Abstract
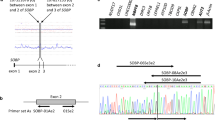
We have shown previously that amplification of chromosomal region 9q34 is the most frequent aberration in enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETL). To determine the minimum amplified 9q34 region and identify possible candidate gene(s), we performed a detailed microsatellite screening and quantitative real-time PCR (QPCR) on 26 ETL cases. Microsatellite analysis revealed allelic imbalance in both ABL1 and NOTCH1 gene loci (microsatellites D9S290–D9S1847 and D9S158 flanking the former and latter genes, respectively) localized in the band 9q34. The results were confirmed by TaqMan-based QPCR showing amplification of ABL1 and NOTCH1 exons in 50% and 65% of cases, respectively. Amplifications of the NOTCH1 gene were more frequent than of the ABL1 gene; moreover, the analyzed NOTCH1 exon consistently displayed higher levels of amplification than ABL1 coding sequences. From 9q34 known genes, NOTCH1 could thus be the primary target of genomic DNA amplification in ETL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aster JC, Xu L, Karnell FG et al (2000) Essential roles for ankyrin repeat and transactivation domains in induction of T-cell leukemia by notch1. Mol Cell Biol 20:7505–7515
Baumgartner AK, Zettl A, Chott A et al (2003) High frequency of genetic aberrations in enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma. Lab Invest 83:1509–1516
Bush G, diSibio G, Miyamoto A et al (2001) Ligand-induced signaling in the absence of furin processing of Notch1. Dev Biol 229:494–502
Carbonnel F, Lavergne A, Messing B et al (1994) Extensive small enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma of low-grade malignancy associated with a new chromosomal translocation. Cancer 73:1286–1291
Collins SJ, Groudine MT (1983) Rearrangement and amplification of c-abl sequences in the human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K-562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80:4813–4817
De Klein A, van Kessel AG, Grosveld G et al (1982) A cellular oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 300:765–767
De Klein A, Hagemeijer A, Bartram CR et al (1986) bcr rearrangement and translocation of the c-abl oncogene in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 68:1369–1375
Deftos ML, Bevan MJ (2000) Notch signaling in T cell development. Curr Opin Immunol 12:166–172
Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC et al (1991) TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell 66:649–661
Ferguson A, Kingstone K (1996) Coeliac disease and malignancies. Acta Paediatr Suppl 412:78–81
Golub TR, Goga A, Barker GF et al (1996) Oligomerization of the ABL tyrosine kinase by the Ets protein TEL in human leukemia. Mol Cell Biol 16:4107–4116
Graux C, Cools J, Melotte C et al (2004) Fusion of NUP214 to ABL1 on amplified episomes in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 36:1084–1089
Howell WM, Leung ST, Jones DB et al (1995) HLA-DRB, -DQA, and -DQB polymorphism in celiac disease and enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Common features and additional risk factors for malignancy. Hum Immunol 43:29–37
Iso T (2001) HERP, a novel heterodimer partner of HES/E(spl) in Notch signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21:6080–6089
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H et al (2001) Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. World Health Organization classification of tumours. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 157–160
Jaiswal S, Traver D, Miyamoto T et al (2003) Expression of BCR/ABL and BCL-2 in myeloid progenitors leads to myeloid leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10002–10007
Jundt F, Anagnostopoulos I, Forster R et al (2002) Activated Notch1 signaling promotes tumor cell proliferation and survival in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 99:3398–3403
Kenner L, Beham-Schmid C, Kerbl R et al (1999) ABL amplification in a patient with lymphoid blast crisis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Virchows Arch 434:255–257
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Morimura T, Goitsuka R, Zhang Y et al (2000) Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by Notch1 in B cells. J Biol Chem 275:36523–36531
Nair P, Somasundaram K, Krishna S (2003) Activated Notch1 inhibits p53-induced apoptosis and sustains transformation by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncogenes through a PI3K-PKB/Akt-dependent pathway. J Virol 77:7106–7112
Nakagawa O (2000) Members of the HRT family of basic helix–loop–helix proteins act as transcriptional repressors downstream of Notch signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13655–13660
Ordentlich P, Lin A, Shen CP et al (1998) Notch inhibition of E47 supports the existence of a novel signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 18:2230–2239
Ott G, Katzenberger T, Siebert R et al (1998) Chromosomal abnormalities in nodal and extranodal CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphomas: infrequent detection of the t(2;5) in extranodal lymphomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 22:114–121
Pear WS, Aster JC, Scott ML et al (1996) Exclusive development of T cell neoplasms in mice transplanted with bone marrow expressing activated Notch alleles. J Exp Med 183:2283–2291
Sade H, Krishna S, Sarin A (2004) The anti-apoptotic effect of Notch-1 requires p56lck-dependent, Akt/PKB-mediated signaling in T cells. J Biol Chem 279:2937–2944
Skorski T, Bellacosa A, Nieborowska-Skorska M et al (1997) Transformation of hematopoietic cells by BCR/ABL requires activation of a PI-3k/Akt-dependent pathway. EMBO J 16:6151–6161
Tanaka K, Arif M, Eguchi M et al (1997) Frequent jumping translocations of chromosomal segments involving the ABL oncogene alone or in combination with CD3-MLL genes in secondary leukemias. Blood 89:596–600
Trainor KJ, Brisco MJ, Wan JH et al (1991) Gene rearrangement in B- and T-lymphoproliferative disease detected by the polymerase chain reaction. Blood 78:192–196
Wright DH, Jones DB, Clark H et al (1991) Is adult-onset coeliac disease due to a low-grade lymphoma of intraepithelial T lymphocytes? Lancet 337:1373–1374
Xie S, Wang Y, Liu J et al (2001) Involvement of Jak2 tyrosine phosphorylation in Bcr–Abl transformation. Oncogene 20:6188–6195
Zettl A, Ott G, Makulik A et al (2002) Chromosomal gains at 9q characterize enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol 161:1635–1645
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cejkova, P., Zettl, A., Baumgärtner, A.K. et al. Amplification of NOTCH1 and ABL1 gene loci is a frequent aberration in enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma. Virchows Arch 446, 416–420 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1214-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1214-6