Abstract
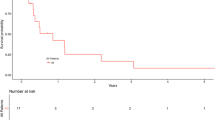
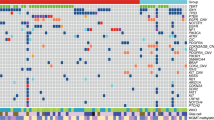
To optimize treatment strategies for patients with glioblastoma, a more precise understanding of the molecular basis of this disease clearly is necessary. Therefore, numerous studies have focused on the molecular biology of glioblastoma and its linkage to clinical behavior. Here we investigated 70 glioblastomas using the array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH) with GenoSensor Array 300 to identify recurrent DNA copy number imbalances associated with patient outcomes. Univariate log-rank analysis of array-CGH data revealed 46 copy number aberrations (CNAs) associated with outcome. Among them, 26 CNAs were associated with shortened survival whereas the remaining 20 CNAs correlated with good prognosis. A hierarchical cluster analysis disclosed two genetically distinct groups of glioblastomas (1 and 2; 56 and 14 tumors, respectively). Univariate log-rank test discerned significant difference in survival between both genetic subsets while the 5-year survival rate consisted of 0 for group 1 and 63% for group 2. Multivariate analysis revealed that unfavorable genetic signature is an independent prognostic factor increasing a risk of patient death (hazard ratio, 4.38; P=0.00001). In conclusion, our current study suggests that glioblastomas can be subdivided into clinically relevant genetic subsets. Therefore, array-CGH screening of glioblastomas could provide clinically useful information and, perhaps, potentially improve the quality of treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto S, Nakanishi Y, Sakamoto M, Kanai Y, Hirohashi S (2004) Laminin 5 beta and gamma 2 chains are frequently co-expressed in cancer cells. Pathol Int 54:688–692
Arslantas A, Artan S, Oner U, Muslumanoglu H, Durmaz R, Cosan E, Atasoy MA, Basaran N, Tel E (2004) The importance of genomic copy number changes in the prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurg Rev 27:58–64
Baron V, Adamson ED, Calogero A, Ragona G, Mercola D (2005) The transcriptional factor EGR1 is a direct regulator of multiple tumor suppressors including TGFbeta1, PTEN, p53 and fibronectin. Cancer Gene Ther 13:115–124
Bassi DE, Fu J, Lopez de Cicco R Klein-Szanto AJ (2005) Proprotein convertases: “Master switches” in the regulation of tumor growth and progression. Mol Carcinogen 44:151–161
Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Harsh GR, Vogel H, Recht LD, Sikic BI (2005) High-resolution genome-wide mapping of genetic alterations in human glial brain tumors. Cancer Res 65:4088–4096
Burton E, Lamborn KR, Feuerstein BG, Prados M, Scott J, Forsyth P, Passe S, Jenkins RB, Aldape KD (2002) Genetic aberrations defined by comparative genome hybridization distinguish long-term from typical survivors in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 62:6205–6210
Bussey KJ, Lawce HJ, Himoe E, Shu XO, Heerema NA, Perlman EJ, Olson SB, Magenis RE (2001) SNRPN methylation patterns in the germ cell tumors as a reflection of primordial germ cell development. Genes Chromosome Cancer 32:342–352
Callucci M, Merola R, Farsetti A, Orlandi G, Sentinelli S, De Carli P, Leonardo C, Carlini P, Guadangi F, Sperduti I, Cianciulli AM (2005) Cytogenetic profile as an additional marker to pathological features in clinically localized prostate carcinoma. Cancer Lett (in press)
Coleman WB, Tsongalis GJ (2002) The molecular basis of human cancer. Humana Press, Totowa, 588 pp
Cowell JK, Matsui S, Wang YD, LaDuca J, Conroy J, McQuad D, Nowak NJ (2004) Application of bacterial artificial chromosome array-based comparative genomic hybridization and spectral karyotyping to the analysis of glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 151:36–51
Grifoni D, Garoia F, Schimanski CC, Smitz G, Laureneti E, Galle PR, Pession A, Cavicci S, Strand D (2004) The human protein Hugl-1 substitutes for Drosophila lethal giant larvae tumor suppressor function in vivo. Oncogene 23:8688–8694
Grossman SA, Batara JF (2004) Current management of glioblastoma multiforme. Semin Oncol 31:635–644
Hibi K, Trink B, Patturajan M, Westra WH, Caballero OI, Hill DE, Ratovitski EA, Jen J, Sidransky D (2000) AIS is an oncogene amplified in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 97:5462–5477
Hidalgo A, Baudis M, Pedersen I, Arreola H, Pina P, Vazquez-Ortiz G, Hernandez D, Gonzalez D, Lazos M, Lopez R, Perez C, Carcia J (2005) Microarray comparative genomic hybridization detection of chromosomal imbalances in uterine cervix carcinoma. BMC Cancer 5:77
Holland EC (2000) Glioblastoma multiforme: the terminator. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 97:6242–6244
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D, Hallek M, Van Etten RA, Li S (2004) Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck, and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 36:453–461
Huhn SL, Mohapatra G, Bollen A, Lamborn K, Prados MD, Feuerstein BG (1999) Chromosomal abnormalities in glioblastoma multiforme by comparative genomic hybridization: correlation with radiation treatment outcome. Clin Cancer Res 5:1435–1433
Ichimura K, Ohgaki H, Kleihues P, Collins VP (2004) Molecular pathogenesis of astrocytic tumors. J Neurooncol 70:137–160
Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (2000) Tumors of the nervous system. Pathology and genetics: World Health Organization international classification of tumours. WHO/IARC, Lyon, France
Korshunov A, Golanov A, Sycheva R, Pronin I (1999) Prognostic value of tumour-associated antigens immunoreactivity and apoptosis in cerebral glioblastomas: an analysis of 168 cases. J Clin Pathol 52:574–580
Korshunov A, Sycheva R, Golanov A (2004) Molecular stratification of diagnostically challenging high-grade gliomas composed of small cells. The utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clin Cancer Res 10:7820–7826
Koschny R, Koschny T, Froster UG, Krupp W, Zuber MA (2002) Comparative genomic hybridization in glioma: a meta-analysis of 509 cases. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 135:147–159
Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD (2004) Prognostic factors for survival of patients with glioblastoma. Recursive portioning analysis. Neuro-oncology 6:227–235
Lutterbach J, Saurbrei W, Guttenberg R (2003) Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in patients with glioblastomas. Strahlenther Onkol 179:8–15
Misra A, Pellarin M, Nigro J, Smirnov I, Moore D, Lamborn KR, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Feuerstein BG (2005) Array comparative genomic hybridization identifies genetic subgroups in grade 4 human astrocytoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:2907–2918
Melino G, De LV, Vousden KH (2002) P73: friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2:605–615
Mohapatra G, Bollen AW, Kim DH, Lamborn K, Moore DH, Prados MD, Feuerstein BG (1998) Genetic analysis of glioblastoma multiforme provides evidence for subgroups within the grade. Genes Chromosome Cancer 21:195–206
Nakahara Y, Shiraishi T, Okamoto H, Mineta T, Oishi T, Sasaki T, Tabuchi K (2004) Detrended fluctuation analysis of genome-wide copy number profiles of glioblastomas using array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Neuro-Oncology 6:281–289
Nigro J, Misra A, Zhang L, Smirnov I, Colman H, Griffin C, Ozburn N, Chen M, Pan E, Koul P, Yung WKA, Feuerstein BG, Aldape KD (2005) Integrated array-comparative genomic hybridization and expression array profiles identify clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma. Cancer Res 65:1678–1686
Parrella P, Scintu M, Prencipe M, Poeta ML, Gallo AP, Rabitti C, Rinaldi M, Tommasi S, Paradiso A, Schittulli F, Vallori MF, Toma S, Altomare V, Fazio VM (2005) HIC1 promoter methylation and 17p13.3 allelic loss in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Cancer Lett 222:75–81
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Budrick MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorini S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, Maric D, Eberhart CG, Fine HA (2005) Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and jagged-1, is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res 65:2353–2363
Roerig P, Nessling M, Radlwimmer B, Joos S, Wrobel G, Schwanen C, Reifenberger G, Lichter P (2005) Molecular classification of human gliomas using matrix-based comparative genomic hybridization. Int J Cancer 117:95–103
Roussel MF, Sherr CG (2003) Oncogenic potential of the c-FMS protooncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Cell Cycle 2:5–6
Sasaki T, Arai H, Beppu T, Ogasawara K (2003) Detection of gene amplification and deletion in high-grade gliomas using a genome DNA microarray (GenoSensor Array 300). Brain Tumor Pathol 20:59–63
Schmidt MC, Antweiler S, Urban N, Mueller W, Kuklik A, Meyer-Puttlitz B, Wiestler OD, Louis DN, Fimmers R, von Deimling A (2002) Impact of genotype and morphology on the prognosis of glioblastoma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:321–328
Sloane BF, Yan S, Podgorsky I, Linebaugh BE, Cher ML, Mai J, Cavallo-Medved D, Sameni M, Dosescu J, Moin K (2005) Cathepsin B and tumor proteolysis: contribution of tumor microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol 15:149–157
Smith JS, Tachibana I, Pohl U, Lee HK, Thanarajasingam U, Portier BP, Ueki K, Ramaswamy S, Billings SJ, Mohrenweiser HW, Louis DN, Jenkins RB (2000) A transcript map of of the chromosome 19q-arm glioma tumor suppressor region. Genomics 64:44–50
Snidjers AM, Pinkel D, Albertson DG (2003) Current status and future prospects of array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 2:37–45
Strefford JC, Stasevich I, Lane TM, Lu YJ, Oliver T, Young BD (2005) A combination of molecular cytogenetic analyses reveals complex genetic alterations in conventional renal-cell carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 159:1–9
Suzuki T, Maruno M, Wada K, Kagawa N, Fujimoto Y, Hashimoto N, Izumoto S, Yoshimine T (2004) Genetic analysis of human glioblastoma using a genomic microarray system. Brain Tumor Pathol 21:27–34
Thorburn A (2004) Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 16:139–144
Unoki M, Nakamura U (2001) Growth suppressive effects of BZOP and EGR2, two genes involving in the PTEN signaling pathway. Oncogene 20:4457–4465
Wiltshire RN, Herndon JE, Lloyd A, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Bigner SH, McLendon RE (2004) Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of astrocytomas. Prognostic and diagnostic implications. J Mol Diagn 6:166–179
Xing X, Du X, Lu Z, Ning T, Su X, Ke Y (2005) Characterization of the promoter 1A6/DRIM, a novel cancer-related gene, and identification of its transcriptional activator. Gene 344:161–169
Yokota J, Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y, Battifora H (1986) Alterations of myc, myb, and ras-Ha proto-oncogenes in cancers are frequent and show clinical correlation. Science 231:261–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korshunov, A., Sycheva, R. & Golanov, A. Genetically distinct and clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma defined by array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH). Acta Neuropathol 111, 465–474 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0057-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0057-9