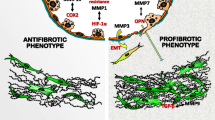
Abstract
Lung tissue remodeling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) involves diverse processes characterized by epithelial disruption, smooth muscle hypertrophy/hyperplasia, airway wall fibrosis, and alveolar destruction. According to the accepted current theory of COPD pathogenesis, tissue remodeling in COPD is predominantly a consequence of an imbalance between proteolytic and antiproteolytic activities. However, most of the studies carried out during the last few years have focused on mechanisms related to degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) structural proteins, neglecting those involved in ECM protein deposition. This review revisits some of the latest findings related to fibrotic changes that occur in the airway wall of COPD patients, as well as the main cellular phenotypes relevant to these processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopez AD, Murray CC (1998) The global burden of disease, 1990–2020. Nat Med 4:1241–1243
Terzano C, Conti V, Di Stefano F, Petroianni A, Ceccarelli D, Graziani E, Mariotta S, Ricci A, Vitarelli A, Puglisi G, De Vito C, Villari P, Allegra L (2010) Comorbidity, hospitalization, and mortality in COPD: results from a longitudinal study. Lung 188:321–329
Zandvoort A, Postma DS, Jonker MR, Noordhoek JA, Vos JT, van der Geld YM, Timens W (2006) Altered expression of the Smad signalling pathway: implications for COPD pathogenesis. Eur Respir J 28:533–541
Saetta M, Turato G, Baraldo S, Zanin A, Braccioni F, Mapp CE, Maestrelli P, Cavallesco G, Papi A, Fabbri LM (2000) Goblet cell hyperplasia and epithelial inflammation in peripheral airways of smokers with both symptoms of chronic bronchitis and chronic airflow limitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:1016–1021
Atzori L, Lucattelli M, Scotton CJ, Laurent GJ, Bartalesi B, De Cunto G, Lunghi B, Chambers RC, Lungarella G (2009) Absence of proteinase-activated receptor-1 signaling in mice confers protection from fMLP-induced goblet cell metaplasia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:680–687
Zanini A, Chetta A, Saetta M, Baraldo S, Castagnetti C, Nicolini G, Neri M, Olivieri D (2009) Bronchial vascular remodelling in patients with COPD and its relationship with inhaled steroid treatment. Thorax 64:1019–1024
Rufino R, Madi K, Souza HS, Costa CH, Saito EH, Silva JR (2007) Quantitative assessment of elastic fibers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Bras Pneumol 33:502–509
Falk JA, Martin UJ, Scharf S, Criner GJ (2007) Lung elastic recoil does not correlate with pulmonary hemodynamics in severe emphysema. Chest 132:1476–1484
Murarescu ED, Eloae-Zugun F, Mihailovici MS (2008) Experimental COPD induced by solid combustible burn smoke in rats: a study of the emphysematous changes of the pulmonary parenchyma. Rom J Morphol Embryol 49:495–505
Inoue K, Koike E, Yanagisawa R, Takano H (2010) Extensive analysis of elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema in rats: ALP in the lung, a new biomarker for disease progression? J Clin Biochem Nutr 46:168–176
Chaouat A, Naeije R, Weitzenblum E (2008) Pulmonary hypertension in COPD. Eur Respir J 32:1371–1385
Chung KF, Adcock IM (2008) Multifaceted mechanisms in COPD: inflammation, immunity, and tissue repair and destruction. Eur Respir J 31:1334–1356
Leopold JG, Gough J (1957) The centrilobular form of hypertrophic emphysema and its relation to chronic bronchitis. Thorax 12:219–235
Churg A, Zhou S, Preobrazhenska O, Tai H, Wang R, Wright JL (2009) Expression of profibrotic mediators in small airways versus parenchyma after cigarette smoke exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 40:268–276
Shapiro SD (1995) The pathogenesis of emphysema: the elastase:antielastase hypothesis 30 years later. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 107:346–352
Baraldo S, Bazzan E, Zanin ME, Turato G, Garbisa S, Maestrelli P, Papi A, Miniati M, Fabbri LM, Zuin R, Saetta M (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 protein in lung periphery is related to COPD progression. Chest 132:1733–1740
Ilumets H, Rytila P, Demedts I, Brusselle GG, Sovijarvi A, Myllarniemi M, Sorsa T, Kinnula VL (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases-8, -9 and -12 in smokers and patients with stage 0 COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2:369–379
Brajer B, Batura-Gabryel H, Nowicka A, Kuznar-Kaminska B, Szczepanik A (2008) Concentration of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in serum of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and a degree of airway obstruction and disease progression. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 6):145–152
Chen Y, Chen P, Hanaoka M, Droma Y, Kubo K (2008) Enhanced levels of prostaglandin E2 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 correlate with the severity of airflow limitation in stable COPD. Respirology 13:1014–1021
Lowrey GE, Henderson N, Blakey JD, Corne JM, Johnson SR (2008) MMP-9 protein level does not reflect overall MMP activity in the airways of patients with COPD. Respir Med 102:845–851
Wallace AM, Sandford AJ, English JC, Burkett KM, Li H, Finley RJ, Muller NL, Coxson HO, Pare PD, Abboud RT (2008) Matrix metalloproteinase expression by human alveolar macrophages in relation to emphysema. COPD 5:13–23
Cheng SL, Yu CJ, Yang PC (2009) Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome p450 and matrix metalloproteinase in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biochem Genet 47:591–601
Deshmukh HS, McLachlan A, Atkinson JJ, Hardie WD, Korfhagen TR, Dietsch M, Liu Y, Di PY, Wesselkamper SC, Borchers MT, Leikauf GD (2009) Matrix metalloproteinase-14 mediates a phenotypic shift in the airways to increase mucin production. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 180:834–845
Hunninghake GM, Cho MH, Tesfaigzi Y, Soto-Quiros ME, Avila L, Lasky-Su J, Stidley C, Melen E, Soderhall C, Hallberg J, Kull I, Kere J, Svartengren M, Pershagen G, Wickman M, Lange C, Demeo DL, Hersh CP, Klanderman BJ, Raby BA, Sparrow D, Shapiro SD, Silverman EK, Litonjua AA, Weiss ST, Celedon JC (2009) MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations. N Engl J Med 361:2599–2608
McAloon CJ, Wood AM, Gough SC, Stockley RA (2009) Matrix metalloprotease polymorphisms are associated with gas transfer in alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency. Ther Adv Respir Dis 3:23–30
Qu P, Du H, Wang X, Yan C (2009) Matrix metalloproteinase 12 overexpression in lung epithelial cells plays a key role in emphysema to lung bronchioalveolar adenocarcinoma transition. Cancer Res 69:7252–7261
Schirmer H, Basso da Silva L, Teixeira PJ, Moreira JS, Moreira AL, Simon D (2009) Matrix metalloproteinase gene polymorphisms: lack of association with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a Brazilian population. Genet Mol Res 8:1028–1034
Wong S, Belvisi MG, Birrell MA (2009) MMP/TIMP expression profiles in distinct lung disease models: implications for possible future therapies. Respir Res 10:72
Haq I, Chappell S, Johnson SR, Lotya J, Daly L, Morgan K, Guetta-Baranes T, Roca J, Rabinovich R, Millar AB, Donnelly SC, Keatings V, MacNee W, Stolk J, Hiemstra PS, Miniati M, Monti S, O’Connor CM, Kalsheker N (2010) Association of MMP-2 polymorphisms with severe and very severe COPD: a case control study of MMPs-1, 9 and 12 in a European population. BMC Med Genet 11:7
Lee SY, Kim MJ, Kang HG, Yoo SS, Choi YY, Lee WK, Cha SI, Kim CH, Jung TH, Park JY (2010) Polymorphisms in matrix metalloproteinase-1, -9 and -12 genes and the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a Korean population. Respiration 80:133–138
Louhelainen N, Stark H, Mazur W, Rytila P, Djukanovic R, Kinnula VL (2010) Elevation of sputum matrix metalloproteinase-9 persists up to 6 months after smoking cessation: a research study. BMC Pulm Med 10:13
Churg A, Tai H, Coulthard T, Wang R, Wright JL (2006) Cigarette smoke drives small airway remodeling by induction of growth factors in the airway wall. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:1327–1334
Girod CE, King TE Jr (2005) COPD: a dust-induced disease? Chest 128:3055–3064
Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, Buzatu L, Cherniack RM, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Coxson HO, Pare PD (2004) The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 350:2645–2653
Jeffery PK (2001) Remodeling in asthma and chronic obstructive lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:S28–S38
Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS, GOLD Scientific Committee (2001) Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:1256–1276
Bousquet J, Jeffery PK, Busse WW, Johnson M, Vignola AM (2000) Asthma. From bronchoconstriction to airways inflammation and remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:1720–1745
Petecchia L, Sabatini F, Varesio L, Camoirano A, Usai C, Pezzolo A, Rossi GA (2009) Bronchial airway epithelial cell damage following exposure to cigarette smoke includes disassembly of tight junction components mediated by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Chest 135:1502–1512
Tilley AE, Harvey BG, Heguy A, Hackett NR, Wang R, O’Connor TP, Crystal RG (2009) Down-regulation of the notch pathway in human airway epithelium in association with smoking and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179:457–466
Lapperre TS, Sont JK, van Schadewijk A, Gosman MM, Postma DS, Bajema IM, Timens W, Mauad T, Hiemstra PS, GLUCOLD Study Group (2007) Smoking cessation and bronchial epithelial remodelling in COPD: a cross-sectional study. Respir Res 8:25
Araya J, Cambier S, Markovics JA, Wolters P, Jablons D, Hill A, Finkbeiner W, Jones K, Broaddus VC, Sheppard D, Barzcak A, Xiao Y, Erle DJ, Nishimura SL (2007) Squamous metaplasia amplifies pathologic epithelial–mesenchymal interactions in COPD patients. J Clin Invest 117:3551–3562
Bolton SJ, Pinnion K, Oreffo V, Foster M, Pinkerton KE (2009) Characterisation of the proximal airway squamous metaplasia induced by chronic tobacco smoke exposure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Respir Res 10:118
Polosukhin VV, Lawson WE, Milstone AP, Egunova SM, Kulipanov AG, Tchuvakin SG, Massion PP, Blackwell TS (2007) Association of progressive structural changes in the bronchial epithelium with subepithelial fibrous remodeling: a potential role for hypoxia. Virchows Arch 451:793–803
Innes AL, Woodruff PG, Ferrando RE, Donnelly S, Dolganov GM, Lazarus SC, Fahy JV (2006) Epithelial mucin stores are increased in the large airways of smokers with airflow obstruction. Chest 130:1102–1108
Haswell LE, Hewitt K, Thorne D, Richter A, Gaca MD (2010) Cigarette smoke total particulate matter increases mucous secreting cell numbers in vitro: a potential model of goblet cell hyperplasia. Toxicol In Vitro 24:981–987
Williams OW, Sharafkhaneh A, Kim V, Dickey BF, Evans CM (2006) Airway mucus: from production to secretion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 34:527–536
Hirst SJ, Walker TR, Chilvers ER (2000) Phenotypic diversity and molecular mechanisms of airway smooth muscle proliferation in asthma. Eur Respir J 16:159–177
Shao J, Xia ZW, Li YZ, Yu SC, Deng WW (2006) Expression of cellular phenotype switching markers-matrix protein Gla, mRNA and collagen I, III and V of human airway smooth muscle cells in vitro after TGF-beta1 stimulation. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 44:531–534
Xie M, Liu XS, Xu YJ, Zhang ZX, Bai J, Ni W, Chen SX (2007) ERK1/2 signaling pathway modulates the airway smooth muscle cell phenotype in the rat model of chronic asthma. Respiration 74:680–690
Halayko AJ, Tran T, Gosens R (2008) Phenotype and functional plasticity of airway smooth muscle: role of caveolae and caveolins. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:80–88
Dekkers BG, Schaafsma D, Nelemans SA, Zaagsma J, Meurs H (2007) Extracellular matrix proteins differentially regulate airway smooth muscle phenotype and function. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L1405–L1413
Dekkers BG, Schaafsma D, Tran T, Zaagsma J, Meurs H (2009) Insulin-induced laminin expression promotes a hypercontractile airway smooth muscle phenotype. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:494–504
Dekkers BG, Maarsingh H, Meurs H, Gosens R (2009) Airway structural components drive airway smooth muscle remodeling in asthma. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:683–692
Pera T, Gosens R, Lesterhuis AH, Sami R, Toorn M, Zaagsma J, Meurs H (2010) Cigarette smoke and lipopolysaccharide induce a proliferative airway smooth muscle phenotype. Respir Res 11:48
Panettieri RA Jr, Kotlikoff MI, Gerthoffer WT, Hershenson MB, Woodruff PG, Hall IP, Banks-Schlegel S, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (2008) Airway smooth muscle in bronchial tone, inflammation, and remodeling: basic knowledge to clinical relevance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:248–252
Jarai G, Sukkar M, Garrett S, Duroudier N, Westwick J, Adcock I, Chung KF (2004) Effects of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-13 and transforming growth factor-beta on gene expression in human airway smooth muscle using gene microarrays. Eur J Pharmacol 497:255–265
Fernandes DJ, Bonacci JV, Stewart AG (2006) Extracellular matrix, integrins, and mesenchymal cell function in the airways. Curr Drug Targets 7:567–577
Parameswaran K, Willems-Widyastuti A, Alagappan VK, Radford K, Kranenburg AR, Sharma HS (2006) Role of extracellular matrix and its regulators in human airway smooth muscle biology. Cell Biochem Biophys 44:139–146
Schuliga M, Ong SC, Soon L, Zal F, Harris T, Stewart AG (2010) Airway smooth muscle remodels pericellular collagen fibrils: implications for proliferation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298:L584–L592
James AL, Wenzel S (2007) Clinical relevance of airway remodelling in airway diseases. Eur Respir J 30:134–155
Malmstrom J, Larsen K, Malmstrom L, Tufvesson E, Parker K, Marchese J, Williamson B, Hattan S, Patterson D, Martin S, Graber A, Juhasz HP, Westergren-Thorsson G, Marko-Varga G (2004) Proteome annotations and identifications of the human pulmonary fibroblast. J Proteome Res 3:525–537
Zandvoort A, Postma DS, Jonker MR, Noordhoek JA, Vos JT, Timens W (2008) Smad gene expression in pulmonary fibroblasts: indications for defective ECM repair in COPD. Respir Res 9:83
Hallgren O, Nihlberg K, Dahlback M, Bjermer L, Eriksson LT, Erjefalt JS, Lofdahl CG, Westergren-Thorsson G (2010) Altered fibroblast proteoglycan production in COPD. Respir Res 11:55
Roberts AB, McCune BK, Sporn MB (1992) TGF-beta: regulation of extracellular matrix. Kidney Int 41:557–559
Schiller M, Javelaud D, Mauviel A (2004) TGF-beta-induced SMAD signaling and gene regulation: consequences for extracellular matrix remodeling and wound healing. J Dermatol Sci 35:83–92
Morty RE, Konigshoff M, Eickelberg O (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling across ages: from distorted lung development to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:607–613
Sugiura H, Ichikawa T, Liu X, Kobayashi T, Wang XQ, Kawasaki S, Togo S, Kamio K, Mao L, Ann Y, Ichinose M, Rennard SI (2009) N-acetyl-L-cysteine inhibits TGF-beta1-induced profibrotic responses in fibroblasts. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 22:487–491
Araya J, Nishimura SL (2010) Fibrogenic reactions in lung disease. Annu Rev Pathol 5:77–98
Camara J, Jarai G (2010) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in primary human bronchial epithelial cells is Smad-dependent and enhanced by fibronectin and TNF-alpha. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 3(1):2
Kranenburg AR, Willems-Widyastuti A, Moori WJ, Sterk PJ, Alagappan VK, de Boer WI, Sharma HS (2006) Enhanced bronchial expression of extracellular matrix proteins in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Pathol 126:725–735
Lagente V, Manoury B, Nenan S, Le Quement C, Martin-Chouly C, Boichot E (2005) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the development of airway inflammation and remodeling. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:1521–1530
Li H, Cui D, Ma N, Lu L, Gao Y, Cui X, Wang D (2002) The effect of extracellular matrix remodeling on airflow obstruction in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 25:403–407
Li H, Cui D, Tong X, Ma N, Gao Y, Cui X, Lu L, Wang D, Liang Y (2002) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in extracellular matrix remodelling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rat models. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 41:393–398
Hogg JC, McDonough JE, Gosselink JV, Hayashi S (2009) What drives the peripheral lung-remodeling process in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:668–672
Papakonstantinou E, Karakiulakis G (2009) The ‘sweet’ and ‘bitter’ involvement of glycosaminoglycans in lung diseases: pharmacotherapeutic relevance. Br J Pharmacol 157:1111–1127
Klagas I, Goulet S, Karakiulakis G, Zhong J, Baraket M, Black JL, Papakonstantinou E, Roth M (2009) Decreased hyaluronan in airway smooth muscle cells from patients with asthma and COPD. Eur Respir J 34:616–628
van Straaten JF, Coers W, Noordhoek JA, Huitema S, Flipsen JT, Kauffman HF, Timens W, Postma DS (1999) Proteoglycan changes in the extracellular matrix of lung tissue from patients with pulmonary emphysema. Mod Pathol 12:697–705
Noordhoek JA, Postma DS, Chong LL, Menkema L, Kauffman HF, Timens W, van Straaten JF, van der Geld YM (2005) Different modulation of decorin production by lung fibroblasts from patients with mild and severe emphysema. COPD 2:17–25
Hogg JC, Timens W (2009) The pathology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Annu Rev Pathol 4:435–459
Bracke KR, Dentener MA, Papakonstantinou E, Vernooy JH, Demoor T, Pauwels NS, Cleutjens J, van Suylen RJ, Joos GF, Brusselle GG, Wouters EF (2010) Enhanced deposition of low-molecular-weight hyaluronan in lungs of cigarette smoke-exposed mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42:753–761
McKee CM, Penno MB, Cowman M, Burdick MD, Strieter RM, Bao C, Noble PW (1996) Hyaluronan (HA) fragments induce chemokine gene expression in alveolar macrophages. The role of HA size and CD44. J Clin Invest 98:2403–2413
Khan AI, Kerfoot SM, Heit B, Liu L, Andonegui G, Ruffell B, Johnson P, Kubes P (2004) Role of CD44 and hyaluronan in neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol 173:7594–7601
Dentener MA, Louis R, Cloots RH, Henket M, Wouters EF (2006) Differences in local versus systemic TNFalpha production in COPD: inhibitory effect of hyaluronan on LPS induced blood cell TNFalpha release. Thorax 61:478–484
Cantor JO (2007) Potential therapeutic applications of hyaluronan in the lung. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2:283–288
Scotton CJ, Chambers RC (2007) Molecular targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus. Chest 132:1311–1321
Westergren-Thorsson G, Larsen K, Nihlberg K, Andersson-Sjoland A, Hallgren O, Marko-Varga G, Bjermer L (2010) Pathological airway remodelling in inflammation. Clin Respir J 4(Suppl 1):1–8
Phan SH (2008) Biology of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:334–337
Kaarteenaho-Wiik R, Paakko P, Sormunen R (2009) Ultrastructural features of lung fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts. Ultrastruct Pathol 33:6–15
Watsky MA, Weber KT, Sun Y, Postlethwaite A (2010) New insights into the mechanism of fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation and associated pathologies. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 282:165–192
McAnulty RJ (2007) Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts: their source, function and role in disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:666–671
Wynn TA (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210
Wicks J, Haitchi HM, Holgate ST, Davies DE, Powell RM (2006) Enhanced upregulation of smooth muscle related transcripts by TGF beta2 in asthmatic (myo) fibroblasts. Thorax 61:313–319
Choe MM, Sporn PH, Swartz MA (2006) Extracellular matrix remodeling by dynamic strain in a three-dimensional tissue-engineered human airway wall model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35:306–313
Singh SR, Hall IP (2008) Airway myofibroblasts and their relationship with airway myocytes and fibroblasts. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:127–132
Michalik M, Pierzchalska M, Legutko A, Ura M, Ostaszewska A, Soja J, Sanak M (2009) Asthmatic bronchial fibroblasts demonstrate enhanced potential to differentiate into myofibroblasts in culture. Med Sci Monit 15:194–201
Schmidt M, Sun G, Stacey MA, Mori L, Mattoli S (2003) Identification of circulating fibrocytes as precursors of bronchial myofibroblasts in asthma. J Immunol 171:380–389
Hong KM, Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, Strieter RM (2007) Differentiation of human circulating fibrocytes as mediated by transforming growth factor-beta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J Biol Chem 282:22910–22920
Andersson-Sjoland A, de Alba CG, Nihlberg K, Becerril C, Ramirez R, Pardo A, Westergren-Thorsson G, Selman M (2008) Fibrocytes are a potential source of lung fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:2129–2140
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada H, Neilson EG (2002) Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest 110:341–350
Willis BC, Liebler JM, Luby-Phelps K, Nicholson AG, Crandall ED, du Bois RM, Borok Z (2005) Induction of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 166:1321–1332
Kasai H, Allen JT, Mason RM, Kamimura T, Zhang Z (2005) TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir Res 5:56
Kim KK, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Robillard L, Galvez MG, Brumwell AN, Sheppard D, Chapman HA (2006) Alveolar epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13180–13185
Kim JH, Jang YS, Eom KS, Hwang YI, Kang HR, Jang SH, Kim CH, Park YB, Lee MG, Hyun IG, Jung KS, Kim DG (2007) Transforming growth factor beta1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of A549 cells. J Korean Med Sci 22:898–904
Kim KK, Wei Y, Szekeres C, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Hill ML, Frank JA, Brumwell AN, Wheeler SE, Kreidberg JA, Chapman HA (2009) Epithelial cell alpha3beta1 integrin links beta-catenin and Smad signaling to promote myofibroblast formation and pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 119:213–224
Zhang M, Zhang Z, Pan HY, Wang DX, Deng ZT, Ye XL (2009) TGF-beta1 induces human bronchial epithelial cell-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Lung 187:187–194
Ramos C, Becerril C, Montano M, Garcia-De-Alba C, Ramirez R, Checa M, Pardo A, Selman M (2010) FGF-1 reverts epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-{beta}1 through MAPK/ERK kinase pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 299(2):L222–L231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salazar, L.M., Herrera, A.M. Fibrotic Response of Tissue Remodeling in COPD. Lung 189, 101–109 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9279-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9279-2