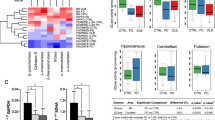
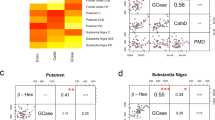
Abstract
Previous studies have shown altered synuclein, increased oxidative stress damage and increased oxidative stress responses in patients with sporadic Parkinson’s disease (PD) without cognitive impairment. Yet no information exists about possible molecular alterations in the cerebral cortex in familial PD. The present study shows abnormal α-synuclein solubility and aggregation, and aggregated nitrated α-synuclein, in the cerebral cortex (area 8) in cases with long-lasting PD linked with the G2019S LRRK2 mutation, one of them with a few Lewy bodies (LBs) and the other two without LBs in the cerebral cortex. Increased expression of the oxidative stress marker malondialdehyde-lysine (MDAL), together with increased oxidative stress responses, AGE receptors (RAGE) and superoxide dismutase 2, occurred in the frontal cortex in the three LRRK2 cases compared with three controls processed in parallel. Bi-dimensional gel electrophoresis, western blotting, in-gel digestion and mass spectrometry disclosed glial fibrillary acidic protein as a target of MDAL adducts. Tubulin β4 and enolase 2 were also identified as targets of oxidative damage. These results demonstrate biochemical abnormalities of α-synuclein, and increased oxidative stress damage and oxidative stress responses in the frontal cortex in PD linked with G2019S LRRK2 mutation not related with the presence of cortical LBs and in the absence of apparent cognitive deficits. These findings show that the cerebral cortex in familial PD linked with G2019S LRRK2 is affected in a similar way than that seen in sporadic PD without cognitive impairment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chartaway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ (2006) Phosphorylation of Ser 129 is the dominant pathological modification of synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281:29739–29759
Arima K, Hirai S, Sunohara N, Aoto K, Izumiyama Y, Ueda K, Ikeda K, Kawai M (1999) Cellular co-localization of phosphorylated tau- and NACP/alpha-synuclein-epitopes in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res 843:53–61
Baba M, Nakajo S, Tu PH, Tomita T, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Iwatsubo T (1998) Aggregation of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 152:879–884
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibañez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Ooostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RAI, Jansen Steur ENH, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Braak H, Sandmann-Keil D, Gai W, Braak E (1999) Extensive axonal Lewy neurites in Parkinson’s disease: a novel pathological feature revealed by alpha-synuclein immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 265:67–69
Butterfield DA, Sultana R, Poon HF (2006) Redox proteomics: a new approach to investigate oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. In: Dalle-Donne I, Scaloni A, Butterfield DA (eds) Redox proteomics: from protein modifications to cellular dysfunction and diseases. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 563–603
Choi J, Levey AI, Weintraub ST, Rees HD, Gearing M, Chin LS, Li L (2004) Oxidative modifications and down-regulation of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. J Biol Chem 279:13256–13264
Choi J, Rees HD, Weintraub ST, Levey AI, Chin LS, Li L (2005) Oxidative modifications and aggregation of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase associated with Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. J Biol Chem 280:11648–11655
Choi J, Sullards MC, Olzmann JA, Rees HD, Weintraub ST, Bostwick DE, Gearing M, Levey AI, Chin LS, Li L (2006) Oxidative damage of DJ-1 is linked to sporadic Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases. J Biol Chem 281:10816–10824
Chung KKK, Thomas B, Li X, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Marsh L, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2004) S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates ubiquitination and compromises Parkin’s protective function. Science 304:1328–1331
Dalfó E, Gómez-Isla T, Rosa JL, Nieto Bodelón M, Cuadrado Tejedor M, Barrachina M, Ambrosio S, Ferrer I (2004) Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with Rab proteins in alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:302–313
Dalfó E, Portero-Otín M, Ayala V, Martínez A, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2005) Evidence of oxidative stress in the neocortex in incidental Lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:816–830
Dickson DW (2001) Alpha-synuclein and the Lewy body disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 14:423–432
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Chen Q, Gur TL, Hurtig HI, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2000) Widespread nitration of pathological inclusions in neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. Am J Pathol 157:1439–1445
El-Agnaf OM, Jakes R, Curran MD, Wallace A (1998) Effects of the mutations Ala30 to Pro and Ala53 to Thr on the physical and morphological properties of alpha-synuclein protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett 440:67–70
Elbaz A (2008) LRRK2: bridging the gap between sporadic and hereditary Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 7:562–564
Ferrer I (2009) Early involvement of the cerebral cortex in Parkinson disease: convergence of multiple metabolic defects. Prog Neurobiol 88:89–103
Ferrer I, Martinez A, Boluda S, Parchi P, Barrachina M (2008) Brain banks: benefits, limitations and cautions concerning the use of post-mortem brain tissue for molecular studies. Cell Tissue Bank 9:181–194
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) α-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4:160–164
Gaig C, Ezquerra M, Marti MJ, Vallderiola F, Muñoz E, Lladó A, Rey MJ, Cardozo A, Molinuevo JL, Tolosa E (2008) Screening for the LRRK2 G2019S and codon1441 mutations in a pathological series of parkinsonian syndromes and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Neurol Sci 270:94–98
Gaig C, Marti MJ, Ezquerra M, REy MJ, Cardozo A, Tolosa E (2007) G2019S LRRK2 mutation causing Parkinson’s disease without Lewy bodies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 78:626–628
Galvin JE, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Synucleinopathies: clinical and pathological implications. Arch Neurol 58:186–190
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropuolos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective α-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Gómez A, Ferrer I (2009) Increased oxidation of certain glycolysis and energy metabolism enzymes in the frontal cortex in Lewy body diseases. J Neurosci Res 87:1002–1013
Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ, Xia Y, Takeda A, Sisk A, Sundsmo M, Masliah E (1999) Oxidative stress induces amyloid-like aggregates formation of NACP/α-synuclein in vitro. NeuroReport 10:717–721
Hashimoto M, Masliah E (1999) α-Synuclein in Lewy body disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:707–720
Iwatsubo T (2003) Aggregation of α-synuclein in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 250(Suppl 3):11–14
Jellinger KA (2008) A critical reappraisal of current staging of Lewy-related pathology in human brain. Acta Neuropathol 116:1–16
Jellinger K, Mizuno Y (2003) Parkinson’s disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 159–187
Kahle PJ, Newmann M, Ozmen L, Mülkler V, Odoy S, Okamoto N, Jacobsen H, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K, Bogdanovic N, Riederer P, Kretzschmar HA, Haass C (2001) Selective insolubility of alpha-synuclein in human Lewy body diseases is recapitulated in a transgenic mouse model. Am J Pathol 159:2215–2225
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Korolainen MA, Auriola S, Nyman TA, Alafuzoff I, Pirttilä T (2005) Proteomic analysis of glial fibrillary acidic protein in Alzheimer’s disease and aging brain. Neurobiol Dis 20:858–870
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452
Li J, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2001) Effects of familial Parkinson’s disease point mutations A30P and A53T on the structural properties, aggregation, and fibrillation of human α-synuclein. Biochemistry 40:11604–11613
Li Y, Liu W, Oo TF, Wang L, Tang Y, Jackson-Lewis V, Zhou C, Geghman K, Bogdanov M, Przedborski S, Beal MF, Burke RE, Li C (2009) Mutant LRRK2(R1441G) BAC transgenic mice recapitulate cardinal features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 12:826–828
Martínez A, Portero-Otin M, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2009) Protein targets of oxidative damage in human neurodegenerative diseases with abnormal protein aggregates. Brain Pathol 2010; Epub ahead of print
Martínez A, Carmona M, Portero-Otin M, Naudí A, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2008) Type-dependent oxidative damage in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: cortical astrocytes are targets of oxidative damage. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:1122–1136
Martí-Massó JF, Ruiz-Martinez J, Bolaño MJ, Ruiz I, Gorostidi A, Moreno F, Ferrer I, López de Munain A (2009) Neuropathology of Parkinson disease with the R1441G mutation in LRRK2. Mov Disord (accepted)
Muntané G, Dalfó E, Martínez A, Rey MJ, Avila J, Pérez M, Portero M, Pamplona R, Ayala V, Ferrer I (2006) Glial fibrillary acidic protein is a major target of glycoxidative and lipoxidative damage in Pick’s disease. J Neurochem 99:177–185
Neumann M, Kahle PJ, Giassonb BI, Ozmen L, Borroni E, Spoore W, Muller V, Odoy S, Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ, Kretzschmar H, Haass C (2002) Misfolded proteinase K-resistant hyperphosphorylated alpha-synuclein in aged transgenic mice with locomotor deterioration and in human alpha-synucleinopathies. J Clin Invest 110:1429–1439
Paik SR, Shin HJ, Lee JM (2000) Metal-catalyzed oxidation of α-synuclein in the presence of copper(II) and hydrogen peroxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 378:269–277
Paisanz-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, van der Grug M, Lopez de Munain A, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martínez JR, Nicholl D, Carrera IM, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Martí-Massó JF, Pérez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singletomn AB (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44:595–600
Pamplona R, Dalfó E, Ayala V, Bellmunt MJ, Prat J, Ferrer I, Portero-Otín M (2005) Proteins in human brain cortex are modified by oxidation, glycoxidation, and lipoxidation. Effects of Alzheimer disease and identification of lipoxidation targets. J Biol Chem 280:21522–21530
Parkkinen L, Kauppinen T, Pirttila T, Autere JM, Alafuzoff I (2005) α-Synuclein pathology does not predict extrapyramidal symptoms or dementia. Ann Neurol 57:82–91
Parkkinen L, Pirttilä T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Applicability of current staging/categorization of alpha-synuclein pathology and their clinical relevance. Acta Neuropathol 115:399–407
Paxinou E, Chen Q, Weisse M, Giasson BI, Norris EH, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Ischiropoulos H (2001) Induction of alpha-synuclein aggregation by intracellular nitrative insult. J Neurosci 21:8053–8061
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Rajput A, Dickson DW, Robinson CA, Ross OA, Dächael JC, Lincoln SJ, Cobb SA, Rajput ML, Farrer MJ (2006) Parkinsonism, Lrrk2 G2019S, and tau neuropathology. Neurology 67:1506–1508
Saito Y, Kawashima A, Ruberu NN, Fujiwara H, Koyama S, Sawabe M, Arai T, Nagura H, Yamanouchi H, Hasegawa M, Iwatsubo T, Murayama S (2003) Accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein in aging human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:644–654
Santpere G, Ferrer I (2008) Delineation of progressive supranuclear palsy-like pathology. Astrocytes in striatum are primary targets of tau phosphorylation and GFAP oxidation. Brain Pathol 19:177–187
Santpere G, Ferrer I (2009) LRRK2 and neurodegeneration: a review. Acta Neuropathol 117:227–246
Schults CW (2006) Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:1661–1668
Sorolla MA, Reverter-Branchat G, Tamarit J, Ferrer I, Ros J, Cabiscol E (2008) Proteomic and oxidative stress analysis in human brain samples of Huntington disease. Free Radic Biol Med 45:667–678
Spillantini MG, Schmidt M, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Kaques R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) α-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6469–6473
Strauss KM, Martins LM, Plun-Favreau H, Marx FP, Kautzmann S, Berg D, Gasser T, Wszolek Z, Muller T, Bornemann A, Wolburg H, Downward J, Riess O, Schulz JB, Kruger R (2005) Loss of function mutations in the gene encoding Omi/HrtA2 in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 14:2099–2111
Sultana R, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA (2009) Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: role of Abeta in pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 118:131–150
Takahashi M, Kanuka H, Fujiwara H, Koyama A, Hasegawa M, Miura M, Iwatsubo T (2003) Phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein characteristic of synucleinopathy lesions is recapitulated in alpha-synuclein transgenic Drosophila. Neurosci Lett 336:155–158
Uversky VN (2007) Neuropathology, biochemistry, and biophysics of synuclein aggregation. J Neurochem 103:17–37
Uversky VN, Yamin G, Munishkina LA, Karymov MA, Millet IS, Doniach S, Lyubchenko YL, Fink AL (2005) Effects of nitration on the structure and aggregation of α-synuclein. Mol Brain Res 134:84–102
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Mugit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DC, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160
Wakabayashi K, Matsumoto K, Takayama K, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H (1997) NACP, a presynaptic protein, immunoreactivity in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 249:180–182
Wakabayashi K, Tanji K, Mori F, Takahashi H (2007) The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease: molecules implicated in the formation and degradation of α-synuclein aggregates. Neuropathology 27:494–506
Wakamatsu M, Ishii A, Ukai Y, Sakagami J, Iwata S, Ono M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura A, Tada N, Kobayashi K, Iwatsubo T, Yoshimoto M (2007) Accumulation of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in dopaminergic neurons of transgenic mice that express human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci Res 85:1819–1825
Wszolek ZK, Pfeiffer RF, Tsuboi Y, Uitti RJ, McComb RD, Stoessl AJ, Strongosky AJ, Zimprich A, Müller-Myhsok B, Farrer MJ, Gasser T, Calne DB, Dickson DW (2004) Autosomal dominant parkinsonism associated with variable synuclein and tau pathology. Neurology 62:1619–1622
Yamin G, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2003) Nitration inhibits fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein in vitro by formation of soluble oligomers. FEBS Lett 542:147–152
Yao D, Gu Z, Nakamura T, Shi ZQ, Ma Y, Gaston B, Palmer LA, Rockenstein EM, Zhang Z, Masliah E, Uehara T, Lipton SA (2004) Nitrosative stress linked to sporadic Parkinson’s disease: S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:10810–10814
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uiti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gómez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodríguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gómez-Tortosa E, del Ser T, Muñoz DG, de Yébenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of α-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Health, Instituto de Salud Carlos III PI08/0582, and supported by the European Commission under the Sixth Framework Programme BrainNet Europe II, LSHM-CT-2004-503039 and INDABIP FP6-2005-IFESCIHEALTH-7 Molecular Diagnostics. Thanks to T. Yohannan for editorial help.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations within the 3 years from the beginning of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez, A., Ferrer, I. Involvement of the cerebral cortex in Parkinson disease linked with G2019S LRRK2 mutation without cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol 120, 155–167 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0669-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0669-y