Abstract
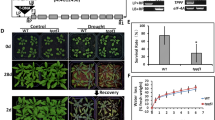
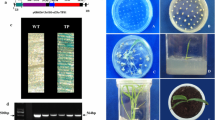
Improving stress tolerance is a major goal for agriculture. Trehalose is a key molecule involved in drought tolerance in anhydrobiotic organisms. Here we describe the construction of a chimeric translational fusion of yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase. This construct was overexpressed in yeast cells displaying both TPS and TPP enzyme activities and trehalose biosynthesis capacity. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the gene fusion was overexpressed using either the 35S promoter or the stress-regulated rd29A promoter. Transgene insertion in the genome was checked by PCR and transcript expression by RT-PCR. Several independent homozygous lines were selected in the presence of kanamycin and further analyzed. Trehalose was accumulated in all these lines at low levels. No morphological or growth alterations were observed in lines overexpressing the TPS1–TPS2 construct, whereas plants overexpressing the TPS1 alone under the control of the 35S promoter had aberrant growth, color and shape. TPS1–TPS2 overexpressor lines were glucose insensitive, consistent with a suggested role of trehalose/T6P in modulating sugar sensing and carbohydrate metabolism. Moreover, TPS1–TPS2 lines displayed a significant increase in drought, freezing, salt and heat tolerance. This is the first time that trehalose accumulation in plants is shown to protect against freezing and heat stress. Therefore, these results demonstrate that engineering trehalose metabolism with a yeast TPS–TPP bifunctional enzyme confers multiple stress protection in plants, comprising a potential tool to improve stress-tolerance in crops.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T6P:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate
- TPS:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase
- TPS1 :
-
Yeast gene encoding TPS
- TPP:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase
- TPS2 :
-
Yeast gene encoding TPP
References
Arenas-Huertero F, Arroyo A, Zhou L, Sheen J, León P (2000) Analysis of Arabidopsis Glc insensitive mutants, gin5 and gin6, reveals a central role of the plant hormone ABA in the regulation of plant vegetative development by sugar. Genes Dev 14:2085–2096
Avonce N, Leyman B, Mascorro-Gallardo JO, Van Dijck P, Thevelein J, Iturriaga G (2004) The Arabidopsis trehalose-6P-synthase AtTPS1 gene is a regulator of glucose, ABA and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 136:3649–3659
Avonce N, Mendoza-Vargas A, Morett E, Iturriaga G (2006) Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol 6:109
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Bell W, Sun W, Hohmann S, Wera S, Reinders A, De Virgilio C, Wiemken A, Thevelein JM (1998) Composition and functional analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae trehalose synthase complex. J Biol Chem 273:33311–33319
Bevan M (1984) Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8711–8721
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bray EA, Bailey-Serres J, Weretilnyk E (2000) Responses to abiotic stresses. In: Gruissem W, Buchanan B, Jones R (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville
Cabib E, Leloir LF (1958) The biosynthesis of trehalose phosphate. J Biol Chem 231: 259–275
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral deep: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Cortina C, Culiáñez-Macià FA (2005) Tomato abiotic stress enhanced tolerance by trehalose biosynthesis. Plant Sci 169:75–82
De Virgilio C, Bürckert N, Bell W, Jenö P, Boller T, Weimken A (1993) Disruption of TPS2, the gene encoding the 100-kDa subunit of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes accumulation of trehalose6-phosphate and loss of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase activity. Eur J Biochem 212:315–323
De Virgilio C, Hottiger T, Domínguez J, Boller T, Wiemken A (1994) The role of trehalose synthesis for the acquisition of thermotolerance in yeast. I. Genetic evidence that trehalose is a thermoprotectant. Eur J Biochem 219:179–186
Eastmond PJ, van Dijken AJH, Spielman M, Kerr A, Tissier AF, Dickinson HG, Jones JDG, Smekeens SC, Graham IA (2002) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1, which catalyses the first step in trehalose synthesis, is essential for Arabidopsis embryo maturation. Plant J 29:225–235
Elbein AD, Pan YT, Pastuszak I, Carroll D (2003) New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiol 13:17R-27R
Elble R (1992) A simple and efficient procedure for transformation of yeasts. Biotechniques 13:18–20
Garg AK, Kim JK, Owens TG, Ranwala AP, Choi YD, Kochian LV, Wu R (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15898–15903
Goddijn OJM, Verwoerd TC, Voogd E, Krutwagen RWHH, de Graaf PTHM, Poels J, van Dun K, Ponstein AS, Damm B, Pen J (1997) Inhibition of thehalase activity enhances trehalose accumulation in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 113:181–190
Holmström KO, Mäntylä E, Welin B, Mandal A, Palva ET, Tunnela OE, Londesborough J (1996) Drought tolerance in tabacco. Nature 379:683–684
Hottiger T, Schmutz P, Wiemken A (1987) Heat-induced accumulation and futile cycling of trehalose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 169:5518–5522
Jang IC, Oh SJ, Seo JS, Choi WB, Song SI, Kim CH, Kim YS, Seo HS, Choi YD, Nahm BH, Kim JK (2003) Expression of a bifunctional fusion of the Escherichia coli genes for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in transgenic rice plants increases trehalose accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 131:516–524
Kim J, Alizadeh P, Harding T, Hefner-Gravink A, Klionsky DJ (1996) Disruption of the yeast ATH1 gene confers better survival after dehydration, freezing, and ethanol shock: potential commercial applications. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1563–1569
Londesborough J, Vuorio OE (1993) Purification of trehalose synthase from baker’s yeast: its temperature-dependent activation by fructose 6-phosphate and inhibition by phosphate. Eur J Biochem 216:841–848
Mackenzie KF, Singh KK, Brown AD (1988) Water stress plating hypersensitivity of yeasts: protective role of trehalose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol 134:1661–1666
Mascorro-Gallardo JO, Covarrubias AA, Gaxiola R (1996) Construction of a CUP1 promoter-based vector to modulate gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 172:169–170
Neves MJ, Terenzi HF, Leone FA, Jorge JA (1994) Quantification of trehalose in biological samples with a conidial trehalase from the thermophilic fungus Humicola grisea var. thermoidea. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 10:17–19
Pilon-Smits EAH, Terry N, Sears T, Kim H, Zayed A, Hwang S, van Dun K, Voogd E, Verwoerd TC, Krutwagen RWHH, Goddijn OJM (1998) Trehalose-producing transgenic tobacco plants show improved growth performance under drought stress. J Plant Physiol 152:525–532
Pramanik MH, Imai R (2005) Functional identification of a trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase gene that is involved in transient induction of trehalose biosynthesis during chilling stress in rice. Plant Mol Biol 58:751–762
Ramon M, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Van Dijck P, Leyman B (2007) ABI4 mediates the effects of exogenous trehalose on Arabidopsis growth and starch breakdown. Plant Mol Biol 63:195–206
Reinders A, Bürckert N, Hohmann S, Thevelein JM, Boller T, Wiemken A, De Virgilio C (1997) Structural analysis of the subunits of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their function during heat shock. Mol Microbiol 24:687–695
Rolland F, Baena-Gonzalez E, Sheen J (2006) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:675–709
Romero C, Belles JM, Vaya JL, Serrano R, Culiañez-Macià FA (1997) Expression of the yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene in transgenic tobacco plants: pleiotropic phenotypes include drought tolerance. Planta 201:293–297
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Nagasawa N, Malcomber S, Sakai H, Jackson D (2006) A trehalose metabolic enzyme controls inflorescence architecture in maize. Nature 441:227–230
Schluepmann H, Pellny T, van Dijken A, Smeekens S, Matthew P (2003) Trehalose 6-phosphate is indispensable for carbohydrate utilization and growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6849–6854
Schluepmann H, van Dijken A, Aghdasi M, Wobbes B, Paul M, Smeekens S (2004) Trehalose mediated growth inhibition of Arabidopsis seedlings is due to trehalose-6-phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 135:879–890
Seo HS, Koo YJ, Lim JY, Song JT, Kim CH, Kim JK, Lee JS, Choi YD (2000) Characterization of a bifunctional enzyme fusion of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2484–2490
Thevelein JM, Hohmann S (1995) Trehalose synthase: guard to the gate of glycolysis in yeast? Trends Biochem Sci 20:3–10
Van Aelst L, Hohmann S, Bulaya B, de Koning W, Sierkstra L, Neves MJ, Luyten K, Alijo R, Ramos J, Coccetti P (1993) Molecular cloning of a gene involved in glucose sensing in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 8:927–943
van Dijken AJ, Schluepmann H, Smeekens SC (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135:969–977
Vandercammen A,François J, Hers HG (1989) Characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 182:613–620
Vogel G, Aeschbacher RA, Muller J, Boller T, Wiemken A (1998). Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatases from Arabidopsis thaliana: identification by functional complementation of the yeast tps2 mutant. Plant J 13:673–683
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264
Yeo ET, Kwon HB, Han SE, Lee JT, Ryu JC, Byun MO (2000) Genetic engineering of drought resistant potato plants by introduction of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS1) gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cells 10:263–268
Zentella R, Mascorro-Gallardo OJ, Van Dijck P, Folch-Mallol J, Bonini B, Van Vaeck C, Gaxiola R, Covarrubias AA, Nieto-Sotelo J, Thevelein JM, Iturriaga G (1999) A Selaginella lepidophylla trehalose-6-phosphate synthase complements growth and stress-tolerance defects in a yeast tps1 mutant. Plant Physiol 119:1473–1482
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Dr. Patricia León (Instituto de Biotecnología-UNAM, Cuernavaca, Mexico) for her kind gift of Col-0 Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and the abi4–1 mutant. We also thank Paul Gaytán and Eugenio López (Instituto de Biotecnología-UNAM, Cuernavaca, Mexico) for oligonucleotide synthesis. G.I. received funding from CONACYT (No. 2004-CO1-46078) and R.S. from PROMEP (No. PTC-137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J.A. Miranda, and N. Avonce contributed equally to the present work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miranda, J.A., Avonce, N., Suárez, R. et al. A bifunctional TPS–TPP enzyme from yeast confers tolerance to multiple and extreme abiotic-stress conditions in transgenic Arabidopsis . Planta 226, 1411–1421 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0579-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0579-y