Abstract
Introduction
There are several practical problems encountered in the TLIF procedure with implantation of two titanium cages, such as difficulty in achieving symmetric positioning with two cages, loosening of the first cage following insertion of the second cage and higher direct costs to the patient.
Method
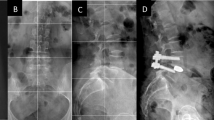
From January 2005 to December 2007, a total of 76 consecutive patients treated with instrumented TLIF with single cage and excised local bone were enrolled in the current study. There were 45 males and 31 females aged between 31 and 75 years (mean 50.9 years). Forty-five patients had degenerative disc diseases alone, 23 had associated isthmic or degenerative spondylolisthesis and 8 had recurrent disc herniations. Clinical outcomes were evaluated using the Oswestry Disability Index and a visual analog scale. Intervertebral height and fusion status were assessed on X-ray and two-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction.
Results
All the patients followed up. The mean follow-up period was 21.8 months (range from 12 to 48 months). No nerve injuries occurred during operation. Postoperative ODI and VAS scores in all the patients were more than the preoperative ones with significant differences. All the patients had complete interbody fusion and, at the final follow-up, none had instrumentation failure. Postoperative intervertebral height in all the patients was better than the preoperative ones with statistical significances.
Conclusions
Instrumented TLIF with single cage is a safe and effective method for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blume HG, Rojas CH (1981) Unilateral lumbar interbody fusion (posterior approach) utilizing dowel graft. J Neurol Orthop Surg 2:171–175
Harms J, Rolinger H (1982) Die operative Behandlung der Spondylolisthese durch dorsale Aufrichtung und ventrale Verblockung a one-stager procedure in operative treatment of spondylolistheses: dorsal traction–reposition and anterior fusion. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 120:343–347
Lauber S, Schulte TL, Liljenqvist U, Harm H, Hackenberg L (2006) Clinical and radiologic 2–4-year results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Spine 31:1693–1698
Murakami H, Horton WC, Tomita K, Hutton WC (2004) A two-cage reconstruction versus a single mega-cage reconstruction for lumbar interbody fusion: an experimental comparison. Eur Spine J 13:432–440
Kettler A, Schmoelz W, Kast E, Gottwald M, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2005) In vitro stabilizing effect of a transforaminal compared with two posterior lumbar interbody fusion cages. Spine 30:E665–E670
Murakami H, Horton WC, Kawahara N, Tomita K, Hutton WC (2001) Anterior lumbar interbody fusion using two standard cylindrical threaded cages, a single mega-cage, or dual nested cages: a biomechanical comparison. J Orthop Sci 6:343–348
Cole CD, McCall TD, Schmidt MH, Dailey AT (2009) Comparison of low back fusion techniques: transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) or posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) approaches. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2:118–126
Hackenberg L, Halm H, Bullmann V, Vieth V, Schneider M, Liljenqvist U (2005) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a safe technique with satisfactory three to five year results. Eur Spine J 14:551–558
Ames CP, Acosta FL, Chi J, Lyengar J, Muiru W, Acaroglu E et al (2005) Biomechanical comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion performed at 1 and 2 levels. Spine 30:E562–E566
Schwender JD, Holly LT, Rouben DP, Foley KT (2005) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:S1–S6
Holly LT, Schwender JD, Roben DP, Foley KT (2006) Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: indications, technique, and complications. Neurosurg Focus 20:1–5
Zaveri GR, Mehta SS (2009) Surgical treatment of lumbar tuberculous spondylodiscitis by transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and posterior instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:257–262
Brislin B, Vaccaro AR (2002) Advances in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Clin N Am 33:367–374
Humphreys SC, Hodges SD, Patwardhan AG, Eck JC, Murphy RB, Covington LA (2001) Comparison of posterior and transforaminal approaches to lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 26:567–571
Hee HT, Castro FP, Majd ME, Holt RT, Myers L (2001) Anterior/posterior lumbar fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: analysis of complications and predictive factors. J Spinal Disord Tech 14:533–540
Matsumura A, Taneichi H, Suda K, Kajino T, Moridaira H, Kaneda K (2006) Comparative study of radiographic disc height changes using two different interbody devices for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: open box vs. fenestrated tube interbody cage. Spine 31:E871–E876
Taneichi H, Suda K, Kajino T, Matsumara A, Moridaira H, Kaneda K (2006) Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and bilateral anterior-column fixation with two Brantigan I/F cages per level: clinical outcomes during a minimum 2-year follow-up period. J Neurosurg Spine 4:198–205
Lowe TG, Tahernia AD, O’Brien MF, Smith DBA (2002) Unilateral transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): indications, technique, and 2-year results. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:31–38
McAfee PC, DeVine JG, Chaput CD, Prybis BG, Fedder IL, Cunningham BW et al (2005) The indications for interbody fusion cages in the treatment of spondylolisthesis: analysis of 120 cases. Spine 30:S60–S65
Masry EIMA, Khayal H, Salah H (2008) Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) using a single cage for treatment of low grade lytic spondylolisthesis. Acta Orthop Belg 74:667–671
Mummaneni PV, Haid RW, Rodts GE (2004) Lumbar interbody fusion: state-of-the-art technical advances. J Neurosurg Spine 1:24–30
Weiner BE, Fraser RD (1998) Spine update lumbar interbody cages. Spine 23:634–640
Biyani A, Rodway I (2007) Breakage and malposition of banana shaped carbon fiber reinforced polymer cage during TLIF procedure. Spine J 7:141–142
Acknowledgments
This work was supported partly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970718), partly by the Program of Shanghai Subject Chief Scientist (A type) (07XD14006), partly by the National High tech Research and Development Program (863 program) (2007AA03Z313), partly by the Shanghai International Science and Technology Partnership Program (09410702700), partly by the “Technology Innovation Action Plan” Key Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (08411952500), partly by the “Technology Innovation Action Plan” Key Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (09411953800) and partly by the Program for Outstanding Medical Academic Leader.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial ties to any of the companies that manufacture the materials used in the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wang, B., Dong, J. et al. Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with single cage for the treatment of degenerative lumbar disease. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 1239–1245 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1292-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1292-7