Abstract
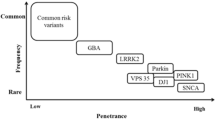
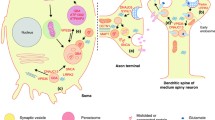
Genetic findings have changed our views on Parkinson’s disease (PD) and parkinsonism, which will be collectively referred to as Parkinsonian Syndrome (PS) in the present manuscript. Mutations in several genes are found to cause monogenic forms of the disorder. Point mutations, duplications and triplications in the α-synuclein gene cause a rare dominant form of PS in families. Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene have been identified as a much more common cause for dominant PS, especially in certain ethnic groups, while mutations in the parkin gene, in DJ-1, PINK1 and ATP13A2 cause autosomal recessive parkinsonism of early onset. The monogenic variants are important tools in identifying cellular pathways that also shed light on the molecular pathogenesis of sporadic PS and some of these genes may play a role in the etiology of the common sporadic form of PS. Here we add recent findings to a greatly challenging puzzle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25:239–252
Aharon-Peretz J, Rosenbaum H, Gershoni-Baruch R (2004) Mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med 351:1972–1977
Berg D, Niwar M, Maass S, Zimprich A, Moller JC, Wuellner U, Schmitz-Hubsch T, Klein C, Tan EK, Schols L, Marsh L, Dawson TM, Janetzky B, Muller T, Woitalla D, Kostic V, Pramstaller PP, Oertel WH, Bauer P, Krueger R, Gasser T, Riess O (2005) Alpha-synuclein and Parkinson’s disease: implications from the screening of more than 1,900 patients. Mov Disord 20:1191–1194
Biskup S, Moore DJ, Celsi F, Higashi S, West AB, Andrabi SA, Kurkinen K, Yu SW, Savitt JM, Waldvogel HJ, Faull RL, Emson PC, Torp R, Ottersen OP, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2006) Localization of LRRK2 to membranous and vesicular structures in mammalian brain. Ann Neurol 60:557–569
Biskup S, Moore DJ, Rea A, Lorenz-Deperieux B, Coombes CE, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, West AB (2007) Dynamic and redundant regulation of LRRK2 and LRRK1 expression. BMC Neurosci 8:102
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Canet-Aviles RM, Wilson MA, Miller DW, Ahmad R, McLendon C, Bandyopadhyay S, Baptista MJ, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Cookson MR (2004) The Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteine-sulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9103–9108
Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernandez-Chacon R, Schluter OM, Sudhof TC (2005) Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 123:383–396
Chen L, Thiruchelvam MJ, Madura K, Richfield EK (2006) Proteasome dysfunction in aged human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis 23:120–126
Chung KK, Zhang Y, Lim KL, Tanaka Y, Huang H, Gao J, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2001) Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1: implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 7:1144–1150
Clark IE, Dodson MW, Jiang C, Cao JH, Huh JR, Seol JH, Yoo SJ, Hay BA, Guo M (2006) Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature 441:1162–1166
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 305:1292–1295
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
DeStefano AL, Lew MF, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Lazzarini AM, Guttman M, Montgomery E, Waters CH, Singer C, Watts RL, Currie LJ, Wooten GF, Maher NE, Wilk JB, Sullivan KM, Slater KM, Saint-Hilaire MH, Feldman RG, Suchowersky O, Lafontaine AL, Labelle N, Growdon JH, Vieregge P, Pramstaller PP, Klein C, Hubble JP, Reider CR, Stacy M, MacDonald ME, Gusella JF, Myers RH (2002) PARK3 influences age at onset in Parkinson disease: a genome scan in the GenePD study. Am J Hum Genet 70:1089–1095
Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM, Avadhani NG, Anandatheerthavarada HK (2008) Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem 283:9089–9100
Engelender S, Kaminsky Z, Guo X, Sharp AH, Amaravi RK, Kleiderlein JJ, Margolis RL, Troncoso JC, Lanahan AA, Worley PF, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ross CA (1999) Synphilin-1 associates with alpha-synuclein and promotes the formation of cytosolic inclusions. Nat Genet 22:110–114
Fallon L, Moreau F, Croft BG, Labib N, Gu WJ, Fon EA (2002) Parkin and CASK/LIN-2 associate via a PDZ-mediated interaction and are co-localized in lipid rafts and postsynaptic densities in brain. J Biol Chem 277:486–491
Farrer MJ, Stone JT, Lin CH, Dachsel JC, Hulihan MM, Haugarvoll K, Ross OA, Wu RM (2007) Lrrk2 G2385R is an ancestral risk factor for Parkinson’s disease in Asia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13:89–92
Funayama M, Hasegawa K, Kowa H, Saito M, Tsuji S, Obata F (2002) A new locus for Parkinson’s disease (PARK8) maps to chromosome 12p11.2–q13.1. Ann Neurol 51:296–301
Gasser T, Muller-Myhsok B, Wszolek ZK, Oehlmann R, Calne DB, Bonifati V, Bereznai B, Fabrizio E, Vieregge P, Horstmann RD (1998) A susceptibility locus for Parkinson’s disease maps to chromosome 2p13. Nat Genet 18:262–265
Gong B, Cao Z, Zheng P, Vitolo OV, Liu S, Staniszewski A, Moolman D, Zhang H, Shelanski M, Arancio O (2006) Ubiquitin hydrolase Uch-L1 rescues beta-amyloid-induced decreases in synaptic function and contextual memory. Cell 126:775–788
Hardy J, Cai H, Cookson MR, Gwinn-Hardy K, Singleton A (2006) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 60:389–398
Hatano T, Kubo S, Imai S, Maeda M, Ishikawa K, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2007) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 associates with lipid rafts. Hum Mol Genet 16:78–690
Hatano Y, Li Y, Sato K, Asakawa S, Yamamura Y, Tomiyama H, Yoshino H, Asahina M, Kobayashi S, Hassin-Baer S, Lu CS, Ng AR, Rosales RL, Shimizu N, Toda T, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2004) Novel PINK1 mutations in early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 56:424–427
Healy DG, Falchi M, O’Sullivan SS, Bonifati V, Durr A, Bressman S, Brice A, Aasly J, Zabetian CP, Goldwurm S, Ferreira JJ, Tolosa E, Kay DM, Klein C, Williams DR, Marras C, Lang AE, Wszolek ZK, Berciano J, Schapira AH, Lynch T, Bhatia KP, Gasser T, Lees AJ, Wood NW (2008) Phenotype, genotype, and worldwide genetic penetrance of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 7:583–590
Hedrich K, Djarmati A, Schafer N, Hering R, Wellenbrock C, Weiss PH, Hilker R, Vieregge P, Ozelius LJ, Heutink P, Bonifati V, Schwinger E, Lang AE, Noth J, Bressman SB, Pramstaller PP, Riess O, Klein C (2004) DJ-1 (PARK7) mutations are less frequent than Parkin (PARK2) mutations in early-onset Parkinson disease. Neurology 62:389–394
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A, Rockenstein E, Sisk A, Mallory M, Wong J, Takenouchi T, Hashimoto M, Masliah E (2000) alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157:401–410
Imai Y, Soda M, Takahashi R (2000) Parkin suppresses unfolded protein stress-induced cell death through its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity. J Biol Chem 275:35661–35664
Jones JM, Datta P, Srinivasula SM, Ji W, Gupta S, Zhang Z, Davies E, Hajnoczky G, Saunders TL, Van Keuren ML, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Meisler MH, Alnemri ES (2003) Loss of Omi mitochondrial protease activity causes the neuromuscular disorder of mnd2 mutant mice. Nature 425:721–727
Karamohamed S, DeStefano AL, Wilk JB, Shoemaker CM, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Lazzarini AM, Suchowersky O, Labelle N, Guttman M, Currie LJ, Wooten GF, Stacy M, Saint-Hilaire M, Feldman RG, Sullivan KM, Xu G, Watts R, Growdon J, Lew M, Waters C, Vieregge P, Pramstaller PP, Klein C, Racette BA, Perlmutter JS, Parsian A, Singer C, Montgomery E, Baker K, Gusella JF, Fink SJ, Myers RH, Herbert A (2003) A haplotype at the PARK3 locus influences onset age for Parkinson’s disease: the GenePD study. Neurology 61:1557–1561
Khan NL, Graham E, Critchley P, Schrag AE, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Bhatia KP, Quinn N (2003) Parkin disease: a phenotypic study of a large case series. Brain 126:1279–1292
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov SV, Murchison E, Hannon G, Abeliovich A (2007) A MicroRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 317:1220–1224
Klivenyi P, Siwek D, Gardian G, Yang L, Starkov A, Cleren C, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Abeliovich A, Beal MF (2006) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein are resistant to mitochondrial toxins. Neurobiol Dis 21:541–548
Kramer ML, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2007) Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurosci 27:1405–1410
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Kubo SI, Kitami T, Noda S, Shimura H, Uchiyama Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2001) Parkin is associated with cellular vesicles. J Neurochem 78:42–54
Kuhn K, Zhu XR, Lubbert H, Stichel CC (2004) Parkin expression in the developing mouse. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 149:131–142
Kumazawa R, Tomiyama H, Li Y, Imamichi Y, Funayama M, Yoshino H, Yokochi F, Fukusako T, Takehisa Y, Kashihara K, Kondo T, Elibol B, Bostantjopoulou S, Toda T, Takahashi H, Yoshii F, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2008) Mutation analysis of the PINK1 gene in 391 patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65:802–808
Kuroda Y, Mitsui T, Kunishige M, Shono M, Akaike M, Azuma H, Matsumoto T (2006) Parkin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis in proliferating cells. Hum Mol Genet 15:883–895
Larsen KE, Schmitz Y, Troyer MD, Mosharov E, Dietrich P, Quazi AZ, Savalle M, Nemani V, Chaudhry FA, Edwards RH, Stefanis L, Sulzer D (2006) Alpha-synuclein overexpression in PC12 and chromaffin cells impairs catecholamine release by interfering with a late step in exocytosis. J Neurosci 26:11915–11922
Le WD, Xu P, Jankovic J, Jiang H, Appel SH, Smith RG, Vassilatis DK (2003) Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease. Nat Genet 33:85–89
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452
Li X, Tan YC, Poulose S, Olanow CW, Huang XY, Yue Z (2007) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)/PARK8 possesses GTPase activity that is altered in familial Parkinson’s disease R1441C/G mutants. J Neurochem 103:238–247
Lim KL, Chew KC, Tan JM, Wang C, Chung KK, Zhang Y, Tanaka Y, Smith W, Engelender S, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Parkin mediates nonclassical, proteasomal-independent ubiquitination of synphilin-1: implications for Lewy body formation. J Neurosci 25:2002–2009
Lim KL, Tan JM (2007) Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in Parkinson’s disease. BMC Biochem 8(Suppl 1):S13
Ltic S, Perovic M, Mladenovic A, Raicevic N, Ruzdijic S, Rakic L, Kanazir S (2004) Alpha-synuclein is expressed in different tissues during human fetal development. J Mol Neurosci 22:199–204
Lucking CB, Durr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A (2000) Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. N Engl J Med 342:1560–1567
Marazziti D, Mandillo S, Di Pietro C, Golini E, Matteoni R, Tocchini-Valentini GP (2007) GPR37 associates with the dopamine transporter to modulate dopamine uptake and behavioral responses to dopaminergic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:9846–9851
Maroteaux L, Campanelli JT, Scheller RH (1988) Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci 8:2804–2815
Martinez M, Brice A, Vaughan JR, Zimprich A, Breteler MM, Meco G, Filla A, Farrer MJ, Betard C, Hardy J, De Michele G, Bonifati V, Oostra B, Gasser T, Wood NW, Durr A (2004) Genome-wide scan linkage analysis for Parkinson’s disease: the European genetic study of Parkinson’s disease. J Med Genet 41:900–907
Marx FP, Holzmann C, Strauss KM, Li L, Eberhardt O, Gerhardt E, Cookson MR, Hernandez D, Farrer MJ, Kachergus J, Engelender S, Ross CA, Berger K, Schols L, Schulz JB, Riess O, Kruger R (2003) Identification and functional characterization of a novel R621C mutation in the synphilin-1 gene in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 12:1223–1231
Moore DJ (2006) Parkin: a multifaceted ubiquitin ligase. Biochem Soc Trans 34:749–753
Murphy DD, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alphasynuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 20:3214–3220
Myhre R, Klungland H, Farrer MJ, Aasly JO (2008) Genetic association study of synphilin-1 in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. BMC Med Genet 9:19
Nie GY, Hampton A, Li Y, Findlay JK, Salamonsen LA (2003) Identification and cloning of two isoforms of human high-temperature requirement factor A3 (HtrA3), characterization of its genomic structure and comparison of its tissue distribution with HtrA1 and HtrA2. Biochem J 371:39–48
Nunes I, Tovmasian LT, Silva RM, Burke RE, Goff SP (2003) Pitx3 is required for development of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4245–4250
Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, van der Brug M, Lopez de Munain A, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martinez JR, Nicholl D, Carrera IM, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Marti-Masso JF, Perez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singleton AB (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44:595–600
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1969–1978
Pankratz N, Uniacke SK, Halter CA, Rudolph A, Shults CW, Conneally PM, Foroud T, Nichols WC (2004) Genes influencing Parkinson disease onset: replication of PARK3 and identification of novel loci. Neurology 62:1616–1618
Plun-Favreau H, Klupsch K, Moisoi N, Gandhi S, Kjaer S, Frith D, Harvey K, Deas E, Harvey RJ, McDonald N, Wood NW, Martins LM, Downward J (2007) The mitochondrial protease HtrA2 is regulated by Parkinson’s disease-associated kinase PINK1. Nat Cell Biol 9:1243–1252
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Nussbaum RL (1997) α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Poole AC, Thomas RE, Andrews LA, McBride HM, Whitworth AJ, Pallanck LJ (2008) The PINK1/Parkin pathway regulates mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1638–1643
Pridgeon JW, Olzmann JA, Chin LS, Li L (2007) PINK1 Protects against Oxidative Stress by Phosphorylating Mitochondrial Chaperone TRAP1. PLoS Biol 5:e172
Ramirez A, Heimbach A, Grundemann J, Stiller B, Hampshire D, Cid LP, Goebel I, Mubaidin AF, Wriekat AL, Roeper J, Al-Din A, Hillmer AM, Karsak M, Liss B, Woods CG, Behrens MI, Kubisch C (2006) Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2, encoding a lysosomal type 5 P-type ATPase. Nat Genet 38:1184–1191
Riparbelli MG, Callaini G (2007) The Drosophila parkin homologue is required for normal mitochondrial dynamics during spermiogenesis. Dev Biol 303:108–120
Rogaeva E, Johnson J, Lang AE, Gulick C, Gwinn-Hardy K, Kawarai T, Sato C, Morgan A, Werner J, Nussbaum R, Petit A, Okun MS, McInerney A, Mandel R, Groen JL, Fernandez HH, Postuma R, Foote KD, Salehi-Rad S, Liang Y, Reimsnider S, Tandon A, Hardy J, St George-Hyslop P, Singleton AB (2004) Analysis of the PINK1 gene in a large cohort of cases with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 61:1898–1904
Saigoh K, Wang YL, Suh JG, Yamanishi T, Sakai Y, Kiyosawa H, Harada T, Ichihara N, Wakana S, Kikuchi T, Wada K (1999) Intragenic deletion in the gene encoding ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase in gad mice. Nat Genet 23:47–51
Sakaguchi-Nakashima A, Meir JY, Jin Y, Matsumoto K, Hisamoto N (2007) LRK-1, a C. elegans PARK8-related kinase, regulates axonal-dendritic polarity of SV proteins. Curr Biol 17:592–598
Sakurada K, Ohshima-Sakurada M, Palmer TD, Gage FH (1999) Nurr1, an orphan nuclear receptor, is a transcriptional activator of endogenous tyrosine hydroxylase in neural progenitor cells derived from the adult brain. Development 126:4017–4026
Sakurai M, Ayukawa K, Setsuie R, Nishikawa K, Hara Y, Ohashi H, Nishimoto M, Abe T, Kudo Y, Sekiguchi M, Sato Y, Aoki S, Noda M, Wada K (2006) Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 regulates the morphology of neural progenitor cells and modulates their differentiation. J Cell Sci 119:162–171
Schapira AH (2008) Mitochondria in the aetiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 7:97–109
Sharma M, Mueller JC, Zimprich A, Lichtner P, Hofer A, Leitner P, Maass S, Berg D, Durr A, Bonifati V, De Michele G, Oostra B, Brice A, Wood NW, Muller-Myhsok B, Gasser T (2006) The sepiapterin reductase gene region reveals association in the PARK3 locus: analysis of familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease in European populations. J Med Genet 43:557–562
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo S, Mizuno Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Iwai K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat Genet 25:302–305
Shin N, Jeong H, Kwon J, Heo HY, Kwon JJ, Yun HJ, Kim CH, Han BS, Tong Y, Shen J, Hatano T, Hattori N, Kim KS, Chang S, Seol W (2008) LRRK2 regulates synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Exp Cell Res 314:2055–2065
Simon-Sanchez J, Singleton AB (2008) Sequencing analysis of OMI/HTRA2 shows previously reported pathogenic mutations in neurologically normal controls. Hum Mol Genet 17:1988–1993
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Stefanis L, Larsen KE, Rideout HJ, Sulzer D, Greene LA (2001) Expression of A53T mutant but not wild-type alpha-synuclein in PC12 cells induces alterations of the ubiquitin-dependent degradation system, loss of dopamine release, and autophagic cell death. J Neurosci 21:9549–9560
Stichel CC, Zhu XR, Bader V, Linnartz B, Schmidt S, Lubbert H (2007) Mono- and double-mutant mouse models of Parkinson’s disease display severe mitochondrial damage. Hum Mol Genet 16:2377–2393
Strauss KM, Martins LM, Plun-Favreau H, Marx FP, Kautzmann S, Berg D, Gasser T, Wszolek Z, Muller T, Bornemann A, Wolburg H, Downward J, Riess O, Schulz JB, Kruger R (2005) Loss of function mutations in the gene encoding Omi/HtrA2 in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 14:2099–2111
Suzuki Y, Imai Y, Nakayama H, Takahashi K, Takio K, Takahashi R (2001) A serine protease, HtrA2, is released from the mitochondria and interacts with XIAP, inducing cell death. Mol Cell 8:613–621
Tan EK (2006) Identification of a common genetic risk variant (LRRK2 Gly2385Arg) in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Acad Med Singapore 35:840–842
Tanaka Y, Engelender S, Igarashi S, Rao RK, Wanner T, Tanzi RE, Sawa A, V LD, Dawson TM, Ross CA (2001) Inducible expression of mutant alpha-synuclein decreases proteasome activity and increases sensitivity to mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet 10:919–926
Thomas B, Beal MF (2007) Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 16 Spec No. 2:R183–R194
Tobin JE, Latourelle JC, Lew MF, Klein C, Suchowersky O, Shill HA, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Growdon JH, Wooten GF, Racette BA, Perlmutter JS, Watts R, Guttman M, Baker KB, Goldwurm S, Pezzoli G, Singer C, Saint-Hilaire MH, Hendricks AE, Williamson S, Nagle MW, Wilk JB, Massood T, Laramie JM, Destefano AL, Litvan I, Nicholson G, Corbett A, Isaacson S, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF, Pramstaller PP, Sherman S, Al-Hinti J, Drasby E, Nance M, Moller AT, Ostergaard K, Roxburgh R, Snow B, Slevin JT, Cambi F, Gusella JF, Myers RH (2008) Haplotypes and gene expression implicate the MAPT region for Parkinson disease. The GenePD Study. Neurology 71:28–34
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160
Valente EM, Salvi S, Ialongo T, Marongiu R, Elia AE, Caputo V, Romito L, Albanese A, Dallapiccola B, Bentivoglio AR (2004) PINK1 mutations are associated with sporadic early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 56:336–341
Wang G, van der Walt JM, Mayhew G, Li YJ, Zuchner S, Scott WK, Martin ER, Vance JM (2008) Variation in the miRNA-433 binding site of FGF20 confers risk for Parkinson disease by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Am J Hum Genet 82:283–289
West AB, Moore DJ, Biskup S, Bugayenko A, Smith WW, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16842–16847
Yang Y, Ouyang Y, Yang L, Beal MF, McQuibban A, Vogel H, Lu B (2008) Pink1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics through interaction with the fission/fusion machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7070–7075
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Zetterstrom RH, Solomin L, Jansson L, Hoffer BJ, Olson L, Perlmann T (1997) Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science 276:248–250
Zhang L, Shimoji M, Thomas B, Moore DJ, Yu SW, Marupudi NI, Torp R, Torgner IA, Ottersen OP, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2005) Mitochondrial localization of the Parkinson’s disease related protein DJ-1: implications for pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 14:2063–2073
Zhang NY, Tang Z, Liu CW (2008) Alpha-synuclein protofibrils inhibit 26S proteasome-mediated protein degradation understanding the cytotoxicity of protein protofibrils in neurodegenerative diseases pathogenesis. J Biol Chem 283:20288–20298
Zhang Y, Gao J, Chung KK, Huang H, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2000) Parkin functions as an E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase and promotes the degradation of the synaptic vesicle-associated protein, CDCrel-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13354–13359
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biskup, S., Gerlach, M., Kupsch, A. et al. Genes associated with Parkinson syndrome. J Neurol 255 (Suppl 5), 8–17 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-5005-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-5005-2