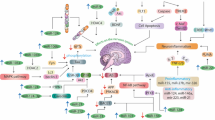
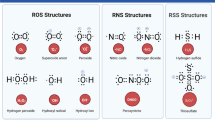
Abstract
RNA oxidation and its biological effects are less well studied compared to DNA oxidation. However, RNA may be more susceptible to oxidative insults than DNA, for RNA is largely single-stranded and its bases are not protected by hydrogen bonding and less protected by specific proteins. Also, cellular RNA locates in the vicinity of mitochondria, the primary source of reactive oxygen species. Oxidative modification can occur not only in protein-coding RNAs, but also in non-coding RNAs that have been recently revealed to contribute towards the complexity of the mammalian brain. Damage to coding and non-coding RNAs will cause errors in proteins and disturbances in the regulation of gene expression. While less lethal than mutations in the genome and not inheritable, such sublethal damage to cells might be associated with underlying mechanisms of degeneration, especially age-associated neurodegeneration that is commonly found in the elderly population. Indeed, oxidative RNA damage has been described recently in most of the common neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Of particular interest, the accumulating evidence obtained from studies on either human samples or experimental models coincidentally suggests that oxidative RNA damage is a feature in vulnerable neurons at early-stage of these neurodegenerative disorders, indicating that RNA oxidation actively contributes to the onset or the development of the disorders. Further investigations aimed at understanding of the processing mechanisms related to oxidative RNA damage and its consequences may provide significant insights into the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders and lead to better therapeutic strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PO et al (2003) Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature 421:859–863. doi:10.1038/nature01363
Abe T, Isobe C, Murata T, Sato C, Tohgi H (2003) Alteration of 8-hydroxyguanosine concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 336:105–108. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)01259-4
Abe T, Tohgi H, Isobe C, Murata T, Sato C (2002) Remarkable increase in the concentration of 8-hydroxyguanosine in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 70:447–450. doi:10.1002/jnr.10349
Ames BN, Gold LS (1991) Endogenous mutagens and the causes of aging and cancer. Mutat Res 250:3–16. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(91)90157-J
Andersen JK (2004) Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence? Nat Med 10(Suppl):S18–S25. doi:10.1038/nrn1434
Barber SC, Mead RJ, Shaw PJ (2006) Oxidative stress in ALS: a mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:1051–1067
Barciszewski J, Barciszewska MZ, Siboska G, Rattan SI, Clark BF (1999) Some unusual nucleic acid bases are products of hydroxyl radical oxidation of DNA and RNA. Mol Biol Rep 26:231–238. doi:10.1023/A:1007058602594
Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:205–214. doi:10.1038/nrd1330
Bellacosa A, Moss EG (2003) RNA repair: damage control. Curr Biol 13:R482–R484. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00408-1
Berg D, Roggendorf W, Schroder U et al (2002) Echogenicity of the substantia nigra: association with increased iron content and marker for susceptibility to nigrostriatal injury. Arch Neurol 59:999–1005. doi:10.1001/archneur.59.6.999
Brégeon D, Sarasin A (2005) Hypothetical role of RNA damage avoidance in preventing human disease. Mutat Res 577:293–302. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.04.002
Butterfield DA, Reed TT, Perluigi M et al (2007) Elevated levels of 3-nitrotyrosine in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: implications for the role of nitration in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1148:243–248. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.02.084
Cao X, Yeo G, Muotri AR, Kuwabara T, Gage FH (2006) Noncoding RNAs in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:77–103. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112839
Casadesus G, Smith MA, Basu S et al (2007) Increased isoprostane and prostaglandin are prominent in neurons in Alzheimer disease. Mol Neurodegener 2:2. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-2-2
Castellani RJ, Harris PL, Sayre LM et al (2001) Active glycation in neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer disease: N(epsilon)-(carboxymethyl) lysine and hexitol-lysine. Free Radic Biol Med 31:175–180. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00570-6
Chang Y, Kong Q, Shan X et al (2008) Messenger RNA oxidation occurs early in disease pathogenesis and promotes motor neuron degeneration in ALS. PLoS One 3:e2849. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002849
Cooke MS, Olinski R, Evans MD (2006) Does measurement of oxidative damage to DNA have clinical significance? Clin Chim Acta 365:30–49. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2005.09.009
Costa FF (2005) Non-coding RNAs: new players in eukaryotic biology. Gene 357:83–94. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.019
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695. doi:10.1126/science.7901908
Deutscher MP (2006) Degradation of RNA in bacteria: comparison of mRNA and stable RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 34:659–666. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj472
Ding Q, Cecarini V, Keller JN (2007) Interplay between protein synthesis and degradation in the CNS: physiological and pathological implications. Trends Neurosci 30:31–36. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2006.11.003
Ding Q, Dimayuga E, Markesbery WR, Keller JN (2004) Proteasome inhibition increases DNA and RNA oxidation in astrocyte and neuron cultures. J Neurochem 91:1211–1218. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02802.x
Ding Q, Markesbery WR, Cecarini V, Keller JN (2006) Decreased RNA, and increased RNA oxidation, in ribosomes from early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 31:705–710. doi:10.1007/s11064-006-9071-5
Ding Q, Markesbery WR, Chen Q, Li F, Keller JN (2005) Ribosome dysfunction is an early event in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 25:9171–9175. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3040-05.2005
Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Cooke MS (2004) Oxidative DNA damage and disease: induction, repair and significance. Mutat Res 567:1–61. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2003.11.001
Fiala ES, Conaway CC, Mathis JE (1989) Oxidative DNA and RNA damage in the livers of Sprague-Dawley rats treated with the hepatocarcinogen 2-nitropropane. Cancer Res 49:5518–5522
Foksinski M, Rozalski R, Guz J et al (2004) Urinary excretion of DNA repair products correlates with metabolic rates as well as with maximum life spans of different mammalian species. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1449–1454. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.07.014
Furuta A, Iida T, Nakabeppu Y, Iwaki T (2001) Expression of hMTH1 in the hippocampi of control and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 12:2895–2899. doi:10.1097/00001756-200109170-00028
Gong X, Tao R, Li Z (2006) Quantification of RNA damage by reverse transcription polymerase chain reactions. Anal Biochem 357:58–67. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2006.06.025
Görg B, Qvartskhava N, Keitel V et al (2008) Ammonia induces RNA oxidation in cultured astrocytes and brain in vivo. Hepatology 48:567–579. doi:10.1002/hep.22345
Gu G, Reyes PE, Golden GT et al (2002) Mitochondrial DNA deletions/rearrangements in Parkinson disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:634–639
Guentchev M, Siedlak SL, Jarius C et al (2002) Oxidative damage to nucleic acids in human prion disease. Neurobiol Dis 9:275–281. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2002.0477
Guidi I, Galimberti D, Lonati S et al (2006) Oxidative imbalance in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:262–269. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.01.001
Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY et al (1994) Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264:1772–1775. doi:10.1126/science.8209258
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10990.x
Hayakawa H, Hofer A, Thelander L et al (1999) Metabolic fate of oxidized guanine ribonucleotides in mammalian cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 38:3610–3614. doi:10.1021/bi982361l
Hayakawa H, Kuwano M, Sekiguchi M (2001) Specific binding of 8-oxoguanine-containing RNA to polynucleotide phosphorylase protein. Biochemistry (Mosc) 40:9977–9982. doi:10.1021/bi010595q
Hayakawa H, Sekiguchi M (2006) Human polynucleotide phosphorylase protein in response to oxidative stress. Biochemistry (Mosc) 45:6749–6755. doi:10.1021/bi052585l
Hayakawa H, Uchiumi T, Fukuda T et al (2002) Binding capacity of human YB-1 protein for RNA containing 8-oxoguanine. Biochemistry (Mosc) 41:12739–12744. doi:10.1021/bi0201872
Hayashi M, Arai N, Satoh J et al (2002) Neurodegenerative mechanisms in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Child Neurol 17:725–730. doi:10.1177/08830738020170101101
Hayashi M, Araki S, Kohyama J, Shioda K, Fukatsu R (2005) Oxidative nucleotide damage and superoxide dismutase expression in the brains of xeroderma pigmentosum group A and Cockayne syndrome. Brain Dev 27:34–38. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2004.04.001
Hirai K, Aliev G, Nunomura A et al (2001) Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 21:3017–3023
Hirtz D, Thurman DJ, Gwinn-Hardy K, Mohamed M, Chaudhuri AR, Zalutsky R (2007) How common are the “common” neurologic disorders? Neurology 68:326–337. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000252807.38124.a3
Hofer T, Badouard C, Bajak E, Ravanat JL, Mattsson A, Cotgreave IA (2005) Hydrogen peroxide causes greater oxidation in cellular RNA than in DNA. Biol Chem 386:333–337. doi:10.1515/BC.2005.040
Hofer T, Fontana L, Anton SD et al (2008) Long-term effects of caloric restriction or exercise on DNA and RNA oxidation levels in white blood cells and urine in humans. Rejuvenation Res 11:793–799. doi:10.1089/rej.2008.0712
Hofer T, Marzetti E, Xu J et al (2008) Increased iron content and RNA oxidative damage in skeletal muscle with aging and disuse atrophy. Exp Gerontol 43:563–570. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2008.02.007
Hofer T, Seo AY, Prudencio M, Leeuwenburgh C (2006) A method to determine RNA and DNA oxidation simultaneously by HPLC-ECD: greater RNA than DNA oxidation in rat liver after doxorubicin administration. Biol Chem 387:103–111. doi:10.1515/BC.2006.014
Honda K, Smith MA, Zhu X et al (2005) Ribosomal RNA in Alzheimer disease is oxidized by bound redox-active iron. J Biol Chem 280:20978–20986. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500526200
Honig LS, Kukull W, Mayeux R (2005) Atherosclerosis and AD: analysis of data from the US National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center. Neurology 64:494–500
Huang WL, King VR, Curran OE et al (2007) A combination of intravenous and dietary docosahexaenoic acid significantly improves outcome after spinal cord injury. Brain 130:3004–3019. doi:10.1093/brain/awm223
Ischiropoulos H, Beckman JS (2003) Oxidative stress and nitration in neurodegeneration: cause, effect, or association? J Clin Invest 111:163–169
Ishibashi T, Hayakawa H, Ito R, Miyazawa M, Yamagata Y, Sekiguchi M (2005) Mammalian enzymes for preventing transcriptional errors caused by oxidative damage. Nucleic Acids Res 33:3779–3784. doi:10.1093/nar/gki682
Ito R, Hayakawa H, Sekiguchi M, Ishibashi T (2005) Multiple enzyme activities of Escherichia coli MutT protein for sanitization of DNA and RNA precursor pools. Biochemistry (Mosc) 44:6670–6674. doi:10.1021/bi047550k
Javitch JA, D’Amato RJ, Strittmatter SM, Snyder SH (1985) Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin, N-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6 -tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the metabolite N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains selective toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:2173–2177. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.7.2173
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53(Suppl 3):S26–S36. doi:10.1002/ana.10483
Joenje H (1989) Genetic toxicology of oxygen. Mutat Res 219:193–208
Kajitani K, Yamaguchi H, Dan Y, Furuichi M, Kang D, Nakabeppu Y (2006) MTH1, an oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphatase, suppresses the accumulation of oxidative damage of nucleic acids in the hippocampal microglia during kainate-induced excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 26:1688–1698. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4948-05.2006
Kasai H, Crain PF, Kuchino Y, Nishimura S, Ootsuyama A, Tanooka H (1986) Formation of 8-hydroxyguanine moiety in cellular DNA by agents producing oxygen radicals and evidence for its repair. Carcinogenesis 7:1849–1851. doi:10.1093/carcin/7.11.1849
Kedersha N, Stoecklin G, Ayodele M et al (2005) Stress granules and processing bodies are dynamically linked sites of mRNP remodeling. J Cell Biol 169:871–884. doi:10.1083/jcb.200502088
Keller JN, Schmitt FA, Scheff SW et al (2005) Evidence of increased oxidative damage in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 64:1152–1156
Kikuchi A, Takeda A, Onodera H et al (2002) Systemic increase of oxidative nucleic acid damage in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Neurobiol Dis 9:244–248. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2002.0466
King VR, Huang WL, Dyall SC, Curran OE, Priestley JV, Michael-Titus AT (2006) Omega-3 fatty acids improve recovery, whereas omega-6 fatty acids worsen outcome, after spinal cord injury in the adult rat. J Neurosci 26:4672–4680. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5539-05.2006
Krokan HE, Kavli B, Slupphaug G (2004) Novel aspects of macromolecular repair and relationship to human disease. J Mol Med 82:280–297. doi:10.1007/s00109-004-0528-1
Lee JW, Beebe K, Nangle LA et al (2006) Editing-defective tRNA synthetase causes protein misfolding and neurodegeneration. Nature 443:50–55. doi:10.1038/nature05096
Li Z, Wu J, Deleo CJ (2006) RNA damage and surveillance under oxidative stress. IUBMB Life 58:581–588. doi:10.1080/15216540600946456
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795. doi:10.1038/nature05292
Liu J, Head E, Gharib AM et al (2002) Memory loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-l-carnitine and/or R-alpha -lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2356–2361. doi:10.1073/pnas.261709299
Liu Q, Xie F, Rolston R et al (2007) Prevention and treatment of Alzheimer disease and aging: antioxidants. Mini Rev Med Chem 7:171–180. doi:10.2174/138955707779802552
Lovell MA, Markesbery WR (2008) Oxidatively modified RNA in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Dis 29:169–175. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.07.030
Martinet W, de Meyer GR, Herman AG, Kockx MM (2004) Reactive oxygen species induce RNA damage in human atherosclerosis. Eur J Clin Invest 34:323–327. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2004.01343.x
Mattson MP, Chan SL, Duan W (2002) Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol Rev 82:637–672
Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2006) Non-coding RNAs in the nervous system. J Physiol 575:333–341. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113191
Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2007) Noncoding RNAs and RNA editing in brain development, functional diversification, and neurological disease. Physiol Rev 87:799–823. doi:10.1152/physrev.00036.2006
Migliore L, Fontana I, Trippi F et al (2005) Oxidative DNA damage in peripheral leukocytes of mild cognitive impairment and AD patients. Neurobiol Aging 26:567–573. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.07.016
Moreira PI, Honda K, Zhu X et al (2006) Brain and brawn: parallels in oxidative strength. Neurology 66(Suppl 1):S97–S101. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000192307.15103.83
Moreira PI, Nunomura A, Nakamura M et al (2008) Nucleic acid oxidation in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1493–1505. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.01.002
Moreira PI, Zhu X, Nunomura A, Smith MA, Perry G (2006) Therapeutic options in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 6:897–910. doi:10.1586/14737175.6.6.897
Mundt JM, Hah SS, Sumbad RA, Schramm V, Henderson PT (2008) Incorporation of extracellular 8-oxodG into DNA and RNA requires purine nucleoside phosphorylase in MCF-7 cells. Nucleic Acids Res 36:228–236. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm1032
Nakabeppu Y, Kajitani K, Sakamoto K, Yamaguchi H, Tsuchimoto D (2006) MTH1, an oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphatase, prevents the cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity of oxidized purine nucleotides. DNA Repair (Amst) 5:761–772. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.03.003
Nakabeppu Y, Tsuchimoto D, Ichinoe A et al (2004) Biological significance of the defense mechanisms against oxidative damage in nucleic acids caused by reactive oxygen species: from mitochondria to nuclei. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1011:101–111. doi:10.1196/annals.1293.011
Nelson PT, Wang WX, Rajeev BW (2008) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol 18:130–138. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00120.x
Nunomura A, Castellani RJ, Zhu X, Moreira PI, Perry G, Smith MA (2006) Involvement of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:631–641. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000228136.58062.bf
Nunomura A, Chiba S, Kosaka K et al (2002) Neuronal RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuroreport 13:2035–2039. doi:10.1097/00001756-200211150-00009
Nunomura A, Chiba S, Lippa CF et al (2004) Neuronal RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 17:108–113. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.06.003
Nunomura A, Moreira PI, Lee HG et al (2007) Neuronal death and survival under oxidative stress in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6:411–423. doi:10.2174/187152707783399201
Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliev G et al (2001) Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:759–767
Nunomura A, Perry G, Pappolla MA et al (2000) Neuronal oxidative stress precedes amyloid-β deposition in Down syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:1011–1017
Nunomura A, Perry G, Pappolla MA et al (1999) RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 19:1959–1964
Park EM, Shigenaga MK, Degan P et al (1992) Assay of excised oxidative DNA lesions: isolation of 8-oxoguanine and its nucleoside derivatives from biological fluids with a monoclonal antibody column. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3375–3379. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.8.3375
Perkins DO, Jeffries C, Sullivan P (2005) Expanding the ‘central dogma’: the regulatory role of nonprotein coding genes and implications for the genetic liability to schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 10:69–78. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001577
Perry G, Nunomura A, Cash AD et al (2002) Reactive oxygen: its sources and significance in Alzheimer disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 62:69–75
Perry G, Nunomura A, Hirai K et al (2002) Is oxidative damage the fundamental pathogenic mechanism of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases? Free Radic Biol Med 33:1475–1479. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01113-9
Petersen RB, Siedlak SL, Lee HG et al (2005) Redox metals and oxidative abnormalities in human prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol 110:232–238. doi:10.1007/s00401-005-1034-4
Praticò D, Clark CM, Liun F, Rokach J, Lee VY, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Increase of brain oxidative stress in mild cognitive impairment: a possible predictor of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 59:972–976. doi:10.1001/archneur.59.6.972
Rahkonen T, Eloniemi-Sulkava U, Rissanen S, Vatanen A, Viramo P, Sulkava R (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies according to the consensus criteria in a general population aged 75 years or older. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:720–724. doi:10.1136/jnnp.74.6.720
Rhee Y, Valentine MR, Termini J (1995) Oxidative base damage in RNA detected by reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3275–3282. doi:10.1093/nar/23.16.3275
Rinaldi P, Polidori MC, Metastasio A et al (2003) Plasma antioxidants are similarly depleted in mild cognitive impairment and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:915–919. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00031-9
Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D et al (1993) Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362:59–62. doi:10.1038/362059a0
Row BW, Liu R, Xu W, Kheirandish L, Gozal D (2003) Intermittent hypoxia is associated with oxidative stress and spatial learning deficits in the rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1548–1553. doi:10.1164/rccm.200209-1050OC
Satterlee JS, Barbee S, Jin P et al (2007) Noncoding RNAs in the brain. J Neurosci 27:11856–11859. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3624-07.2007
Sayre LM, Perry G, Smith MA (1999) In situ methods for detection and localization of markers of oxidative stress: application in neurodegenerative disorders. Methods Enzymol 309:133–152. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(99)09012-6
Sayre LM, Smith MA, Perry G (2001) Chemistry and biochemistry of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disease. Curr Med Chem 8:721–738
Sayre LM, Zelasko DA, Harris PL, Perry G, Salomon RG, Smith MA (1997) 4-Hydroxynonenal-derived advanced lipid peroxidation end products are increased in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 68:2092–2097
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 54:823–827. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02325.x
Schneider JE Jr, Phillips JR, Pye Q, Maidt ML, Price S, Floyd RA (1993) Methylene blue and rose bengal photoinactivation of RNA bacteriophages: comparative studies of 8-oxoguanine formation in isolated RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys 301:91–97. doi:10.1006/abbi.1993.1119
Schubert J, Wilmer JW (1991) Does hydrogen peroxide exist “free” in biological systems? Free Radic Biol Med 11:545–555. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(91)90135-P
Shan X, Chang Y, Lin CL (2007) Messenger RNA oxidation is an early event preceding cell death and causes reduced protein expression. FASEB J 21:2753–2764. doi:10.1096/fj.07-8200com
Shan X, Lin CL (2006) Quantification of oxidized RNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:657–662. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.03.022
Shan X, Tashiro H, Lin CL (2003) The identification and characterization of oxidized RNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 23:4913–4921
Shao C, Xiong S, Li GM et al (2008) Altered 8-oxoguanine glycosylase in mild cognitive impairment and late-stage Alzheimer’s disease brain. Free Radic Biol Med 45:813–819. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.06.003
Shen Z, Wu W, Hazen SL (2000) Activated leukocytes oxidatively damage DNA, RNA, and the nucleotide pool through halide-dependent formation of hydroxyl radical. Biochemistry (Mosc) 39:5474–5482. doi:10.1021/bi992809y
Sheth U, Parker R (2003) Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science 300:805–808. doi:10.1126/science.1082320
Shimura-Miura H, Hattori N, Kang D, Miyako K, Nakabeppu Y, Mizuno Y (1999) Increased 8-oxo-dGTPase in the mitochondria of substantia nigral neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 46:920–924. doi:10.1002/1531-8249(199912)46:6<920::AID-ANA17>3.0.CO;2-R
Smith MA, Nunomura A, Zhu X, Takeda A, Perry G (2000) Metabolic, metallic, and mitotic sources of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2:413–420. doi:10.1089/15230860050192198
Smith MA, Perry G, Richey PL et al (1996) Oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s. Nature 382:120–121. doi:10.1038/382120b0
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heinsen H et al (1988) Increased iron (III) and total iron content in postmortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural Transm 74:199–205. doi:10.1007/BF01244786
Szymanski M, Barciszewska MZ, Erdmann VA, Barciszewski J (2005) A new frontier for molecular medicine: noncoding RNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1756:65–75
Taddei F, Hayakawa H, Bouton M et al (1997) Counteraction by MutT protein of transcriptional errors caused by oxidative damage. Science 278:128–130. doi:10.1126/science.278.5335.128
Taft RJ, Pheasant M, Mattick JS (2007) The relationship between non-protein-coding DNA and eukaryotic complexity. Bioessays 29:288–299. doi:10.1002/bies.20544
Takahashi MA, Asada K (1983) Superoxide anion permeability of phospholipid membranes and chloroplast thylakoids. Arch Biochem Biophys 226:558–566. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(83)90325-9
Tanaka M, Chock PB, Stadtman ER (2007) Oxidized messenger RNA induces translation errors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:66–71. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609737104
Tateyama M, Takeda A, Onodera Y et al (2003) Oxidative stress and predominant Aβ42(43) deposition in myopathies with rimmed vacuoles. Acta Neuropathol 105:581–585
Taylor JP, Hardy J, Fischbeck KH (2002) Toxic proteins in neurodegenerative disease. Science 296:1991–1995. doi:10.1126/science.1067122
van Leeuwen FW, de Kleijn DP, van den Hurk HH et al (1998) Frameshift mutants of β amyloid precursor protein and ubiquitin-B in Alzheimer’s and Down patients. Science 279:242–247. doi:10.1126/science.279.5348.242
Wamer WG, Wei RR (1997) In vitro photooxidation of nucleic acids by ultraviolet A radiation. Photochem Photobiol 65:560–563. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1997.tb08605.x
Wang J, Markesbery WR, Lovell MA (2006) Increased oxidative damage in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in mild cognitive impairment. J Neurochem 96:825–832. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03615.x
Wang Q, Yu S, Simonyi A, Sun GY, Sun AY (2005) Kainic acid-mediated excitotoxicity as a model for neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 31:3–16. doi:10.1385/MN:31:1-3:003
Weimann A, Belling D, Poulsen HE (2002) Quantification of 8-oxo-guanine and guanine as the nucleobase, nucleoside and deoxynucleoside forms in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e7. doi:10.1093/nar/30.2.e7
Weissman L, Jo DG, Sørensen MM et al (2007) Defective DNA base excision repair in brain from individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Nucleic Acids Res 35:5545–5555. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm605
Wu J, Li Z (2008) Human polynucleotide phosphorylase reduces oxidative RNA damage and protects HeLa cell against oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372:288–292. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.058
Yamaguchi H, Kajitani K, Dan Y et al (2006) MTH1, an oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphatase, protects the dopamine neurons from oxidative damage in nucleic acids caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine. Cell Death Differ 13:551–563. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401788
Yanagawa H, Ogawa Y, Ueno M (1992) Redox ribonucleosides. Isolation and characterization of 5-hydroxyuridine, 8-hydroxyguanosine, and 8-hydroxyadenosine from Torula yeast RNA. J Biol Chem 267:13320–13326
Yang WH, Bloch DB (2007) Probing the mRNA processing body using protein macroarrays and “autoantigenomics”. RNA 13:704–712. doi:10.1261/rna.411907
Yin B, Whyatt RM, Perera FP, Randall MC, Cooper TB, Santella RM (1995) Determination of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine by an immunoaffinity chromatography-monoclonal antibody-based ELISA. Free Radic Biol Med 18:1023–1032. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(95)00003-G
Zhang J, Perry G, Smith MA et al (1999) Parkinson’s disease is associated with oxidative damage to cytoplasmic DNA and RNA in substantia nigra neurons. Am J Pathol 154:1423–1429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunomura, A., Hofer, T., Moreira, P.I. et al. RNA oxidation in Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol 118, 151–166 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0508-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0508-1