Abstract
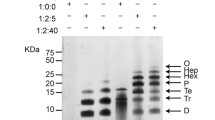
The formation of low-order oligomers of β-amyloid (Aβ) within the brain is widely believed to be a central component of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. However, despite advances in high-throughput and high-resolution techniques such as xMAP and mass spectrometry (MS), investigations into these oligomeric species have remained reliant on low-resolution Western blots and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The current investigation compared Aβ profiles within human cortical tissue using sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), xMAP and surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight MS and found that whilst there was significant correlation across the techniques regarding levels of monomeric Aβ, only SDS-PAGE was capable of detecting dimeric isoforms of Aβ. The addition of synthetic di-tyrosine cross-linked Aβ1–40Met35(O) to the AD tissue demonstrated that the MS methodology was capable of observing dimeric Aβ at femto-molar concentrations, with no noticeable effect on monomeric Aβ levels. Focus turned to the association between SDS-PAGE and levels of observable dimeric Aβ within the AD brain tissue. These investigations revealed that increased levels of dimeric Aβ were observed with increasing concentrations of SDS in the sample buffer. This finding was subsequently confirmed using synthetic Aβ1–42 and suggests that SDS was inducing the formation of dimeric Aβ. The findings that SDS promotes Aβ dimerization have significant implications for the putative role of low-order oligomers in AD pathogenesis and draw into question the utility of oligomeric Aβ as a therapeutic target.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnham KJ, Ciccotosto GD, Tickler AK, Ali FE, Smith DG, Williamson NA, Lam YH, Carrington D, Tew D, Kocak G, Volitakis I, Separovic F, Barrow CJ, Wade JD, Masters CL, Cherny RA, Curtain CC, Bush AI, Cappai R (2003) Neurotoxic, redox-competent Alzheimer’s b-amyloid is released from lipid membrane by methionine oxidation. J Biol Chem 278(44):42959–42965
Barnham KJ, Haeffner F, Ciccotosto GD, Curtain CC, Tew D, Mavros C, Beyreuther K, Carrington D, Masters CL, Cherny RA, Cappai R, Bush AI (2004) Tyrosine gated electron transfer is key to the toxic mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease b-amyloid. Faseb J 18(12):1427. doi:10.1096/fj.04-1890fje
Bitan G, Kirkitadze MD, Lomakin A, Vollers SS, Benedek GB, Teplow DB (2003) Amyloid b-protein (Ab) assembly: Ab40 and Ab42 oligomerize through distinct pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(1):330–335
Cacquevel M, Aeschbach L, Houacine J, Fraering PC (2012) Alzheimer’s disease-linked mutations in presenilin-1 result in a drastic loss of activity in purified γ-secretase complexes. PLoS ONE 7(4):e35133. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035133
Carson RT, Vignali DAA (1999) Simultaneous quantitation of 15 cytokines using a multiplexed flow cytometric assay. J Immunol Methods 227(1–2):41–52. doi:10.1016/s0022-1759(99)00069-1
The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease Neurobiol Aging 18(4 Suppl):S1–2
Crouch PJ, Hung LW, Adlard PA, Cortes M, Lal V, Filiz G, Perez KA, Nurjono M, Caragounis A, Du T, Laughton K, Volitakis I, Bush AI, Li QX, Masters CL, Cappal R, Cherny RA, Donnelly PS, White AR, Barnham KJ (2009) Increasing Cu bioavailability inhibits Ab oligomers and tau phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(2):381–386. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809057106
Curtain CC, Ali F, Volitakis I, Cherny RA, Norton RS, Beyreuther K, Barrow CJ, Masters CL, Bush AI, Barnham KJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-b binds copper and zinc to generate an allosterically ordered membrane-penetrating structure containing superoxide dismutase-like subunits. J Biol Chem 276:20466–20473
Dickson DW, Crystal HA, Bevona C, Honer W, Vincent I, Davies P (1995) Correlations of synaptic and pathological markers with cognition of the elderly. Neurobiol Aging 16(3):285–298
Figurski MJ, Waligórska T, Toledo J, Vanderstichele H, Korecka M, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2012) Improved protocol for measurement of plasma β-amyloid in longitudinal evaluation of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative study patients. Alzheimer Dement 8(4):250–260
Gellermann GP, Byrnes H, Striebinger A, Ullrich K, Mueller R, Hillen H, Barghorn S (2008) Ab-globulomers are formed independently of the fibril pathway. Neurobiol Dis 30(2):212–220
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356. doi:10.1126/science.1072994
Hung LW, Ciccotosto GD, Giannakis E, Tew DJ, Perez K, Masters CL, Cappai R, Wade JD, Barnham KJ (2008) Amyloid-b peptide (Ab) neurotoxicity is modulated by the rate of peptide aggregation: Abeta dimers and trimers correlate with neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 28(46):11950–11958
Ida N, Hartmann T, Pantel J, Schroder J, Zerfass R, Forstl H, Sandbrink R, Masters CL, Beyreuther K (1996) Analysis of heterogeneous b-A4 peptides in human cerebrospinal fluid and blood by a newly developed sensitive western blot assay. J Biol Chem 271:22908–22914
Karran E (2012) Current status of vaccination therapies in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 123(5):647–651. doi:10.1111/jnc.12009
Klyubin I, Walsh DM, Lemere CA, Cullen WK, Shankar GM, Betts V, Spooner ET, Jiang L, Anwyl R, Selkoe DJ, Rowan MJ (2005) Amyloid-b protein immunotherapy neutralizes Ab oligomers that disrupt synaptic plasticity in vivo. Nat Med 11(5):556–561
Koivunen J, Verkkoniemi A, Aalto S, Paetau A, Ahonen J-P, Viitanen M, Någren K, Rokka J, Haaparanta M, Kalimo H, Rinne JO (2008) PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake shows predominantly striatal increase in variant Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 131(7):1845–1853. doi:10.1093/brain/awn107
Kok WM, Scanlon DB, Karas JA, Miles LA, Tew DJ, Parker MW, Barnham KJ, Hutton CA (2009) Solid-phase synthesis of homodimeric peptides: preparation of covalently-linked dimers of amyloid-b peptide. Chem Commun (Camb) 41:6228–6230. doi:10.1039/b912784d
Lewis H, Beher D, Cookson N, Oakley A, Piggott M, Morris CM, Jaros E, Perry R, Ince P, Kenny RA, Ballard CG, Shearman MS, Kalaria RN (2006) Quantification of Alzheimer pathology in ageing and dementia: age-related accumulation of amyloid-β(42) peptide in vascular dementia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32(2):103–118. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00696.x
Lui JK, Laws SM, Li QX, Villemagne VL, Ames D, Brown B, Bush AI, De Ruyck K, Dromey J, Ellis KA, Faux NG, Foster J, Fowler C, Gupta V, Hudson P, Laughton K, Masters CL, Pertile K, Rembach A, Rimajova M, Rodrigues M, Rowe CC, Rumble R, Szoeke C, Taddei K, Taddei T, Trounson B, Ward V, Martins RN, Grp AR (2010) Plasma amyloid-b as a biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease: the AIBL study of aging. J Alzheimers Dis 20(4):1233–1242. doi:10.3233/jad-2010-090249
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Baborie A, Sampathu DM, Du Plessis D, Jaros E, Perry RH, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DM, Lee VM (2011) A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol 122(1):111–113. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0845-8
Mann DM, Takeuchi A, Sato S, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Rossor MN, Haltia M, Kalimo H, Iwatsubo T (2001) Cases of Alzheimer’s disease due to deletion of exon 9 of the presenilin-1 gene show an unusual but characteristic b-amyloid pathology known as ‘cotton wool’ plaques. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27(3):189–196
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
McColl G, Roberts BR, Gunn AP, Perez KA, Tew DJ, Masters CL, Barnham KJ, Cherny RA, Bush AI (2009) The Caenorhabditis elegans Ab 1–42 model of Alzheimer disease predominantly expresses Ab 3–42. J Biol Chem 284(34):22697–22702. doi:10.1074/jbc.C109.028514
McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick’s Disease. Arch Neurol 58(11):1803–1809. pii:nsa10000
McLean CA, Cherny RA, Fraser FW, Fuller SJ, Smith MJ, Beyreuther K, Bush AI, Masters CL (1999) Soluble pool of Ab amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 46:860–866
Mintun MA, Larossa GN, Sheline YI, Dence CS, Lee SY, Mach RH, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, DeKosky ST, Morris JC (2006) [11C]PIB in a nondemented population: potential antecedent marker of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 67(3):446–452. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000228230.26044.a4
Montine TJ, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW, Duyckaerts C, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Mirra SS, Nelson PT, Schneider JA, Thal DR, Trojanowski JQ, Vinters HV, Hyman BT (2012) National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol 123(1):1–11. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0910-3
Moore B, Chakrabarty P, Levites Y, Kukar T, Baine A-M, Moroni T, Ladd T, Das P, Dickson D, Golde T (2012) Overlapping profiles of Ab peptides in the Alzheimer’s disease and pathological aging brains. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 4(3):18
Olsson A, Vanderstichele H, Andreasen N, De Meyer G, Wallin A, Holmberg B, Rosengren L, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K (2005) Simultaneous measurement of β-amyloid(1–42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau (Thr181) in cerebrospinal fluid by the xMAP technology. Clin Chem 51(2):336–345. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.039347
Pike CJ, Overman MJ, Cotman CW (1995) Amino-terminal deletions enhance aggregation of b-amyloid peptides in vitro. J Biol Chem 270:23895–23898
Podlisny MB, Ostaszewski BL, Squazzo SL, Koo EH, Rydell RE, Teplow DB, Selkoe DJ (1995) Aggregation of secreted amyloid beta-protein into sodium dodecyl sulfate-stable oligomers in cell culture. J Biol Chem 270(16):9564–9570
Portelius E, Bogdanovic N, Gustavsson MK, Volkmann I, Brinkmalm G, Zetterberg H, Winblad B, Blennow K (2010) Mass spectrometric characterization of brain amyloid beta isoform signatures in familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 120(2):185–193. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0690-1
Portelius E, Olsson M, Brinkmalm G, Ruetschi U, Mattsson N, Andreasson U, Gobom J, Brinkmalm A, Holtta M, Blennow K, Zetterberg H (2013) Mass spectrometric characterization of amyloid-beta species in the 7PA2 cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer Dis 33(1):85–93. doi:10.3233/jad-2012-120994
Rangachari V, Moore BD, Reed DK, Sonoda LK, Bridges AW, Conboy E, Hartigan D, Rosenberry TL (2007) Amyloid-beta(1–42) rapidly forms protofibrils and oligomers by distinct pathways in low concentrations of sodium dodecylsulfatet. Biochemistry 46(43):12451–12462
Roher AE, Chaney MO, Kuo YM, Webster SD, Stine WB, Haverkamp LJ, Woods AS, Cotter RJ, Tuohy JM, Krafft GA, Bonnell BS, Emmerling MR (1996) Morphology and toxicity of Ab-(1–42) dimer derived from neuritic and vascular amyloid deposits of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 271:20631–20635
Rowe CC, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong SJ, Pike K, Savage G, Cowie TF, Dickinson KL, Maruff P, Darby D, Smith C, Woodward M, Merory J, Tochon-Danguy H, O’Keefe G, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Price JC, Masters CL, Villemagne VL (2007) Imaging beta-amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology 68(20):1718–1725
Selkoe DJ (2011) Resolving controversies on the path to Alzheimer’s therapeutics. Nat Med 17(9):1060–1065
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14(8):837–842
Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Clark CM, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, Blennow K, Soares H, Simon A, Lewczuk P, Dean R, Siemers E, Potter W, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann Neurol 65(4):403–413. doi:10.1002/ana.21610
Simmons LK, May PC, Tomaselli KJ, Rydel RE, Fuson KS, Brigham EF, Wright S, Lieberburg I, Becker GW, Brems DN et al (1994) Secondary structure of amyloid b peptide correlates with neurotoxic activity in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 45:373–379
Skaff O, Jolliffe KA, Hutton CA (2005) Synthesis of the side chain cross-linked tyrosine oligomers dityrosine, trityrosine, and pulcherosine. J Org Chem 70(18):7353–7363. doi:10.1021/jo051076m
Smith DP, Smith DG, Curtain CC, Boas JF, Pilbrow JR, Ciccotosto GD, Lau TL, Tew DJ, Perez K, Wade JD, Bush AI, Drew SC, Separovic F, Masters CL, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2006) Copper-mediated amyloid-beta toxicity is associated with an intermolecular histidine bridge. J Biol Chem 281(22):15145–15154
Tabaton M, Piccini A (2005) Role of water-soluble amyloid-beta in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Exp Pathol 86(3):139–145. doi:10.1111/j.0959-9673.2005.00428.x
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30:572–580
Tew DJ, Bottomley SP, Smith DP, Ciccotosto GD, Babon J, Hinds MG, Masters CL, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2008) Stabilization of neurotoxic soluble beta-sheet-rich conformations of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptide. Biophys J 94(7):2752–2766
Tickler AK, Barrow CJ, Wade JD (2001) Improved preparation of amyloid-b peptides using DBU as Na-Fmoc deprotection reagent. J Pept Sci 7:488–494
Toledo J, Vanderstichele H, Figurski M, Aisen P, Petersen R, Weiner M, Jack C, Jagust W, Decarli C, Toga A, Toledo E, Xie S, Lee V, Trojanowski J, Shaw L (2011) Factors affecting Aβ plasma levels and their utility as biomarkers in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol 122(4):401–413. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0861-8
Villemagne VL, Perez KA, Pike KE, Kok WM, Rowe CC, White AR, Bourgeat P, Salvado O, Bedo J, Hutton CA, Faux NG, Masters CL, Barnham KJ (2010) Blood borne amyloid-beta dimer correlates with clinical markers of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 30(18):6315–6322
Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV, Cullen WK, Anwyl R, Wolfe MS, Rowan MJ, Selkoe DJ (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 416(6880):535–539
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ (2007) A beta oligomers—a decade of discovery. J Neurochem 101(5):1172–1184
Walsh DM, Townsend M, Podlisny MB, Shankar GM, Fadeeva JV, El Agnaf O, Hartley DM, Selkoe DJ (2005) Certain inhibitors of synthetic amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta) fibrillogenesis block oligomerization of natural Abeta and thereby rescue long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25(10):2455–2462
Walsh DM, Tseng BP, Rydel RE, Podlisny MB, Selkoe DJ (2000) The oligomerization of amyloid beta-protein begins intracellularly in cells derived from human brain. Biochemistry 39(35):10831–10839
Wang J, Dickson DW, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1999) The levels of soluble versus insoluble brain Ab distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from normal and pathologic aging. Exp Neurol 158:328–337
Yokota O, Terada S, Ishizu H, Ujike H, Ishihara T, Namba M, Hayashi Y, Nishinaka T, Namba R, Nakashima H, Ueda K, Checler F, Kuroda S (2003) Variability and heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease with cotton wool plaques: a clinicopathological study of four autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 106(4):348–356. doi:10.1007/s00401-003-0737-7
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watt, A.D., Perez, K.A., Rembach, A. et al. Oligomers, fact or artefact? SDS-PAGE induces dimerization of β-amyloid in human brain samples. Acta Neuropathol 125, 549–564 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1083-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1083-z