Abstract
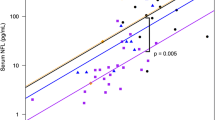
We determined the extent of neuronal and glial cell destruction in 13 patients with herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-1) encephalitis, 15 patients with tick-borne encephalitis (TBE), and 20 noninfectious controls by analyzing the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations of neurofilament protein (a marker of neurons, mainly axons), neuron-specific enolase (a marker of neurons, mainly somas), glial fibrillary acidic protein, and S-100 protein (markers of astrocytes). In addition, in patients with HSV-1 encephalitis CSF samples were collected serially before 7, 8–14, and 18–49 days and 3–10 months after the onset of neurological symptoms. In the acute stage of HSV-1 encephalitis we found markedly higher CSF levels of the cell damage markers than in patients with TBE. The concentration of cell damage markers in HSV-1 encephalitis decreased within 45 days after acute infection, except for neurofilament protein. The CSF concentrations of neurofilament protein increased during the second week, remained extremely high throughout the next month, and decrease thereafter. The changes in these markers of neuronal and glial destruction demonstrate the neuronal and astroglial cell damage during the first month after HSV-1 encephalitis. In contrast, most patients with TBE had signs only of slight astrogliosis, except for two patients with paresis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 November 1999¶Received in revised form: 22 March 2000¶Accepted: 29 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Studahl, M., Rosengren, L., Günther, G. et al. Difference in pathogenesis between herpes simplex virus type 1 encephalitis and tick-borne encephalitis demonstrated by means of cerebrospinal fluid markers of glial and neuronal destruction. J Neurol 247, 636–642 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150070134
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150070134