Abstract.
Background:
Painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathies (HIV-SN) are a common complication of HIV infection. The pathogenesis is unknown and the treatment very limited. Gabapentin (GBP) is effective in painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia and its effectiveness on painful HIV-SN has been reported anecdotally.
Design:
Multicenter, prospective, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Methods:
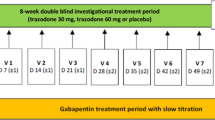
Patients were followed for a 1-week screening, a 4-week double-blind and a 2-week open treatment phase. GBP was initiated at 400 mg/d, titrated over 2 weeks to 1200 mg/d, and then either maintained at this level or—if not beneficial—titrated to 2400 mg/d. After 4 weeks the medication was unblinded and the patient had the choice to begin, to maintain or to increase GBP to 3600 mg/d. The primary outcome measure was an improvement in median pain on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) from the screening week compared to the 4th treatment week. A secondary efficacy measure was the median sleep score (VAS).
Results:
15 patients received GBP and 11 placebo. In each group one patient dropped out during the doubleblind phase. Median pain (GBP 5.1; placebo 4.7) and sleep score (GBP 4.5; placebo 5.6) did not differ between both groups at baseline. In the GBP-group there was a significant decrease of the pain to 2.85 (–44.1 %) as well as of the sleep VAS to 2.3 (–48.9 %). No significant decrease in the pain (median VAS=3.3, –29.8 %) as well as in the sleep score (median VAS=4.95, –11.6 %) was observed in the placebo-group. GBP was generally well tolerated. The most frequent side effect was somnolence reported in 80% of GBP-treated patients.
Conclusions:
GBP was more effective than placebo in reducing pain and sleep interference in patients with HIV-SN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi S, Lee DH, Chung JM (1998) The anti-allodynic effects of amitryptiline, gabapentin and lidocaine in an art model of neuropathic pain. Anesth Analg 87:1360–1366
Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al. (1998) Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280:1831–1836
Childs EA, Lyles RH, Selnes OD, et al. (1999) Plasma viral load and CD4 lymphocytes predict HIV-associated dementia and sensory neuropathy. Neurology 52:607–613
Deutsche Neuro-AIDS-Arbeitsgemeinschaft [DNAA] (2000) Erkrankungen des peripheren Nervensystems und der Muskulatur bei der HIV-Infektion. Nervenarzt 71(6):442–450
Gatti A, Jann S, Sandro B, Manuela B (1998) Gabapentin in the treatment of distal symmetric axonopathy in HIV infected patients. Neurology 50:A216 abstract (P04.053)
Griffin JW, Crawford TO, McArthur JC, et al. (1998) Peripheral neuropathies associated with HIV infection. In: Gendelman HE, Lipton SA, Epstein L, Swindells S (eds) The neurology of AIDS. New York, Chapman & Hall, pp 275–291
Husstedt IW, Grotemeyer KH, Busch J, Zidek W (1994) Early detection of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy during HIV infection by paired stimulation of sural nerve. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 93:169–174
Keswani SC, Pardo C, Cherry CL, Hoke A, McArthur JC (2002) HIV-associated sensory neuropathies. AIDS 16:2105–2117
Kieburtz K, Simpson D, Yiannoutsos C, et al. (1998) A randomized trial of amitriptyline and mexiletine for painful neuropathy in HIV infection. Neurology 51:1682–1688
Lange D (1994) AAEM minimonograph #41: Neuromuscular diseases associated with HIV-1 infection. Muscle Nerve 17:16–30
La Spina I, Porazzi D, Maggiolo F, Bottura P, Suter F (2001) Gabapentin in painful HIV-related neuropathy: a report of 19 patients, preliminary observations. Eur J Neurol 8:71–75
Malessa R, Agelink M, Himmelmann M, Kloss T, Mertins L, Brockmeyer NH (1996) Nerve conduction changes in asymptomatic HIV-1 seropositive individuals in the absence of other risk factors for neuropathy. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 36:3–8
McArthur JC, Yiannoutsos C, Simpson DM, et al. (2000) A phase II trial of nerve growth factor for sensory neuropathy associated with HIV-infection. Neurology 54:1080–1088
McQuay H, Carroll D, Moore A (1995) Variation in the placebo effect in randomised controlled trials of analgesics: all is as blind as it seems. Pain 64:331–335
Newshan G (1998) HIV neuropathy treated with gabapentin. AIDS 12:219–221
Novakovic SD, Tzoumaka E, McGivern JG, et al. (1998) Distribution of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel PN3 in rat sensory neurons in normal and neuropathic conditions. J Neurosci 18:2174–2187
Paice JA, Estwing Ferrans C, Lashley FR, Shott S, Vizgirda V, Pitrak D (2000) Topical capsaicin in the management of HIV-associated peripheral neuropathy. J Pain Symptom Manage 19(1):45–52
Pan HL, Eisenach JC, Chen SR (1999) Gabapentin suppresses ectopic nerve discharges and reverses allodynia in neuropathic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:1026–1030t
Rowbotham M, Harden N, Stacey B, Bernstein P, Magnus-Miller L (1998) Gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280:1837–1842
Schiffito G, Yiannoutsos C, Simpson DM, et al. (2001) Long-term treatment with recombinant nerve growth factor for HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. Neurology 57:1313–1316
Shlay JC, Chaloner K, Max MB, et al. (1998) Acupuncture and amitriptyline for pain due to HIV-related peripheral neuropathy; a randomized trial. JAMA 280(18):1590–1595
Simpson DM, Dorfman D, Olney RK, et al. (1996) Peptide T in the treatment of painful distal neuropathy associated with AIDS: results of a placebo-controlled trial. The peptide T Neuropathy Study Group. Neurology 47:1254–1259
Simpson DM, Olney R, McArthur JC, Khan A, Godbold J, Ebel-Frommer K (2000) A placebo-controlled trial of lamotrigine for painful HIV-associated neuropathy. Neurology 54:2115–2119
Simpson DM, cArthur JC, Olney R, et al. (2003) Lamotrigine for HIV-associated painful sensory neuropathies: A placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 60:1508–1514
Tagliati M, Grinnel J, Godbold J, Simpson DM (1999) Peripheral nerve function in HIV infection: clinical, electrophysiologic, and laboratory findings. Arch Neurol 56:84–89
Taylor CP,Gee NS, Su TZ, et al. (1998) A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res 29:233–249
Woolf CJ, Salter MW (2000) Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science 288:1765–1769
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahn, K., Arendt, G., Braun, J.S. et al. A placebo-controlled trial of gabapentin for painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathies. J Neurol 251, 1260–1266 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0529-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0529-6