Abstract
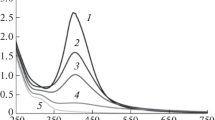
Pd nanoparticles were synthesized by reduction of palladium acetate by ethanol in systems containing tetrahydrofuran (THF) as dispersion medium and tetradodecylammonium bromide (TDABr) surfactant as stabilizer. The polar phase (ethanol) acts at the same time as reducing agent. THF/TDABr/H2O inverse microemulsions containing micelles of various sizes were also prepared, and the structure of complex liquids was studied by density measurements. Sols containing nanosize Pd0 particles were synthesized within the water droplets of this micellar system. The stabilized Pd0/surfactant system was characterized by density measurements, absorption spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The stabilizing surfactant layer adsorbed on the liquid/liquid interface and on the surface of the nanoparticles (i.e., the liquid/solid interface) significantly reduced the excess volume for the palladium nanodispersion in organic solvent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 July 2000 Accepted: 5 October 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papp, S., Dékány, I. Structural properties of palladium nanoparticles embedded in inverse microemulsions. Colloid Polym Sci 279, 449–458 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960000441
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960000441