 year of follow-up period. The mean duration of recurrence-free survival in the rest of the study group was 112 days. In the current pilot study, BC with p16 gene hypermethylation had a lower risk of recurrence after treatment with IL-2, as compared to IL-2 treated BC without p16 hypermethylation (p = 0.02). Significant associations were observed between tumour grade and the mean methylation index (p = 0.003), as well as the hypermethylation of the RARβ gene (p = 0.048).
Conclusion
Our preliminary data suggest that DNA methylation biomarkers may assist in selection of BC patients for efficient IL-2 therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amling CL (2001) Diagnosis and management of superficial bladder cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 25(4):219–278
Bakkar AA, Wallerand H, Radvanyi F et al (2003) FGFR3 and TP53 gene mutations define two distinct pathways in urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res 63(23):8108–8112
Bubeník J (2004) Interleukin-2 therapy of cancer. Folia Biol (Praha) 50(3–4):120–130
Bubeník J, Perlmann P, Indrova M, Simova J, Jandlova T, Neuwirt J (1983) Growth inhibition of an MC-induced mouse sarcoma by TCGF (IL 2)-containing preparations. Preliminary report. Cancer Immunol Immunother 14(3):205–206
Den Otter W, Dobrowolski Z, Bugajski A (1998) Intravesical interleukin-2 in T1 papillary bladder carcinoma: regression of marker lesion in 8 of 10 patients. J Urol 159(4):1183–1186
Dhawan D, Hamdy FC, Rehman I et al (2006) Evidence for the early onset of aberrant promoter methylation in urothelial carcinoma. J Pathol 209:336–343
Dranoff G (2004) Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4(1):11–22
Esteller M (2003) Relevance of DNA methylation in the management of cancer. Lancet Oncol 4(6):351–358
Esteller M, Garcia-Foncillas J, Andion E et al (2000a) Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents. N Engl J Med 343(19):1350–1354
Esteller M, Tortola S, Toyota M, Capella G, Peinado MA, Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000b) Hypermethylation-associated inactivation of p14(ARF) is independent of p16(INK4a) methylation and p53 mutational status. Cancer Res 60(1):129–133
Fischer JR, Ohnmacht U, Rieger N, Zemaitis M, Stoffregen C, Manegold C, Lahm H (2007) Prognostic significance of RASSF1A promoter methylation on survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine. Lung Cancer 56(1):115–123
Friedrich MG, Chandrasoma S, Siegmund KD et al (2005) Prognostic relevance of methylation markers in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 41:2769–2778
Gaffen SL, Liu KD (2004) Overview of interleukin-2 function, production and clinical applications. Cytokine 28(3):109–123
Grasso M, Torelli F, Scannapieco G, Franzoso F, Lania C (2001) Neoadjuvant treatment with intravesical interleukin-2 for recurrent superficial transitional bladder carcinoma Ta-T1/G1–2. J Immunother 24(2):184–187
Grossman HB, Liebert M, Antelo M, Dinney CP, Hu SX, Palmer JL, Benedict WF (1998) p53 and RB expression predict progression in T1 bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 4(4):829–834
Herman JG, Baylin SB (2003) Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med 349(21):2042–2054
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB (1996) Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(18):9821–9826
Holmila R, Husgafvel-Pursiainen K (2006) Analysis of TP53 gene mutations in human lung cancer: comparison of capillary electrophoresis single strand conformation polymorphism assay with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and direct sequencing. Cancer Detect Prev 30(1):1–6
Hoque MO, Begum S, Topalogu O et al (2006) Quantitation of promoter methylation of multiple genes in urine DNA and bladder cancer detection. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(14):996–1004
IUAC (2002) IUAC TNM classification of malignant tumors, 6th edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Jankevicius F, Goebell P, Kushima M, Schulz WA, Ackermann R, Schmitz-Dräger BJ (2002) p21 and p53 Immunostaining and survival following systemic chemotherapy for urothelial cancer. Urol Int 69(3):174–180
Jarmalaite S, Jankevicius F, Kurgonaite K, Suziedelis K, Mutanen P, Husgafvel-Pursiainen K (2008) Promoter hypermethylation in tumour suppressor genes shows association with stage, grade and invasiveness of bladder cancer. Oncology 75(3–4):145–151
Josephson DY, Pasin E, Stein JP (2006) Superficial bladder cancer: part 1. Update on etiology, classification and natural history. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6(12):1723−1734
Kawamoto K, Enokida H, Gotanda T et al (2006) p16 INK4a and p14 ARF and methylation as a potential biomarker for human bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339(3):790–796
Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M et al (2005) Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology 66(6 Suppl 1):4−34
Knowles MA (2001) What we could do now: molecular pathology of bladder cancer. Mol Pathol 54(4):215–221
Mostofi FK, Sobin LH, Torlini H (1973) Histological typing of urinary bladder tumors. In: International histological classification of tumors, No 10. World Health Organization, Geneva
Pyrhönen SO (2004) Systemic therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Scand J Surg 93(2):156–161
Ramirez JL, Rosell R, Taron M et al (2005) 14-3-3sigma methylation in pretreatment serum circulating DNA of cisplatin-plus-gemcitabine-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients predicts survival: The Spanish Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 23(36):9105–9112
Reu FJ, Leaman DW, Maitra RR et al (2006) Expression of RASSF1A, an epigenetically silenced tumour suppressor, overcomes resistance to apoptosis induction by interferons. Cancer Res 66(5):2785–2793
Schulz WA (2006) Understanding urothelial carcinoma through cancer pathways. Int J Cancer 119(7):1513–1518
Tada Y, Wada M, Taguchi K et al (2002) The association of Death-associated Protein Kinase hypermethylation with early recurrence in superficial bladder cancers. Cancer Res 62:4048–4053
Veltri RW, Makarov DV (2006) Nucleic acid-based marker approaches to urologic cancers. Urol Oncol 24(6):510–527
Widschwendter M, Siegmund KD, Müller HM et al (2004) Association of breast cancer DNA methylation profiles with hormone receptor status and response to tamoxifen. Cancer Res 64(11):3807–3813
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants B-17/2005 and C-03/2007 from the Lithuanian State Science and Studies Foundation, and COST grant BM0703. We thank Dr. D. Characiejus for organizing IL-2 treatment at the Oncology Institute of Vilnius University and for valuable comments on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarmalaite, S., Andrekute, R., Scesnaite, A. et al. Promoter hypermethylation in tumour suppressor genes and response to interleukin-2 treatment in bladder cancer: a pilot study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 847–854 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0725-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0725-y