Abstract
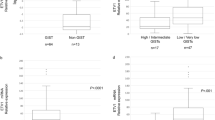
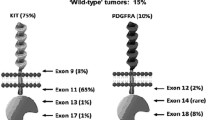
Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs) are rare mesenchymal tumours of the digestive tract and are commonly driven by oncogenic mutations in KIT and PDGFRA genes. Tumour size, location, mitotic index and KIT/PDGFRA mutations are the most important prognostic parameters in GISTs. However, additional studies screening for new molecular prognostic markers in GISTs are missing. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) has been considered as a suppressor of metastasis and a prognostic marker in several neoplasms. In the present study we aimed to examine whether RKIP expression is associated with GIST clinical–pathological features. Using immunohistochemistry, we determined RKIP expression levels in a well-characterised series of 70 GISTs. We found that RKIP is expressed in the great majority of cases, and absent in approximately 9% of GISTs. Additionally, we found that loss of RKIP expression was not due to the promoter methylation as assessed by methylation-specific PCR. Loss of RKIP expression was associated with poor disease-specific survival and with tumour necrosis in GISTs. Furthermore, a statistical tendency was observed between the positive RKIP expression and absence of metastasis. So far, this is the first study assessing RKIP expression levels in GISTs. We conclude that loss of RKIP expression could have an important role as prognostic marker in GISTs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tryggvason G, Gislason HG, Magnusson MK et al (2005) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors in Iceland, 1990–2003: the icelandic GIST study, a population-based incidence and pathologic risk stratification study. Int J Cancer 117:289–293
Nilsson B, Bumming P, Meis-Kindblom JM et al (2005) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: the incidence, prevalence, clinical course, and prognostication in the preimatinib mesylate era—a population-based study in western Sweden. Cancer 103:821–829
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y et al (1998) Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 279:577–580
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A et al (2003) PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 299:708–710
Heinrich MC, Blanke CD, Druker BJ et al (2002) Inhibition of KIT tyrosine kinase activity: a novel molecular approach to the treatment of KIT-positive malignancies. J Clin Oncol 20:1692–1703
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Demetri GD et al (2003) Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol 21:4342–4349
Tornillo L, Terracciano LM (2006) An update on molecular genetics of gastrointestinal stromal tumours. J Clin Pathol 59:557–563
Miettinen M, Lasota J (2006) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology, prognosis, and differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 130:1466–1478
Corless CL, Heinrich MC (2008) Molecular pathobiology of gastrointestinal stromal sarcomas. Annu Rev Pathol 3:557–86
Gouveia AM, Pimenta AP, Capelinha AF et al (2008) Surgical margin status and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. World J Surg 32(11):2375–82
Takahashi T, Nakajima K, Nishitani A et al (2007) An enhanced risk-group stratification system for more practical prognostication of clinically malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Clin Oncol 12:369–374
Wardelmann E, Buttner R, Merkelbach-Bruse S et al (2007) Mutation analysis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: increasing significance for risk assessment and effective targeted therapy. Virchows Arch 451:743–749
Wardelmann E, Losen I, Hans V et al (2003) Deletion of Trp-557 and Lys-558 in the juxtamembrane domain of the c-kit protooncogene is associated with metastatic behavior of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Cancer 106:887–895
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O et al (2007) MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26:3279–3290
Agaram NP, Wong GC, Guo T et al (2008) Novel V600E BRAF mutations in imatinib-naive and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47:853–859
Martinho O, Gouveia A, Viana-Pereira M et al (2009) Low frequency of MAP kinase signalling pathway alterations in KIT & PDGFRA wild-type GISTs. Histopathology 55:53–62
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S et al (1999) Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature 401:173–177
Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B et al (2000) Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol 20:3079–3085
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS et al (2001) Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 21:7207–7217
Lorenz K, Lohse MJ, Quitterer U (2003) Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature 426:574–579
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Al-Ali W et al (2008) Raf kinase inhibitor protein: mechanism of loss of expression and association with genomic instability. J Clin Pathol 61:524–529
Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M (2004) The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1049–1053
Klysik J, Theroux SJ, Sedivy JM et al (2008) Signaling crossroads: the function of Raf kinase inhibitory protein in cancer, the central nervous system and reproduction. Cell Signal 20:1–9
Bernier I, Jolles P (1984) Purification and characterization of a basic 23 kDa cytosolic protein from bovine brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 790:174–181
Hori N, Chae KS, Murakawa K et al (1994) A human cDNA sequence homologue of bovine phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein. Gene 140:293–294
Seddiqi N, Bollengier F, Alliel PM et al (1994) Amino acid sequence of the Homo sapiens brain 21–23-kDa protein (neuropolypeptide h3), comparison with its counterparts from Rattus norvegicus and Bos taurus species, and expression of its mRNA in different tissues. J Mol Evol 39:655–660
Fu Z, Smith PC, Zhang L et al (2003) Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on suppression of prostate cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:878–889
Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z et al (2004) RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:17515–17523
Schuierer MM, Bataille F, Hagan S et al (2004) Reduction in Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with increased Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Res 64:5186–5192
Schuierer MM, Bataille F, Weiss TS et al (2006) Raf kinase inhibitor protein is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 16:451–456
Zhang L, Fu Z, Binkley C et al (2004) Raf kinase inhibitory protein inhibits beta-cell proliferation. Surgery 136:708–715
Hagan S, Al-Mulla F, Mallon E et al (2005) Reduction of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 11:7392–7397
Lee HC, Tian B, Sedivy JM et al (2006) Loss of Raf kinase inhibitor protein promotes cell proliferation and migration of human hepatoma cells. Gastroenterology 131:1208–1217
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Behbehani AI et al (2006) Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in a survival analysis of colorectal cancer patients 1. J Clin Oncol 24:5672–5679
Li HZ, Wang Y, Gao Y et al (2008) Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on metastasis and progression of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res 6:917–928
Chatterjee D, Sabo E, Tavares R et al (2008) Inverse association between Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma patients: implications for clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14:2994–3001
Zlobec I, Baker K, Minoo P et al (2008) Node-negative colorectal cancer at high risk of distant metastasis identified by combined analysis of lymph node status, vascular invasion, and raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression. Clin Cancer Res 14:143–148
Fu Z, Kitagawa Y, Shen R et al (2006) Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate 66:248–256
Minoo P, Baker K, Goswami R et al (2006) Extensive DNA methylation in normal colorectal mucosa in hyperplastic polyposis. Gut 55(10):1467–1474
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C et al (2002) Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Int J Surg Pathol 10:81–89
Gomes AL, Gouveia A, Capelinha AF et al (2008) Molecular alterations of KIT and PDGFRA in GISTs: evaluation of a Portuguese series. J Clin Pathol 61:203–208
Basto D, Trovisco V, Lopes JM et al (2005) Mutation analysis of B-RAF gene in human gliomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 109:207–210
Dematteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D et al (2000) Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg 231:51–58
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD et al (2002) Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med 347:472–480
Granovsky AE, Rosner MR (2008) Raf kinase inhibitory protein: a signal transduction modulator and metastasis suppressor. Cell Res 18:452–457
Minoo P, Zlobec I, Baker K et al (2007) Loss of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 127:820–827
Houben R, Michel B, Vetter-Kauczok CS et al (2006) Absence of classical MAP kinase pathway signalling in Merkel cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol 126:1135–1142
Akaishi J, Onda M, Asaka S et al (2006) Growth-suppressive function of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Anticancer Res 26:4437–4442
Eves EM, Shapiro P, Naik K et al (2006) Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates aurora B kinase and the spindle checkpoint. Mol Cell 23:561–574
Zhu S, Mc Henry KT, Lane WS et al (2005) A chemical inhibitor reveals the role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein in cell migration. Chem Biol 12:981–991
Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Chatterjee D et al (2004) Inhibition of the Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling pathway, Bcl-xL down-regulation, and chemosensitization of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma B cells by Rituximab. Cancer Res 64:7117–7126
Fougner SL, Bollerslev J, Latif F et al (2008) Low levels of raf kinase inhibitory protein in growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas correlate with poor response to octreotide treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1211–1216
Bonavida B, Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S et al (2008) Novel therapeutic applications of nitric oxide donors in cancer: roles in chemo- and immunosensitization to apoptosis and inhibition of metastases. Nitric Oxide 19:152–157
Acknowledgements
OM is recipient of a PhD fellowship (SFRH/BD/36463/2007) from FCT, Portugal. This study was partially supported by NOVARTIS Oncology, Portugal.
Conflicts of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Olga Martinho and António Gouveia contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinho, O., Gouveia, A., Silva, P. et al. Loss of RKIP expression is associated with poor survival in GISTs. Virchows Arch 455, 277–284 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0821-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0821-z